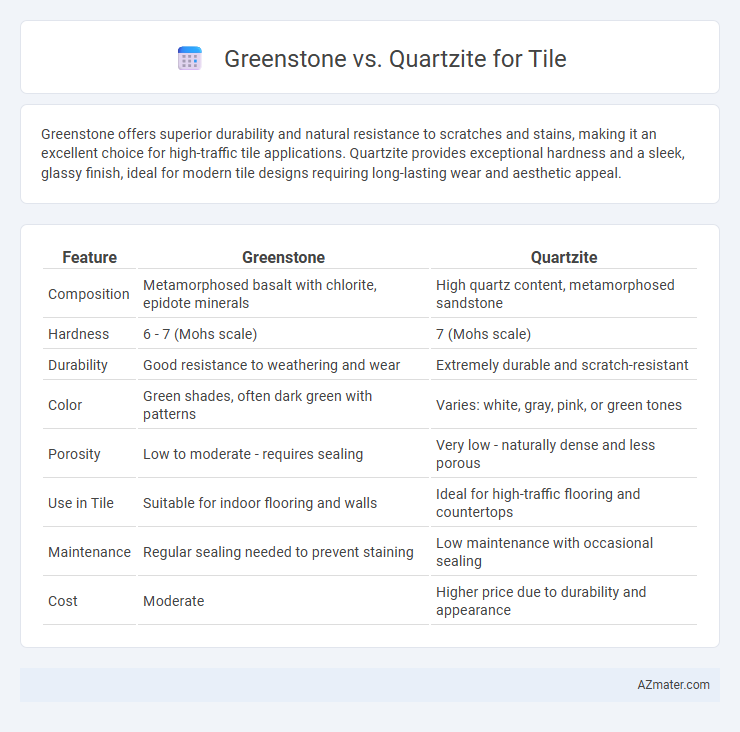
Greenstone offers superior durability and natural resistance to scratches and stains, making it an excellent choice for high-traffic tile applications. Quartzite provides exceptional hardness and a sleek, glassy finish, ideal for modern tile designs requiring long-lasting wear and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Greenstone | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphosed basalt with chlorite, epidote minerals | High quartz content, metamorphosed sandstone |
| Hardness | 6 - 7 (Mohs scale) | 7 (Mohs scale) |
| Durability | Good resistance to weathering and wear | Extremely durable and scratch-resistant |
| Color | Green shades, often dark green with patterns | Varies: white, gray, pink, or green tones |
| Porosity | Low to moderate - requires sealing | Very low - naturally dense and less porous |
| Use in Tile | Suitable for indoor flooring and walls | Ideal for high-traffic flooring and countertops |
| Maintenance | Regular sealing needed to prevent staining | Low maintenance with occasional sealing |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher price due to durability and appearance |
Introduction to Greenstone and Quartzite Tiles
Greenstone tiles feature a unique combination of durability and natural green hues, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Quartzite tiles are renowned for their hardness and resistance to wear, often exhibiting a range of colors from white to gray with occasional pink or red veins. Both materials offer distinct aesthetic appeal and strong performance, suitable for high-traffic areas in residential and commercial spaces.
Geological Origins: Greenstone vs Quartzite
Greenstone originates from metamorphosed basaltic rocks, undergoing low-grade metamorphism that imparts a rich green hue due to chlorite, epidote, and actinolite mineral content. Quartzite forms from the metamorphism of pure quartz sandstone, where recrystallization under high pressure and temperature results in a hard, dense rock primarily composed of interlocking quartz grains. The geological difference impacts tile durability and appearance, with greenstone offering a unique color palette from mafic origins, while quartzite provides a highly durable, glassy surface due to its silica-rich composition.
Appearance and Color Variations
Greenstone tile offers a rich palette of deep greens, blues, and dark grays with subtle texture variations, creating an earthy and natural aesthetic. Quartzite tile showcases a broader range of colors, including whites, grays, pinks, and golds, exhibiting dynamic veining and crystalline patterns that add visual depth and elegance. Both stones provide unique visual character, but greenstone emphasizes muted, uniform tones while quartzite delivers more dramatic color variations and patterns.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Greenstone tiles offer excellent durability due to their dense and fine-grained structure, making them resistant to scratches and chips in high-traffic areas. Quartzite, being a metamorphic rock primarily composed of quartz, ranks higher on the Mohs hardness scale (7) compared to greenstone, providing superior hardness and enhanced resistance to wear and abrasion. Both materials excel in durability, but quartzite's greater hardness makes it more suitable for heavy-use flooring applications where long-term strength and scratch resistance are critical.
Water Absorption and Stain Resistance
Greenstone exhibits lower water absorption rates compared to quartzite, making it more resistant to moisture penetration in tile installations. Quartzite, while highly durable, tends to absorb more water, which can increase susceptibility to staining if not properly sealed. Stain resistance in greenstone is generally superior, providing easier maintenance and longer-lasting aesthetic appeal in wet or high-traffic areas.
Installation Challenges and Techniques
Greenstone and quartzite tiles require specialized installation techniques due to their varying hardness and porosity. Greenstone's softer, more porous nature demands careful sealing and precise cutting tools to prevent chipping and water damage during installation. Quartzite's extreme hardness necessitates diamond-tipped blades and slower cutting speeds, while its resistance to staining minimizes post-installation maintenance challenges.
Maintenance Requirements for Longevity
Greenstone tiles require regular sealing due to their porous nature to prevent staining and moisture damage, with routine cleaning using pH-neutral cleaners to maintain their surface integrity. Quartzite tiles offer superior durability with low porosity, needing less frequent sealing and simple maintenance involving standard mild detergents to preserve their natural sheen. Choosing quartzite for tile applications reduces long-term upkeep efforts and enhances longevity compared to the higher maintenance demands of greenstone.
Cost Analysis: Greenstone vs Quartzite Tiles
Greenstone tiles generally cost between $7 and $30 per square foot, making them a more budget-friendly option compared to quartzite tiles, which range from $20 to $60 per square foot. Quartzite's higher price reflects its superior hardness and durability, offering long-term value despite the upfront investment. Installation expenses for both materials are comparable, but quartzite may require specialized tools due to its hardness, potentially increasing labor costs.
Best Applications: Indoors and Outdoors
Greenstone offers superior durability and natural slip resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as patios, walkways, and pool surrounds. Quartzite, prized for its hardness and resistance to etching, excels in indoor settings like kitchen countertops, bathroom vanities, and high-traffic flooring. Both stones provide aesthetic versatility, but choosing Greenstone for exterior use and Quartzite for interior projects ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Greenstone and quartzite both offer durable options for tile, with greenstone typically sourced from metamorphosed mafic volcanic rocks and quartzite from quartz-rich sandstone, impacting their environmental footprints differently. Greenstone extraction often involves less intensive quarrying due to its more homogeneous structure, which can reduce habitat disruption and waste production compared to quartzite's harder, more brittle nature requiring energy-intensive processing. Both stones are natural, long-lasting materials, contributing to sustainability by minimizing the need for frequent replacement, but sourcing locality and quarry management practices play crucial roles in determining their overall environmental impact.
Infographic: Greenstone vs Quartzite for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com