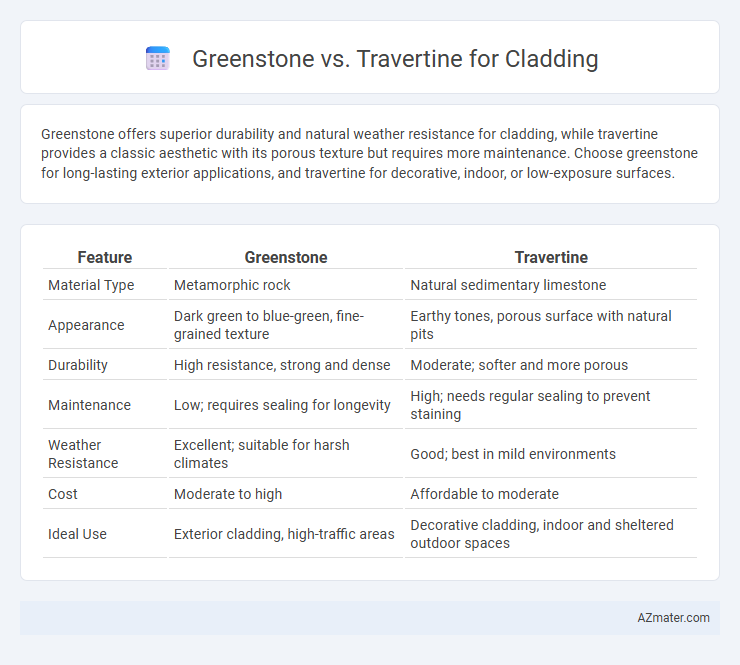
Greenstone offers superior durability and natural weather resistance for cladding, while travertine provides a classic aesthetic with its porous texture but requires more maintenance. Choose greenstone for long-lasting exterior applications, and travertine for decorative, indoor, or low-exposure surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Greenstone | Travertine |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Metamorphic rock | Natural sedimentary limestone |
| Appearance | Dark green to blue-green, fine-grained texture | Earthy tones, porous surface with natural pits |
| Durability | High resistance, strong and dense | Moderate; softer and more porous |
| Maintenance | Low; requires sealing for longevity | High; needs regular sealing to prevent staining |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent; suitable for harsh climates | Good; best in mild environments |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable to moderate |
| Ideal Use | Exterior cladding, high-traffic areas | Decorative cladding, indoor and sheltered outdoor spaces |
Introduction to Cladding: Greenstone and Travertine
Greenstone and travertine are popular natural stone options for cladding, known for their durability and aesthetic appeal in architectural design. Greenstone offers a dense, weather-resistant surface with deep green hues that enhance modern and rustic exteriors, while travertine provides a warm, textured look with its porous, cream to beige tones that age gracefully over time. Both materials excel in exterior and interior cladding applications, delivering unique natural patterns that improve building insulation and add lasting value.
Physical Properties Comparison
Greenstone exhibits high durability and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for cladding in harsh climates, while travertine offers a more porous structure with moderate hardness, requiring sealing to prevent moisture absorption. The density of greenstone typically ranges from 2.8 to 3.0 g/cm3, providing superior structural strength compared to travertine's lower density of approximately 2.5 g/cm3. Thermal conductivity also differs, with greenstone maintaining better temperature regulation due to its compact crystalline structure, whereas travertine's open porosity can influence heat retention and weathering over time.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Greenstone offers a rich, deep green hue with natural veining that creates a luxurious and sophisticated aesthetic for cladding applications. Travertine features a warm, earthy palette ranging from creamy beige to soft gold, providing a timeless and versatile appeal with unique pore patterns that add texture. Both materials enhance architectural design through distinct color variations, with Greenstone emphasizing bold elegance and Travertine delivering classic warmth.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Greenstone offers exceptional durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for cladding in harsh climates due to its dense composition and low porosity. Travertine, while aesthetically appealing with its natural veining, is more porous and can be susceptible to erosion and staining if not properly sealed. When prioritizing long-term resilience and minimal maintenance in exterior cladding, greenstone outperforms travertine in resisting moisture, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion.
Installation Process and Techniques
Greenstone cladding requires specialized cutting tools due to its dense and tough nature, with installation often involving mechanical fixing systems like stainless steel anchors for secure attachment. Travertine, being softer and more porous, allows for easier cutting and shaping, typically installed using adhesive bonding with cement-based mortars or mechanical anchors for enhanced stability. Both materials demand precise substrate preparation to ensure long-term adhesion and prevent moisture infiltration, with Greenstone installations generally taking more time due to the need for heavy-duty equipment and careful handling.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Greenstone offers superior sustainability for cladding due to its natural formation with minimal processing, resulting in lower carbon emissions compared to Travertine, which often requires extensive quarrying and chemical treatments. The dense composition of Greenstone provides enhanced durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and consequently minimizing environmental waste. Travertine's porous structure demands sealing and maintenance, which involves synthetic chemicals that can negatively impact ecosystems, making Greenstone a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable building projects.
Maintenance Requirements
Greenstone cladding requires minimal maintenance due to its natural resistance to weathering, staining, and moss growth, making it ideal for outdoor applications with low upkeep. Travertine, while visually appealing, demands regular sealing and cleaning to prevent water absorption and staining, which can lead to deterioration over time. Maintaining travertine cladding involves more frequent inspections and treatments to preserve its surface integrity compared to the more durable, low-maintenance greenstone.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Greenstone offers a cost-effective solution for cladding with its lower extraction and processing expenses compared to travertine, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects. Travertine, while typically more expensive due to its quarrying and finishing processes, provides a luxurious appearance and greater durability that can justify the higher investment over time. Project budgets should consider the initial material cost differences, maintenance expenses, and the desired aesthetic impact to determine the most affordable and practical cladding option.
Popular Applications in Architecture
Greenstone and travertine are widely favored for architectural cladding due to their distinct aesthetic and functional properties. Greenstone is popular for exterior facades and landscaping projects because of its durability and rich green hues, which complement natural surroundings and modern designs. Travertine's warm tones and porous texture make it a preferred choice for both interior and exterior wall cladding, especially in Mediterranean and contemporary architecture, providing a timeless, elegant finish.
Which is Best for Your Project?
Greenstone offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for exterior cladding in harsh climates, while its natural green hues add unique aesthetic appeal. Travertine, known for its classic, porous texture and warm tones, provides excellent insulation properties and a timeless look, but requires more maintenance to prevent staining and erosion. Choosing the best material depends on project requirements such as climate resilience, maintenance capacity, and desired visual impact.
Infographic: Greenstone vs Travertine for Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com