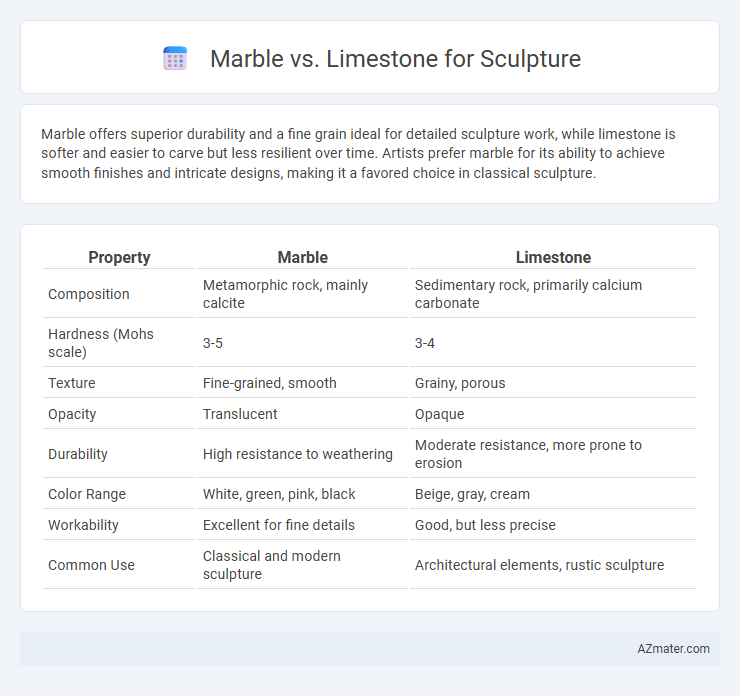
Marble offers superior durability and a fine grain ideal for detailed sculpture work, while limestone is softer and easier to carve but less resilient over time. Artists prefer marble for its ability to achieve smooth finishes and intricate designs, making it a favored choice in classical sculpture.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Marble | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphic rock, mainly calcite | Sedimentary rock, primarily calcium carbonate |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 3-5 | 3-4 |
| Texture | Fine-grained, smooth | Grainy, porous |
| Opacity | Translucent | Opaque |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering | Moderate resistance, more prone to erosion |
| Color Range | White, green, pink, black | Beige, gray, cream |
| Workability | Excellent for fine details | Good, but less precise |
| Common Use | Classical and modern sculpture | Architectural elements, rustic sculpture |
Introduction to Marble and Limestone as Sculpture Materials
Marble and limestone are both popular materials for sculpture, prized for their workability and aesthetic qualities. Marble is a metamorphic rock formed from recrystallized carbonate minerals, typically calcite, known for its fine grain and ability to achieve a smooth, polished finish ideal for detailed, lifelike sculptures. Limestone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcite, is softer and more porous, making it easier to carve but less durable than marble for intricate and outdoor sculptures.
Geological Origins and Composition
Marble originates from the metamorphism of limestone, transforming its calcite crystals into a denser, more crystalline structure that enhances durability and polishability for sculpture. Limestone is a sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcium carbonate from accumulated marine organism shells, offering a softer, more porous texture suited for detailed carving but with less resilience than marble. The geological process of marble formation increases its homogeneity and resistance to weathering, making it preferred for outdoor monuments, while limestone's stratified layers provide varied artistic textures for indoor sculptures.
Aesthetic Qualities: Color, Texture, and Finish
Marble offers a wide range of colors from pure white to shades of pink, green, and black, with a fine, smooth texture that allows for a highly polished finish, making it ideal for detailed and refined sculptures. Limestone typically presents warmer tones such as beige, cream, and light grey, featuring a coarser grain that provides a matte or satin finish, giving sculptures a more natural and rustic appearance. The choice between marble and limestone significantly impacts the visual appeal and tactile qualities of the sculpture, influencing both the light reflection and the perceived depth of the artwork.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Marble's fine-grained texture and relative softness make it ideal for detailed carving and polishing, allowing sculptors to achieve smooth, intricate finishes and realistic forms. Limestone, though softer and easier to carve at first, often lacks the durability and fine detail capability that marble provides, making it suited for larger, less intricate works or initial models. Sculpting techniques with marble often involve meticulous chiseling, rasping, and sanding, while limestone allows faster shaping but may require protective treatments to prevent weathering.
Durability: Weathering and Longevity
Marble demonstrates superior durability in sculpture due to its dense, crystalline structure, providing higher resistance to weathering and erosion compared to limestone's more porous composition. Limestone, composed mainly of calcite, is more vulnerable to acid rain and environmental pollutants, leading to faster surface degradation over time. Sculptors selecting materials for long-lasting outdoor pieces often prefer marble for its enhanced longevity and ability to maintain fine details despite harsh weather conditions.
Historical Significance in Sculpture
Marble has been prized since antiquity for its fine grain and translucence, famously used in iconic works like Michelangelo's David and ancient Greek statues. Limestone, softer and more porous, served as an accessible medium in early Egyptian and Mesopotamian sculptures, shaping many religious and funerary monuments. The historical significance of marble lies in its durability and aesthetic refinement, while limestone's cultural value connects to its widespread use in foundational architectural and sculptural art across civilizations.
Cost and Availability
Marble is generally more expensive than limestone due to its higher demand, durability, and aesthetic qualities, making it a popular choice for fine sculptures. Limestone tends to be more affordable and widely available, with abundant deposits worldwide, which makes it accessible for larger or budget-conscious projects. While marble offers a smoother finish and greater detail retention, limestone's softer composition allows for easier carving but may require more maintenance over time.
Maintenance and Restoration Considerations
Marble requires more careful maintenance due to its susceptibility to acid etching and staining, necessitating regular sealing and gentle cleaning to preserve its polished appearance. Limestone, being softer and more porous, tends to absorb moisture and pollutants, which can lead to surface erosion and discoloration, thus demanding frequent inspections and specialized restoration techniques such as consolidants and lime-based mortars. Both materials benefit from professional conservation efforts, but marble sculptures often involve higher costs for restoration due to the complexity of repairing polished surfaces and addressing micro-cracks.
Choosing the Right Stone for Contemporary Artists
Marble offers unparalleled smoothness and translucency, making it ideal for contemporary artists seeking fine detail and a polished finish in sculpture. Limestone, with its softer texture and varied grain, allows for easier carving and a more rustic, natural aesthetic favored in modern, organic designs. Selecting between marble and limestone depends on the desired durability, carving complexity, and stylistic expression in contemporary sculptural work.
Summary: Marble or Limestone—Which is Best for Sculpture?
Marble offers superior durability, fine grain, and a polished finish ideal for detailed and lasting sculptures, making it the preferred choice among professional sculptors. Limestone is softer and easier to carve, suitable for beginners and projects requiring a rustic or weathered aesthetic but is less durable over time. Choosing between marble and limestone depends on desired detail, longevity, and project budget, with marble excelling in precision and limestone favored for accessibility and texture.
Infographic: Marble vs Limestone for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com