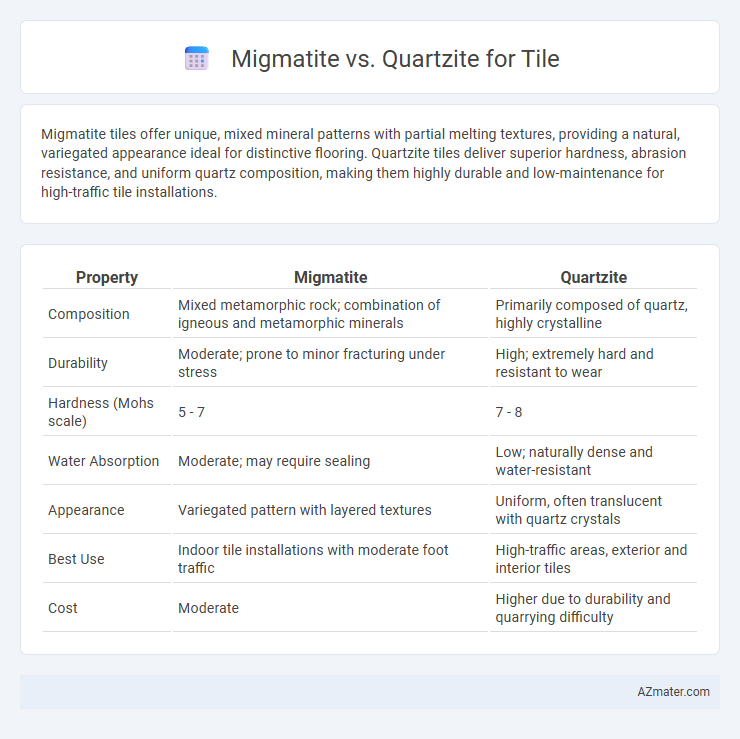
Migmatite tiles offer unique, mixed mineral patterns with partial melting textures, providing a natural, variegated appearance ideal for distinctive flooring. Quartzite tiles deliver superior hardness, abrasion resistance, and uniform quartz composition, making them highly durable and low-maintenance for high-traffic tile installations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Migmatite | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mixed metamorphic rock; combination of igneous and metamorphic minerals | Primarily composed of quartz, highly crystalline |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to minor fracturing under stress | High; extremely hard and resistant to wear |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 5 - 7 | 7 - 8 |
| Water Absorption | Moderate; may require sealing | Low; naturally dense and water-resistant |
| Appearance | Variegated pattern with layered textures | Uniform, often translucent with quartz crystals |
| Best Use | Indoor tile installations with moderate foot traffic | High-traffic areas, exterior and interior tiles |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to durability and quarrying difficulty |
Introduction to Migmatite and Quartzite Tiles
Migmatite and quartzite tiles are highly durable natural stones commonly used in flooring and wall applications, prized for their unique aesthetics and strength. Migmatite combines characteristics of igneous and metamorphic rocks, featuring complex patterns and a mix of light and dark minerals, while quartzite is a hard metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, known for its excellent abrasion resistance and natural quartz content. Both tiles offer superior durability and distinctive appearances, making them popular choices for both residential and commercial interior designs.
Geological Formation of Migmatite vs Quartzite
Migmatite forms through partial melting of pre-existing rocks under high-grade metamorphic conditions, exhibiting a mixture of igneous and metamorphic features with distinct light and dark mineral bands. Quartzite originates from the metamorphism of pure quartz sandstone, where intense heat and pressure recrystallize quartz grains into a dense, hard rock with a glassy luster. The contrasting geological formation processes result in migmatite's complex, heterogeneous texture versus quartzite's uniform, tightly interlocked quartz structure, influencing their appearance and performance as tile materials.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Migmatite exhibits a unique blend of igneous and metamorphic features with a heterogeneous texture, often showcasing intricate patterns and color variations, while quartzite is recognized for its uniform, granular texture and high quartz content, contributing to its exceptional hardness and resistance to abrasion. Migmatite typically has moderate hardness and variable durability depending on its mineral composition, whereas quartzite ranks around 7 on the Mohs scale, offering superior strength and excellent resistance to heat and staining. Both stones provide durable tile options, but quartzite's consistent density and resistance to weathering make it more suitable for high-traffic areas and outdoor use.
Color and Aesthetic Variations
Migmatite tiles showcase a dynamic blend of light and dark mineral bands, offering a unique marbled appearance with rich color contrasts ranging from gray and white to earthy browns and blues. Quartzite tiles present a more uniform, often translucent look with subtle color variations, typically in shades of white, gray, and soft pastels, providing a cleaner and more consistent aesthetic. The choice between migmatite and quartzite tiles depends on the desired visual impact, with migmatite emphasizing bold, dramatic patterns and quartzite favoring elegant simplicity and smooth tones.
Durability and Strength: Which is Superior?
Migmatite exhibits exceptional durability and strength due to its mixed metamorphic and igneous composition, making it highly resistant to cracking and wear. Quartzite, primarily formed from sandstone undergoing intense heat and pressure, offers remarkable hardness and abrasion resistance, often surpassing granite in scratch resistance. While quartzite is generally harder, migmatite's mixed structure provides superior flexibility under stress, making the choice dependent on specific tile installation requirements and expected load conditions.
Suitability for Different Tile Applications
Migmatite offers exceptional durability and natural veining ideal for decorative and high-traffic floor tiles, providing a unique aesthetic appeal. Quartzite's high quartz content ensures superior hardness and resistance to scratches and stains, making it suitable for kitchen countertops, bathroom tiles, and outdoor applications. Both stones excel in durability, but quartzite's resistance to moisture and chemical exposure makes it preferable for wet areas, while migmatite suits more controlled indoor environments.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Migmatite tiles demand careful handling during installation due to their variable mineral composition and potential for fracturing along vein boundaries, requiring skilled labor and specialized adhesives. Quartzite tiles offer easier installation with their uniform hardness and resistance to chipping, reducing the risk of damage during cutting and setting. Maintenance of migmatite involves regular sealing to prevent staining and moisture infiltration, whereas quartzite typically requires less frequent sealing and is more resistant to scratches and etching, making it a low-maintenance option for tile applications.
Cost Comparison of Migmatite and Quartzite Tiles
Migmatite tiles typically cost more than quartzite tiles due to their unique blend of metamorphic textures and variable mineral patterns, which require specialized quarrying and processing techniques. Quartzite tiles offer a more consistent appearance and are generally priced lower, making them a cost-effective choice for large-scale projects or budget-conscious homeowners. The price difference can range from 20% to 50%, depending on tile size, finish, and supplier location.
Environmental Impact of Quarrying and Use
Migmatite quarries often involve extensive extraction processes that disrupt local ecosystems due to the rock's mixed composition, while quartzite quarrying typically results in less environmental degradation because of its homogeneous structure and easier processing. Both stones require significant energy for extraction and transportation, but quartzite's higher durability can lead to longer-lasting tiles, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. The choice between migmatite and quartzite tiles should consider the balance between ecological disturbance from quarrying and the sustainability benefits of tile longevity.
Choosing the Right Tile: Migmatite or Quartzite?
Migmatite tiles offer a unique blend of metamorphic textures with high durability and natural veining, making them ideal for aesthetic-rich interiors requiring strength. Quartzite tiles provide superior hardness and resistance to scratches and stains, perfect for high-traffic areas and kitchens. When choosing between migmatite and quartzite tiles, consider factors like durability, maintenance requirements, and design preferences to ensure the right balance between beauty and functionality.
Infographic: Migmatite vs Quartzite for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com