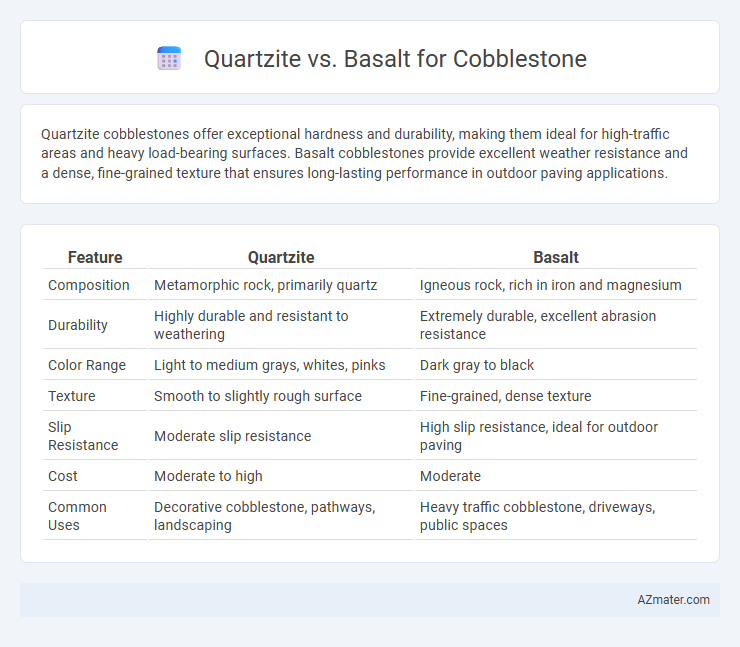
Quartzite cobblestones offer exceptional hardness and durability, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy load-bearing surfaces. Basalt cobblestones provide excellent weather resistance and a dense, fine-grained texture that ensures long-lasting performance in outdoor paving applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Quartzite | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphic rock, primarily quartz | Igneous rock, rich in iron and magnesium |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to weathering | Extremely durable, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Color Range | Light to medium grays, whites, pinks | Dark gray to black |
| Texture | Smooth to slightly rough surface | Fine-grained, dense texture |
| Slip Resistance | Moderate slip resistance | High slip resistance, ideal for outdoor paving |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Common Uses | Decorative cobblestone, pathways, landscaping | Heavy traffic cobblestone, driveways, public spaces |
Introduction to Quartzite and Basalt Cobblestones
Quartzite cobblestones are formed from metamorphosed sandstone, characterized by high durability, natural resistance to weathering, and a distinct crystalline texture that enhances pavement aesthetics. Basalt cobblestones originate from volcanic igneous rock, known for their exceptional hardness, dense composition, and dark coloration ideal for modern, slip-resistant surfaces. Both materials offer unique advantages in landscaping and street paving, with quartzite providing elegant visuals and basalt delivering superior longevity under heavy traffic.
Geological Formation and Characteristics
Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone subjected to intense heat and pressure, exhibits high durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for cobblestone applications requiring long-lasting surface stability. Basalt, an igneous rock created from rapidly cooled lava, features a dense, fine-grained texture and excellent compressive strength, offering robust performance in heavy traffic environments. Both stones provide slip resistance and aesthetic appeal, but quartzite's crystalline structure tends to deliver greater hardness and resistance to abrasion compared to basalt.
Appearance: Color and Texture Comparison
Quartzite cobblestones exhibit a wide range of colors, including shades of white, gray, pink, and red, with a naturally glossy, crystalline texture that enhances durability and visual appeal. Basalt cobblestones typically showcase dark gray to black tones, featuring a fine-grained, dense texture that provides a sleek, modern look with superior resistance to wear and weather. The color vibrancy and natural grain of quartzite create a striking, dynamic surface, whereas basalt offers a consistent, muted aesthetic ideal for contemporary outdoor spaces.
Durability and Strength Ratings
Quartzite demonstrates superior durability and high hardness, making it highly resistant to abrasion and ideal for cobblestone applications exposed to heavy foot and vehicle traffic. Basalt offers excellent compressive strength and weather resistance but is generally less hard than quartzite, which may affect its long-term wear performance under extreme conditions. For cobblestone durability and strength, quartzite rates higher in hardness and abrasion resistance, while basalt provides solid structural integrity with slightly less surface durability.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Quartzite exhibits superior weather resistance compared to basalt, maintaining structural integrity under extreme temperature fluctuations and acidic rain exposure. Its high silica content endows it with exceptional hardness and minimal porosity, contributing to remarkable longevity in cobblestone applications. Basalt, although durable and dense, may be more prone to surface erosion and chemical weathering over extended periods, making quartzite the preferred choice for long-lasting, weather-resistant paving stones.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Quartzite cobblestones offer easier installation due to their consistent hardness and natural cleft surface, which provides better grip and alignment during placement. Basalt, being denser and more abrasive, requires specialized cutting tools and more labor-intensive installation, but offers superior durability against heavy traffic and weathering. Maintenance for quartzite involves periodic sealing to preserve its appearance, while basalt demands minimal upkeep due to its inherent resistance to staining and erosion.
Cost Differences and Budget Planning
Quartzite cobblestones generally cost more than basalt due to their natural hardness, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making them a premium choice for high-end projects. Basalt offers a more budget-friendly option with its abundant availability and lower extraction costs, making it suitable for large-scale paving projects with cost constraints. When planning budgets, factoring in the quartzite's higher installation and maintenance expenses can impact overall project costs, whereas basalt's affordability allows for greater flexibility in design and scale.
Best Uses: Residential vs. Commercial Applications
Quartzite offers exceptional durability and a striking natural sheen, making it ideal for residential cobblestone applications such as patios, walkways, and garden paths where aesthetic appeal and resilience are key. Basalt, known for its dense, hard-wearing structure and dark, uniform appearance, suits commercial environments requiring high-traffic resistance and long-lasting performance, including sidewalks, plazas, and industrial flooring. Choosing quartzite for residential projects enhances visual warmth, while basalt's strength and slip resistance meet the rigorous demands of commercial use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Quartzite cobblestones have a lower environmental impact due to their abundant availability and minimal processing requirements, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Basalt, while durable, often requires intensive quarrying and higher energy input for crushing, increasing its carbon footprint. Sustainable choices favor quartzite for cobblestone applications to balance durability with ecological preservation and reduced environmental degradation.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Quartzite offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for cobblestones in high-traffic areas, while basalt provides a dense, fine-grained texture with excellent hardness and a dark, aesthetic appeal suitable for modern designs. Both stones exhibit high compressive strength, but quartzite's superior slip resistance and varied color options often make it the preferred choice for outdoor paving projects. Selecting between quartzite and basalt depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as desired appearance, slip safety, and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Quartzite vs Basalt for Cobblestone
 azmater.com
azmater.com