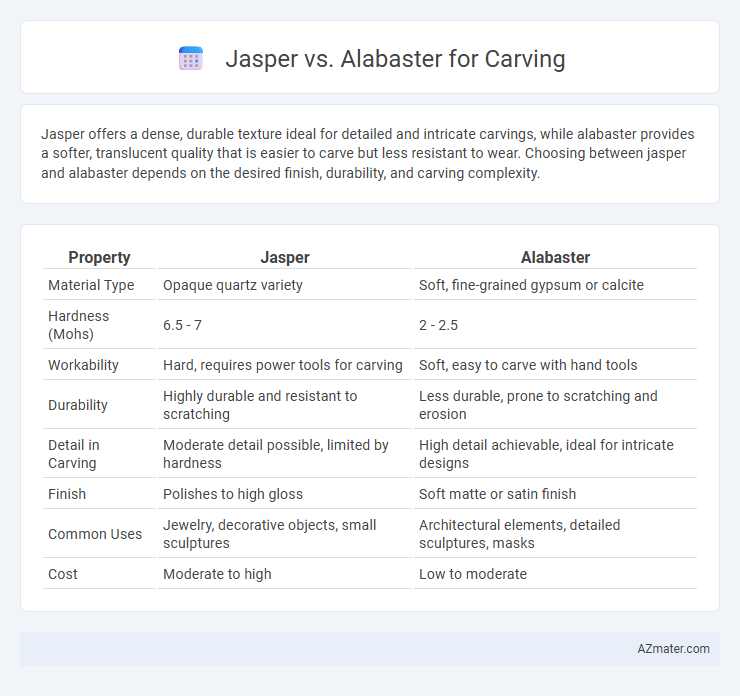
Jasper offers a dense, durable texture ideal for detailed and intricate carvings, while alabaster provides a softer, translucent quality that is easier to carve but less resistant to wear. Choosing between jasper and alabaster depends on the desired finish, durability, and carving complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Jasper | Alabaster |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Opaque quartz variety | Soft, fine-grained gypsum or calcite |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.5 - 7 | 2 - 2.5 |
| Workability | Hard, requires power tools for carving | Soft, easy to carve with hand tools |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to scratching | Less durable, prone to scratching and erosion |
| Detail in Carving | Moderate detail possible, limited by hardness | High detail achievable, ideal for intricate designs |
| Finish | Polishes to high gloss | Soft matte or satin finish |
| Common Uses | Jewelry, decorative objects, small sculptures | Architectural elements, detailed sculptures, masks |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Jasper and Alabaster for Carving
Jasper, a dense, opaque variety of chalcedony, is prized for its hardness and vibrant color variations, making it ideal for detailed and durable carvings. Alabaster, a soft, translucent stone primarily composed of gypsum or calcite, offers easy workability and smooth, elegant finishes favored in delicate sculptures. Both materials serve distinct purposes in carving, with jasper suited for intricate, lasting designs and alabaster valued for its fine texture and light-diffusing properties.
Geological Origins of Jasper and Alabaster
Jasper is an opaque variety of chalcedony, primarily composed of microcrystalline quartz formed through sedimentary processes involving silica-rich fluids. Alabaster is a fine-grained form of gypsum or calcite, originating from evaporative environments where mineral-rich waters deposit layers of calcium sulfate or carbonate. The geological origins significantly influence their hardness and carving properties, with jasper's quartz composition yielding a tougher, more durable stone compared to the softer, more easily carved alabaster.
Physical Properties: Jasper vs Alabaster
Jasper exhibits high hardness with a Mohs scale rating of 6.5 to 7, making it durable and resistant to scratching, while alabaster is much softer, ranging from 1.5 to 2, which allows for easier carving but increases susceptibility to damage. Jasper's dense, microcrystalline quartz composition contributes to its toughness and ability to maintain fine detail in sculptures, whereas alabaster, typically composed of gypsum or calcite, has a fine-grained, pliable texture ideal for smooth finishes but less structural strength. The significant difference in porosity and brittleness affects tools used: harder tools and more effort are required for jasper, while alabaster can be shaped with softer tools and finer blades.
Workability and Tool Requirements
Jasper, being a dense and hard gemstone with a Mohs hardness of 6.5 to 7, requires diamond-tipped tools and slower carving techniques to prevent tool wear and achieve detailed finishes. Alabaster, with its softness rating around 2 to 3 on the Mohs scale, offers superior workability, allowing carvers to use standard steel tools and achieve smooth, intricate designs with less effort. The choice between jasper and alabaster significantly impacts tool requirements and carving precision, making alabaster preferable for beginners and delicate projects.
Color and Aesthetic Differences
Jasper exhibits a rich variety of deep, earthy tones, including reds, browns, yellows, and greens, with intricate patterns that lend each carving a unique, vibrant character. Alabaster offers a softer, more translucent palette, typically in creamy whites, pale pinks, and subtle beige shades, providing a smooth and elegant finish ideal for refined, delicate sculptures. The striking color variability of jasper contrasts with alabaster's consistent, gentle hues, catering to distinct artistic preferences and aesthetic goals in carving projects.
Durability and Longevity
Jasper offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for detailed carving with long-lasting results, while alabaster is softer and more prone to scratches and erosion over time. The hardness of jasper, typically around 6.5-7 on the Mohs scale, ensures it maintains intricate details without significant wear. In contrast, alabaster's lower hardness of about 2 allows for easier carving but requires more careful handling to preserve longevity.
Cost Comparison for Carving Projects
Jasper and alabaster differ significantly in cost for carving projects, with alabaster generally being more affordable due to its softness and abundance. Jasper's higher price reflects its hardness and unique color patterns, making it ideal for detailed, durable sculptures but less budget-friendly. Carvers seeking cost-effective materials often choose alabaster for larger or intricate projects where budget constraints are crucial.
Artistic Applications and Popular Uses
Jasper and alabaster are favored materials in artistic carving, each offering unique qualities for sculptors. Jasper's hardness and vibrant patterns make it ideal for intricate, durable pieces like jewelry and decorative figurines, while alabaster's softness and translucence suit detailed, delicate sculptures and light-diffusing lamps. Both stones are widely used for artistic expression, with jasper prized in ornamental objects and alabaster favored for classical statuary and architectural elements.
Maintenance and Preservation
Jasper, known for its hardness and dense structure, requires careful cleaning with mild soap and water to avoid surface damage, while regular sealing enhances its durability against moisture and stains. Alabaster is softer and more porous, demanding gentle dusting and protection from prolonged exposure to water and acidic substances to prevent erosion or discoloration. Both stones benefit from controlled indoor environments with stable humidity and temperature to maintain their integrity and appearance over time.
Choosing the Right Stone: Jasper or Alabaster
Jasper offers a hard, durable surface ideal for detailed, long-lasting carvings, making it suitable for outdoor sculptures and intricate designs. Alabaster, softer and easier to carve, excels in capturing fine details and smooth textures but requires careful handling due to its fragility and susceptibility to weathering. Choose Jasper for robust, weather-resistant works and Alabaster for delicate indoor carvings emphasizing softness and detail.
Infographic: Jasper vs Alabaster for Carving
 azmater.com
azmater.com