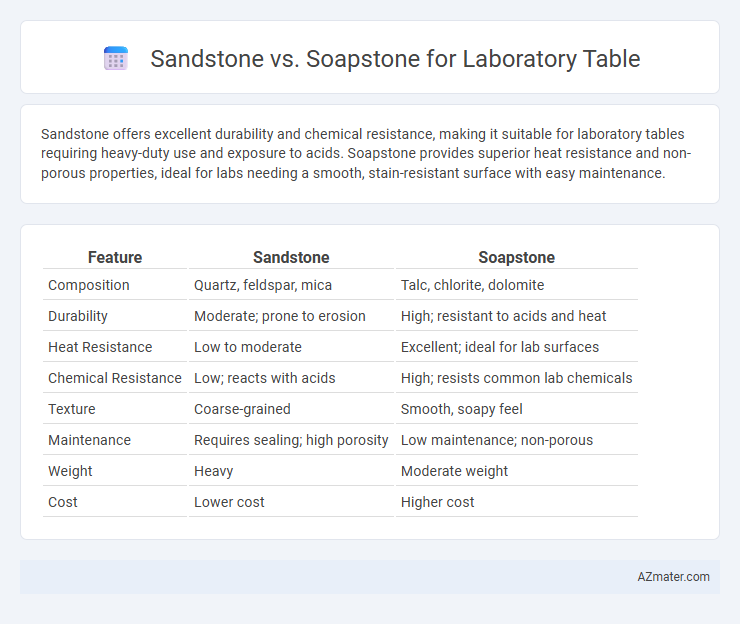
Sandstone offers excellent durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for laboratory tables requiring heavy-duty use and exposure to acids. Soapstone provides superior heat resistance and non-porous properties, ideal for labs needing a smooth, stain-resistant surface with easy maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sandstone | Soapstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Quartz, feldspar, mica | Talc, chlorite, dolomite |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to erosion | High; resistant to acids and heat |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate | Excellent; ideal for lab surfaces |
| Chemical Resistance | Low; reacts with acids | High; resists common lab chemicals |
| Texture | Coarse-grained | Smooth, soapy feel |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing; high porosity | Low maintenance; non-porous |
| Weight | Heavy | Moderate weight |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Laboratory Table Materials
Laboratory tables require materials with high durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making sandstone and soapstone prominent choices for construction. Sandstone offers robust mechanical strength and natural abrasion resistance, while soapstone excels in chemical inertness and heat retention due to its talc-rich composition. Selecting between sandstone and soapstone impacts laboratory performance by balancing structural integrity with resistance to corrosive substances and temperature variations.
Overview of Sandstone and Soapstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of sand-sized mineral particles, known for its durability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for laboratory tables requiring moderate heat and chemical resistance. Soapstone is a metamorphic rock rich in talc, offering excellent heat resistance, chemical inertness, and a smooth, non-porous surface ideal for laboratory environments with exposure to acids and heat. Both materials provide distinct advantages; sandstone excels in structural strength and aesthetic appeal, while soapstone delivers superior chemical stability and thermal insulation for laboratory use.
Physical Properties Comparison
Sandstone offers high compressive strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it durable for laboratory tables subject to heavy use. Soapstone features superior chemical resistance and thermal stability due to its high talc content, ideal for environments exposed to acids and heat. While sandstone is harder and less prone to scratching, soapstone provides greater resistance to staining and easier surface maintenance in lab settings.
Chemical Resistance: Sandstone vs Soapstone
Soapstone exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to sandstone, making it the preferred choice for laboratory tables exposed to acids and solvents. Its high talc content provides excellent resistance against corrosive chemicals, preventing surface degradation and maintaining structural integrity. Sandstone, being more porous and composed mainly of quartz and feldspar, is more susceptible to etching and staining when exposed to harsh laboratory chemicals.
Durability and Lifespan
Sandstone is less durable than soapstone, as it tends to be more porous and prone to scratches and chemical damage, making it less suitable for heavy laboratory use. Soapstone offers superior durability due to its dense, non-porous nature and excellent resistance to acids, heat, and stains, ensuring a longer lifespan in demanding lab environments. Laboratories favor soapstone for worktables because it maintains structural integrity and appearance over many years, minimizing maintenance and replacement costs.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Soapstone offers superior resistance to chemicals and stains, making it easier to maintain and clean in laboratory settings compared to sandstone. Its non-porous surface requires less frequent sealing and resists acidic spills without damage, reducing long-term maintenance efforts. Sandstone, being more porous, demands regular sealing and careful cleaning to prevent staining and degradation from laboratory chemicals.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Sandstone laboratory tables generally offer lower initial costs, making them a budget-friendly option for basic lab setups. Soapstone, while more expensive upfront due to its superior chemical resistance and durability, often proves cost-effective long-term by reducing maintenance and replacement needs. Considering the total cost of ownership helps determine the most economical choice for laboratory environments.
Suitability for Laboratory Types
Sandstone offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for general chemistry and biology laboratories where moderate acid and base exposure occurs. Soapstone provides superior resistance to thermal shock and most chemicals, ideal for laboratories handling strong acids and high-temperature experiments such as analytical chemistry and materials science labs. The choice between sandstone and soapstone depends on the specific laboratory's exposure to chemicals, heat, and mechanical wear requirements.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Sandstone, a natural sedimentary rock, is abundant and requires relatively low energy for extraction, contributing to a lower carbon footprint compared to engineered materials. Soapstone, composed primarily of talc, offers excellent durability and is highly resistant to chemicals, enhancing its longevity and reducing the need for frequent replacements in laboratory tables. Both materials are recyclable and non-toxic, but soapstone's heat resistance and minimal porosity make it a more sustainable choice for environments requiring rigorous chemical handling and thermal stability.
Final Recommendations and Conclusion
Soapstone is highly recommended for laboratory tables due to its superior chemical resistance, heat tolerance, and non-porous surface that prevents absorption of hazardous substances. Sandstone, while aesthetically pleasing and durable, lacks the chemical inertness and stain resistance essential in rigorous lab environments. Prioritizing safety and long-term durability, soapstone offers a more practical and reliable surface for laboratory applications.
Infographic: Sandstone vs Soapstone for Laboratory Table
 azmater.com
azmater.com