Sandstone offers a natural, textured surface ideal for pavements requiring slip resistance and aesthetic appeal, while basalt provides superior durability and high compressive strength, making it suitable for heavy-traffic areas. Basalt's dense structure resists weathering better than sandstone, ensuring longer pavement lifespan with lower maintenance.
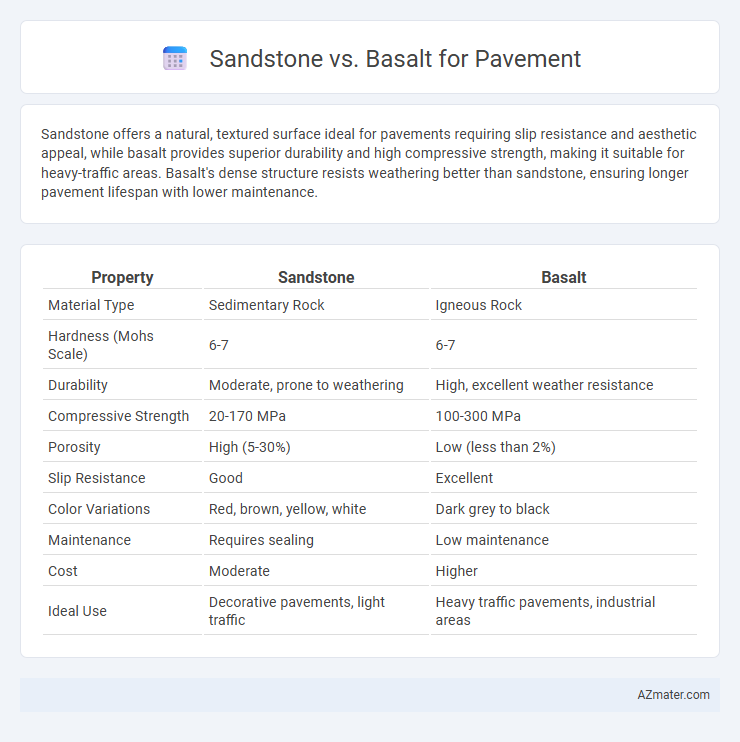
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandstone | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Sedimentary Rock | Igneous Rock |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 6-7 | 6-7 |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to weathering | High, excellent weather resistance |
| Compressive Strength | 20-170 MPa | 100-300 MPa |
| Porosity | High (5-30%) | Low (less than 2%) |
| Slip Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Color Variations | Red, brown, yellow, white | Dark grey to black |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing | Low maintenance |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Ideal Use | Decorative pavements, light traffic | Heavy traffic pavements, industrial areas |
Understanding Sandstone and Basalt: Key Characteristics
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of quartz and feldspar, known for its durability, moderate porosity, and warm earthy tones, making it a popular choice for pavement in areas requiring natural aesthetics. Basalt, an igneous volcanic rock, features a dense, hard structure with low porosity and high compressive strength, offering superior resistance to wear and weathering for high-traffic pavement applications. Understanding these key characteristics helps in selecting the appropriate stone based on environmental exposure, load requirements, and desired visual appeal.
Formation Processes: How Sandstone and Basalt Originate
Sandstone forms through the compaction and cementation of sand-sized mineral particles, primarily quartz, deposited by water or wind in sedimentary basins. Basalt originates from rapid cooling and solidification of low-viscosity lava at the Earth's surface, typically from volcanic eruptions in mafic magma regions. The sedimentary formation of sandstone results in a porous structure, whereas basalt's volcanic origin yields a dense, fine-grained texture ideal for durable pavement applications.
Visual Appeal: Color and Texture Differences
Sandstone offers a warm, earthy palette with hues ranging from beige to reddish-brown, featuring a naturally rough texture that provides excellent slip resistance for pavements. Basalt presents a sleek, modern aesthetic through its deep gray to black tones and fine-grained, smooth surface, creating a contemporary look ideal for urban settings. The choice between sandstone and basalt for pavement hinges on desired visual impact: sandstone enhances rustic, natural charm while basalt delivers a minimalist, polished appearance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Basalt offers superior durability and strength compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic pavement applications due to its dense, fine-grained structure and resistance to weathering. Sandstone, while aesthetically appealing with natural grain patterns, is softer and more porous, leading to faster wear and potential surface erosion under heavy loads. Choosing basalt ensures longer-lasting pavements with higher compressive strength, typically over 200 MPa, versus sandstone's lower range around 20-170 MPa.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Sandstone offers moderate weather resistance but is more porous and prone to erosion over time compared to basalt, making it less durable in harsh climates. Basalt, a dense volcanic rock, exhibits superior weather resistance and can withstand freeze-thaw cycles, acid rain, and heavy wear, ensuring greater longevity for pavement applications. Choosing basalt pavement guarantees enhanced durability and reduced maintenance in environments exposed to extreme weather conditions.
Maintenance Requirements: Sandstone vs Basalt
Sandstone pavement requires regular sealing and cleaning to prevent weathering and surface erosion due to its porous nature, leading to higher maintenance frequency. Basalt pavement, known for its dense, hard composition, demands less frequent upkeep and demonstrates superior resistance to wear and staining. Choosing basalt minimizes long-term maintenance costs and preserves pavement integrity better than sandstone in high-traffic areas.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Long-Term Value
Sandstone pavements typically incur lower initial installation costs due to easier quarrying and processing, while basalt demands higher upfront investment because of its density and hardness. Over time, basalt offers greater durability and resistance to weathering, resulting in reduced maintenance expenses and longer lifespan, which enhances its long-term value compared to sandstone. Choosing basalt often yields better cost-efficiency for heavy-traffic areas despite the higher installation cost, whereas sandstone suits budget-conscious projects with moderate use.
Application Suitability for Various Pavement Types
Sandstone is ideal for pedestrian walkways and low-traffic pavements due to its natural slip resistance and ease of cutting, offering aesthetic appeal in landscaping and garden pathways. Basalt's high compressive strength and durability make it suitable for heavy-traffic roads, highways, and industrial pavements that require long-lasting performance under significant stress. Both materials provide unique benefits, with sandstone favoring decorative and light-use applications, while basalt excels in structural and high-load pavement settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Sandstone pavements are favored for their natural porosity, which allows water permeability and reduces runoff, promoting sustainable urban drainage. Basalt, a dense volcanic rock, offers high durability and long lifespan, minimizing the frequency of repaving and resource consumption. However, sourcing basalt often involves higher energy extraction processes compared to the relatively low-impact quarrying of sandstone, influencing their overall environmental footprints.
Choosing the Right Stone: Sandstone or Basalt for Your Project
Sandstone offers a warm, natural aesthetic with excellent slip resistance, making it ideal for pedestrian-friendly pavements and landscaping projects. Basalt provides superior durability, high compressive strength, and resistance to heavy loads, suitable for high-traffic areas and industrial pavements. Selecting between sandstone and basalt depends on project requirements such as visual appeal, load-bearing capacity, maintenance, and environmental conditions.
Infographic: Sandstone vs Basalt for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com