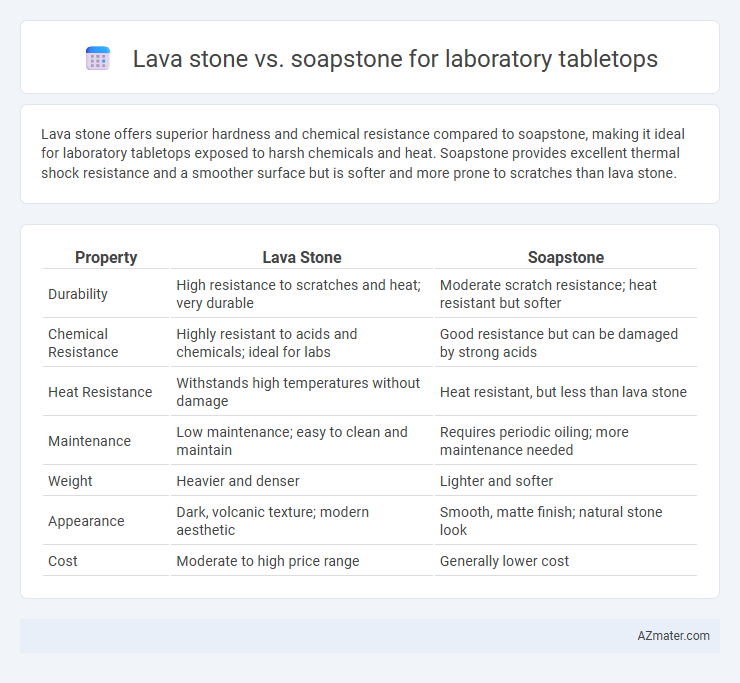
Lava stone offers superior hardness and chemical resistance compared to soapstone, making it ideal for laboratory tabletops exposed to harsh chemicals and heat. Soapstone provides excellent thermal shock resistance and a smoother surface but is softer and more prone to scratches than lava stone.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lava Stone | Soapstone |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and heat; very durable | Moderate scratch resistance; heat resistant but softer |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to acids and chemicals; ideal for labs | Good resistance but can be damaged by strong acids |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures without damage | Heat resistant, but less than lava stone |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean and maintain | Requires periodic oiling; more maintenance needed |
| Weight | Heavier and denser | Lighter and softer |
| Appearance | Dark, volcanic texture; modern aesthetic | Smooth, matte finish; natural stone look |
| Cost | Moderate to high price range | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Laboratory Tabletop Materials
Laboratory tabletops require materials with high chemical resistance, durability, and heat tolerance to maintain safety and functionality. Lava stone offers exceptional hardness and thermal resistance, making it suitable for high-impact laboratory environments, while soapstone provides superior chemical inertness and easy maintenance due to its dense, non-porous surface. Selecting between lava stone and soapstone depends on specific lab needs, balancing impact resistance against chemical stability and ease of care.
Overview of Lava Stone and Soapstone
Lava stone, an igneous rock formed from cooled molten lava, offers high heat resistance, durability, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for laboratory tabletops exposed to thermal and chemical stress. Soapstone, a metamorphic rock primarily composed of talc, features excellent heat retention, resistance to acids, and a smooth, non-porous surface that resists bacteria and stains in lab environments. Both materials ensure longevity and safety in laboratory applications, but lava stone provides superior hardness while soapstone offers enhanced chemical resistance and ease of maintenance.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Lava stone exhibits exceptional hardness and high thermal resistance, making it highly durable and resistant to heat and chemical corrosion, ideal for laboratory tabletops requiring robustness. Soapstone offers superior chemical inertness and excellent heat retention, alongside a softer but dense structure that resists acids and alkalis commonly used in laboratories. The physical hardness of lava stone surpasses soapstone, while soapstone's superior chemical stability under aggressive chemical exposure often favors sensitive laboratory environments.
Heat and Thermal Resistance
Lava stone offers superior heat resistance, tolerating temperatures up to 1200degC, making it ideal for laboratory tabletops exposed to intense thermal conditions. Soapstone exhibits excellent thermal stability as well, with a heat tolerance of around 600degC, and exceptional heat retention due to its talc content. Both materials resist thermal shock effectively, but lava stone's higher heat threshold provides greater durability in high-temperature laboratory environments.
Chemical Resistance and Reactivity
Lava stone offers exceptional chemical resistance against most acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly durable for laboratory tabletops exposed to harsh chemicals. Soapstone exhibits superior non-reactivity due to its natural composition of talc and magnesium silicate, which resists staining and chemical corrosion effectively in acidic and basic environments. Both materials provide strong chemical resistance, but soapstone's inherent non-porosity and softness reduce the risk of reactive damage or surface degradation over time.
Durability and Longevity
Lava stone exhibits exceptional durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for laboratory tabletops subjected to high heat and frequent chemical exposure. Soapstone offers moderate durability with excellent chemical resistance and heat retention but can scratch and wear more easily over time. For long-term laboratory use, lava stone provides superior longevity due to its hardness and minimal maintenance requirements.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Lava stone requires minimal maintenance with its high resistance to staining and heat, making it ideal for laboratory tabletops that face frequent spills and temperature fluctuations. Soapstone, while also durable, demands regular oiling to maintain its non-porous surface and prevent staining, which can be time-consuming in a busy lab environment. Both materials resist chemical damage, but lava stone's lower porosity enhances ease of cleaning, reducing downtime and ensuring a hygienic workspace.
Cost and Availability
Lava stone offers competitive pricing and is widely available due to abundant volcanic rock sources, making it a cost-effective option for laboratory tabletops. Soapstone tends to be more expensive and less accessible, as it requires specific mining regions and processing, which may limit supply. Laboratory designers often consider lava stone for budget-conscious projects while soapstone is preferred where chemical resistance and durability justify the higher cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lava stone offers superior environmental benefits as it is naturally abundant, durable, and requires minimal processing, resulting in lower carbon emissions compared to soapstone, which is softer and often sourced through more intensive quarrying practices. Soapstone's extraction can lead to greater habitat disruption and higher energy consumption due to its denser composition, while lava stone's volcanic origin allows for eco-friendly harvesting with reduced waste. Choosing lava stone for laboratory tabletops supports sustainability goals by promoting recycled material use and extending the lifespan of lab surfaces, minimizing resource depletion and environmental degradation.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Laboratory
Lava stone offers exceptional heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature laboratory applications, while soapstone provides superior chemical resistance and a non-porous surface, reducing contamination risks. Soapstone's ability to withstand acids and alkalis without degradation makes it preferred for laboratories handling corrosive substances. Selecting the right material depends on the specific laboratory tasks, with lava stone suited for heat-intensive work and soapstone optimal for chemical handling and easy maintenance.
Infographic: Lava stone vs Soapstone for Laboratory tabletop
 azmater.com
azmater.com