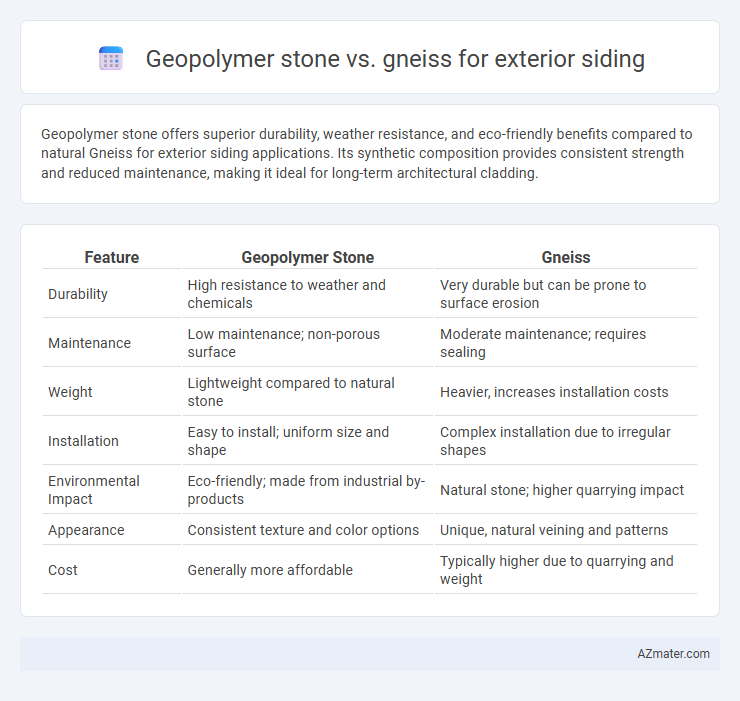
Geopolymer stone offers superior durability, weather resistance, and eco-friendly benefits compared to natural Gneiss for exterior siding applications. Its synthetic composition provides consistent strength and reduced maintenance, making it ideal for long-term architectural cladding.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Stone | Gneiss |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to weather and chemicals | Very durable but can be prone to surface erosion |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; non-porous surface | Moderate maintenance; requires sealing |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to natural stone | Heavier, increases installation costs |
| Installation | Easy to install; uniform size and shape | Complex installation due to irregular shapes |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; made from industrial by-products | Natural stone; higher quarrying impact |
| Appearance | Consistent texture and color options | Unique, natural veining and patterns |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically higher due to quarrying and weight |
Introduction to Geopolymer Stone and Gneiss
Geopolymer stone is an innovative, eco-friendly building material made from industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, offering high durability and resistance to weathering, making it suitable for exterior siding. Gneiss, a natural metamorphic rock characterized by its banded appearance and mineral composition, provides excellent strength and aesthetic appeal for construction applications. Both materials offer unique benefits for exterior siding, with geopolymer stone emphasizing sustainability and customization, while gneiss highlights natural beauty and proven durability.
Geological Formation and Composition
Geopolymer stone is an engineered material created by chemically activating industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, resulting in a dense, durable surface ideal for exterior siding. In contrast, Gneiss is a natural metamorphic rock formed through intense heat and pressure, composed primarily of quartz, feldspar, and mica, offering unique banded patterns and high resistance to weathering. The synthetic origin of geopolymer stone allows precise control over composition and performance, while gneiss's geological formation imparts natural variation and strength suited for long-term exterior applications.
Aesthetic Differences: Color and Texture
Geopolymer stone offers a consistent range of colors and textures due to its manufactured nature, allowing for customizable and uniform exterior siding options that mimic natural stone without variation. Gneiss, a naturally occurring metamorphic rock, exhibits unique color banding and textured patterns, providing a diverse and organic aesthetic with varying shades of gray, white, and black. The natural veining and granular texture of Gneiss create a dynamic visual appeal, contrasting with the smoother, more controlled finish of geopolymer stone siding.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Geopolymer stone exhibits exceptional durability and superior weather resistance compared to natural gneiss, making it highly suitable for exterior siding applications. Its synthetic composition provides enhanced resistance to moisture, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical corrosion, outperforming gneiss, which may show natural variability and susceptibility to erosion in harsh climates. The consistent strength and low porosity of geopolymer stone contribute to long-term structural integrity and reduced maintenance requirements under extreme weather conditions.
Installation Methods and Ease
Geopolymer stone offers a lightweight, uniform composition making installation faster and less labor-intensive compared to natural gneiss, which requires precise handling due to its variable density and natural fractures. Geopolymer stone panels often utilize interlocking systems or adhesive mounting, simplifying alignment and reducing the need for heavy machinery, while gneiss typically demands mechanical anchoring and skilled masons to manage its irregularities. The engineered consistency of geopolymer stone minimizes cutting and fitting challenges, enhancing installation speed and overall ease for exterior siding projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer stone offers a lower environmental impact than gneiss by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, significantly reducing carbon emissions during production. The manufacturing process of geopolymer stone consumes less energy and diverts waste from landfills, promoting circular economy principles. Gneiss, a natural stone, involves quarrying that disturbs ecosystems and requires substantial energy for extraction and transportation, making geopolymer stone a more sustainable choice for exterior siding.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Value
Geopolymer stone offers a lower initial cost compared to natural gneiss, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious exterior siding projects. While gneiss boasts superior durability and weather resistance, geopolymer stone provides enhanced cost-effectiveness through easier installation and lower maintenance expenses over time. Long-term value favors geopolymer stone due to its sustainable manufacturing process and resistance to fading, reducing replacement and upkeep costs compared to gneiss.
Maintenance Requirements
Geopolymer stone offers significantly lower maintenance requirements compared to natural gneiss for exterior siding due to its enhanced resistance to weathering, staining, and mold growth. Gneiss, being a natural metamorphic rock, often necessitates periodic sealing and cleaning to prevent surface degradation and maintain its aesthetic appeal. The durability and non-porous nature of geopolymer stone result in reduced upkeep costs and longer-lasting exterior cladding performance.
Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Geopolymer stone offers superior thermal insulation compared to gneiss, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in exterior siding applications. Its dense, engineered microstructure enhances acoustic performance by absorbing and dampening sound waves more effectively than the natural crystalline structure of gneiss. This makes geopolymer stone a preferred choice for exterior siding where thermal regulation and noise reduction are critical.
Ideal Applications and Design Considerations
Geopolymer stone offers superior durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for exterior siding in harsh climates and high-moisture environments, while gneiss provides rich natural grain patterns and color variations suited for aesthetic-focused architectural designs. Geopolymer's low porosity and thermal stability reduce maintenance needs and enhance longevity, contrasting with gneiss, which requires sealing and periodic upkeep due to its natural mineral composition. Design considerations include selecting geopolymer stone for modern, uniform facades and gneiss for projects seeking authentic natural stone texture and visual complexity.
Infographic: Geopolymer stone vs Gneiss for Exterior Siding
 azmater.com
azmater.com