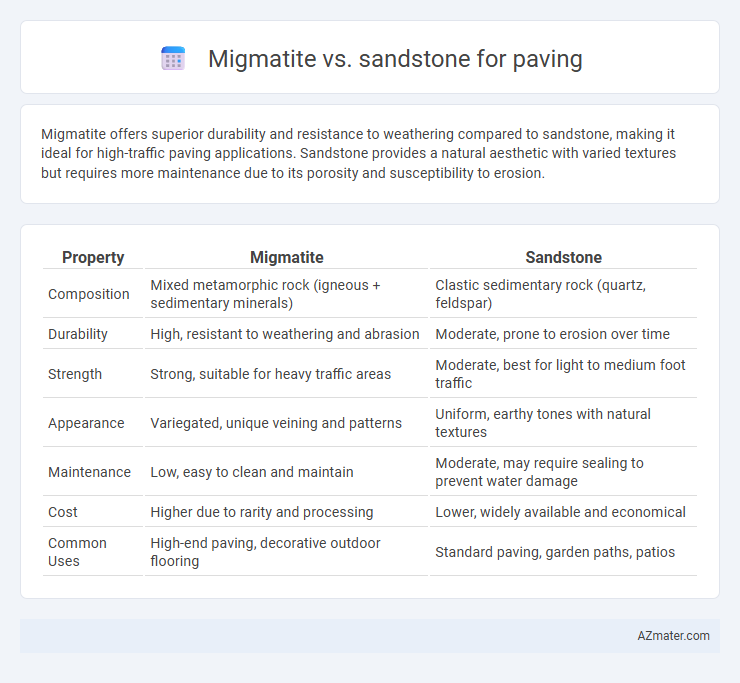
Migmatite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic paving applications. Sandstone provides a natural aesthetic with varied textures but requires more maintenance due to its porosity and susceptibility to erosion.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Migmatite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mixed metamorphic rock (igneous + sedimentary minerals) | Clastic sedimentary rock (quartz, feldspar) |
| Durability | High, resistant to weathering and abrasion | Moderate, prone to erosion over time |
| Strength | Strong, suitable for heavy traffic areas | Moderate, best for light to medium foot traffic |
| Appearance | Variegated, unique veining and patterns | Uniform, earthy tones with natural textures |
| Maintenance | Low, easy to clean and maintain | Moderate, may require sealing to prevent water damage |
| Cost | Higher due to rarity and processing | Lower, widely available and economical |
| Common Uses | High-end paving, decorative outdoor flooring | Standard paving, garden paths, patios |
Introduction to Migmatite and Sandstone
Migmatite is a high-grade metamorphic rock exhibiting a mixed texture of igneous and metamorphic components, characterized by its durability and unique veining patterns, making it ideal for decorative paving. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, offers natural porosity and a range of earthy colors, providing good slip resistance and aesthetic appeal for outdoor paving. Both materials differ in formation, strength, and surface texture, influencing their suitability and maintenance requirements in paving applications.
Geological Origins and Formation
Migmatite, a hybrid rock formed through partial melting and metamorphism of pre-existing rocks, exhibits a unique blend of igneous and metamorphic characteristics ideal for durable paving. Sandstone originates from the sedimentation and compaction of sand-sized mineral grains, typically quartz and feldspar, offering a porous and textured surface suitable for decorative paving applications. The geological formation processes of migmatite result in higher strength and resistance, while sandstone's sedimentary origin provides natural slip resistance and aesthetic appeal for pavement surfaces.
Appearance and Aesthetic Appeal
Migmatite offers a unique, mottled appearance with a blend of light and dark mineral bands, creating a visually striking and dynamic surface ideal for paving. Sandstone provides a more uniform, earthy texture with warm tones and subtle grain patterns, lending a natural and rustic aesthetic that complements outdoor environments. Both materials enhance aesthetic appeal, but migmatite stands out for its dramatic, variegated look while sandstone excels in creating a softer, timeless ambiance.
Durability and Longevity
Migmatite demonstrates superior durability and longevity compared to sandstone due to its metamorphic origin, resulting in higher resistance to weathering, abrasion, and heavy foot traffic. Sandstone, being sedimentary and softer, tends to wear down faster and may require more frequent maintenance or replacement when used for paving. For long-lasting paving solutions in high-traffic or harsh environmental conditions, migmatite offers a more resilient and enduring surface.
Slip Resistance and Safety
Migmatite offers superior slip resistance for paving due to its coarse, interlocking mineral composition, making it a safer choice in wet or high-traffic areas. Sandstone, while aesthetically appealing with its natural textures, tends to be softer and can become slippery when wet, increasing the risk of slips and falls. Choosing migmatite enhances overall safety with its durable, high-friction surface ideal for outdoor paving applications.
Cost Comparison and Value
Migmatite offers greater durability and resistance to wear compared to sandstone, making it a cost-effective choice for long-term paving projects despite a higher upfront price. Sandstone is generally more affordable initially but may incur higher maintenance costs over time due to its softer composition and susceptibility to erosion. Evaluating lifecycle expenses reveals that migmatite delivers better value for paving applications requiring longevity and low upkeep.
Maintenance Requirements
Migmatite offers superior durability and low maintenance requirements compared to sandstone, as it resists weathering and erosion due to its mixed metamorphic composition. Sandstone, being a sedimentary rock, requires more frequent sealing and cleaning to prevent surface wear and staining from moisture absorption. Proper sealing of sandstone is essential to reduce porosity and extend its lifespan when used for paving.
Environmental Impact
Migmatite, a naturally formed blend of metamorphic and igneous rock, offers low porosity and high durability, reducing water runoff and minimizing soil erosion in paving applications, making it environmentally favorable. Sandstone's porous nature allows water infiltration, promoting groundwater recharge but potentially increasing weathering and degradation rates that may require more frequent replacement. Choosing migmatite over sandstone for paving can lead to lower ecological disturbance and extended material lifespan, which contributes to reduced environmental impact over time.
Best Applications for Migmatite Paving
Migmatite is highly durable and resistant to weathering, making it an excellent choice for high-traffic paving areas such as driveways, walkways, and patios. Its unique blend of metamorphic and igneous rock layers provides superior strength and aesthetic appeal, ideal for both residential and commercial outdoor spaces. Compared to sandstone, Migmatite offers enhanced longevity and requires less maintenance, making it a cost-effective solution for long-term paving projects.
Ideal Uses for Sandstone Paving
Sandstone paving is ideal for outdoor spaces such as patios, walkways, and garden paths due to its natural slip resistance and warm, earthy tones that complement various landscape designs. Its porous nature allows for better drainage, reducing the risk of water pooling and enhancing safety in wet conditions. Unlike migmatite, sandstone is easier to cut and shape, making it suitable for intricate patterns and customized paving layouts.
Infographic: Migmatite vs Sandstone for Paving
 azmater.com
azmater.com