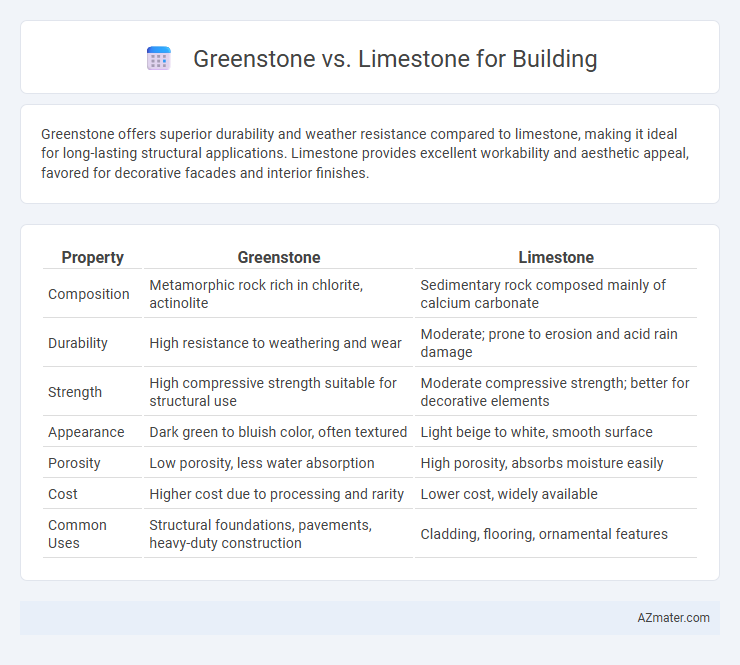
Greenstone offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to limestone, making it ideal for long-lasting structural applications. Limestone provides excellent workability and aesthetic appeal, favored for decorative facades and interior finishes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Greenstone | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphic rock rich in chlorite, actinolite | Sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and wear | Moderate; prone to erosion and acid rain damage |
| Strength | High compressive strength suitable for structural use | Moderate compressive strength; better for decorative elements |
| Appearance | Dark green to bluish color, often textured | Light beige to white, smooth surface |
| Porosity | Low porosity, less water absorption | High porosity, absorbs moisture easily |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing and rarity | Lower cost, widely available |
| Common Uses | Structural foundations, pavements, heavy-duty construction | Cladding, flooring, ornamental features |
Introduction to Greenstone and Limestone
Greenstone is a durable, fine-grained metamorphic rock commonly used in construction for its strength and aesthetic appeal. Limestone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate, is favored for its workability and natural resistance to weathering. Both stones offer distinct advantages in building applications, with greenstone providing enhanced structural stability and limestone contributing to architectural elegance.
Geological Origins and Composition
Greenstone originates from metamorphosed basaltic lava flows, primarily composed of chlorite, actinolite, and epidote minerals, resulting in a dense and durable rock ideal for structural use. Limestone forms from accumulated marine organisms' calcium carbonate, predominantly calcite, offering a softer, more workable stone commonly utilized in architectural detailing and facades. The contrasting geological origins significantly influence their mechanical properties, with greenstone's igneous-metamorphic formation providing higher compressive strength compared to sedimentary limestone.
Physical Properties Comparison
Greenstone exhibits higher compressive strength and superior durability compared to limestone, making it ideal for structures requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity. Limestone's porosity leads to lower density and greater susceptibility to weathering, while greenstone's dense microstructure offers excellent resistance to erosion and abrasion. Thermal conductivity in greenstone is generally lower than limestone, providing better insulation properties for building applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Greenstone offers a unique aesthetic appeal with its deep green hues and natural mottling, creating a distinctive and elegant look for building facades. Limestone presents a wide range of color variations, from creamy whites to warm ochres, allowing for versatile design choices that enhance architectural styles. Both stones provide textured surfaces that add depth and character, but Greenstone's rich color contrasts sharply with Limestone's softer, more neutral palette.
Structural Strength and Durability
Greenstone exhibits superior structural strength compared to limestone due to its dense, fine-grained composition, making it ideal for load-bearing applications in construction. Limestone, while easier to quarry and work with, is more porous and prone to weathering, which can reduce its long-term durability, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Structural durability of greenstone significantly outperforms limestone in resistance to abrasion, chemical attack, and freeze-thaw cycles, ensuring a longer lifespan for built structures.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Greenstone offers superior weather resistance compared to limestone due to its dense, fine-grained structure that withstands moisture, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasive weather conditions better. Limestone, being more porous and softer, is prone to erosion, staining, and surface deterioration under harsh weather exposure. For long-term durability, greenstone's low porosity and high compressive strength contribute to greater longevity in building applications, making it a preferred choice for exterior facades and structures subject to significant environmental stress.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Greenstone offers superior sustainability compared to limestone due to its lower carbon footprint during extraction and processing, making it an eco-friendlier choice for building projects. Its natural durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby minimizing resource consumption and waste over the structure's lifecycle. Limestone, while abundant and versatile, often involves higher CO2 emissions from quarrying and cement production, contributing more significantly to environmental degradation.
Cost and Availability in Construction
Greenstone offers a durable and aesthetically appealing option for construction, but its higher cost and limited availability often make it less accessible for large-scale building projects compared to limestone. Limestone is widely available, more affordable, and easier to quarry and transport, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious construction while still providing adequate structural integrity. The cost-effectiveness and abundant supply of limestone contribute significantly to its dominance in the building material market.
Popular Applications in Modern Architecture
Greenstone is favored in modern architecture for its durability and unique aesthetic, making it popular in exterior cladding, landscaping, and decorative facades. Limestone is widely used for its natural beauty and versatility, often selected for flooring, wall veneers, and sculptural elements in both commercial and residential buildings. Both materials are valued for sustainability, with greenstone offering enhanced weather resistance, while limestone provides ease of carving and a timeless appeal.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Greenstone offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for exterior building facades and landscaping projects. Limestone, valued for its aesthetic versatility and ease of carving, suits detailed architectural elements and interior applications. Selecting between greenstone and limestone depends on factors like structural requirements, environmental exposure, and desired visual appeal for your construction project.
Infographic: Greenstone vs Limestone for Building
 azmater.com
azmater.com