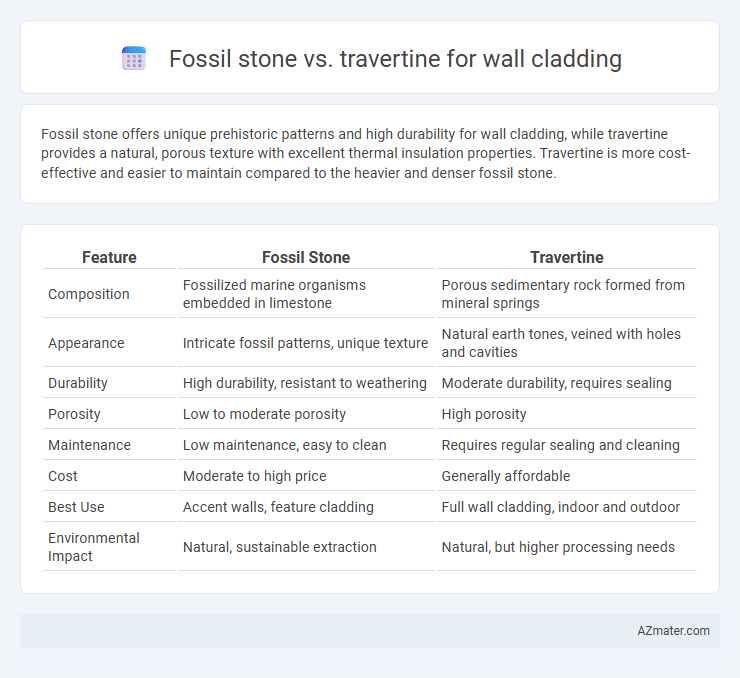
Fossil stone offers unique prehistoric patterns and high durability for wall cladding, while travertine provides a natural, porous texture with excellent thermal insulation properties. Travertine is more cost-effective and easier to maintain compared to the heavier and denser fossil stone.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fossil Stone | Travertine |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fossilized marine organisms embedded in limestone | Porous sedimentary rock formed from mineral springs |
| Appearance | Intricate fossil patterns, unique texture | Natural earth tones, veined with holes and cavities |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to weathering | Moderate durability, requires sealing |
| Porosity | Low to moderate porosity | High porosity |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires regular sealing and cleaning |
| Cost | Moderate to high price | Generally affordable |
| Best Use | Accent walls, feature cladding | Full wall cladding, indoor and outdoor |
| Environmental Impact | Natural, sustainable extraction | Natural, but higher processing needs |
Introduction to Fossil Stone and Travertine
Fossil stone, a sedimentary rock rich in preserved ancient marine life, offers a unique textured appearance with natural fossils embedded, making it ideal for distinctive wall cladding designs. Travertine, a form of limestone deposited by mineral springs, is prized for its rich cream and beige hues along with its porous texture that can be polished or left natural, providing versatility in aesthetic and finish options. Both materials deliver durability and natural beauty, but fossil stone's fossilized patterns create a striking visual contrast compared to the smoother, vein-patterned surface of travertine.
Geological Origins and Formation
Fossil stone, primarily composed of ancient marine fossils embedded in limestone, forms through the gradual accumulation and fossilization of organic remains over millions of years in sedimentary environments. Travertine originates from rapidly precipitated calcium carbonate around mineral-rich hot springs or limestone caves, characterized by its porous texture and banded patterns. While both stones are sedimentary, fossil stone's distinct fossil inclusions highlight its biological origins, contrasting with travertine's chemical precipitation process.
Unique Aesthetic Characteristics
Fossil stone wall cladding features intricate, natural patterns formed by ancient marine fossils, offering a rich texture and a historical narrative that enhances any space with organic beauty. Travertine, characterized by its porous surface and distinctive vein patterns, provides a warm, earthy tone and a smooth, matte finish ideal for elegant, timeless designs. Both stones create unique visual appeal, but fossil stone emphasizes fossil imprints and depth, while travertine highlights subtle color variations and natural holes that can be filled or left open for added rustic charm.
Color Variations and Visual Appeal
Fossil stone offers rich earth tones with intricate patterns featuring embedded fossils, creating a unique texture that enhances wall cladding's natural aesthetic. Travertine presents a lighter palette, ranging from creamy beige to warm honey hues, with distinctive porous surfaces that add depth and a classic elegance to interiors and exteriors. Color variations in fossil stone tend to be more varied and dramatic, while travertine provides a softer, more uniform visual appeal ideal for bright and airy spaces.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Fossil stone offers exceptional durability due to its dense composition and natural fossil inclusions, making it highly resistant to wear and weathering for wall cladding applications. Travertine, while visually appealing with its porous texture, requires sealing to enhance its longevity and prevent damage from moisture and stains. Over time, fossil stone generally outperforms travertine in maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal, proving to be a more robust choice for long-lasting wall cladding.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Fossil stone wall cladding requires minimal maintenance, needing only periodic dusting and occasional wiping with a damp cloth to preserve its natural texture and embedded fossil patterns. Travertine demands more frequent cleaning to prevent staining, often benefiting from the application of a sealant to protect its porous surface from moisture and dirt. Both materials should avoid harsh chemicals, but travertine's softer composition makes it more susceptible to scratches and etching during cleaning.
Installation Process and Challenges
Fossil stone wall cladding requires precise cutting techniques to preserve embedded fossils, making installation labor-intensive and demanding skilled craftsmanship. Travertine, known for its porous surface, often necessitates reinforcement and sealing during installation to prevent water infiltration and damage, posing challenges in maintaining durability. Both materials require specialized tools and meticulous handling to ensure stability and aesthetic integrity in wall cladding applications.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Fossil stone wall cladding typically incurs higher costs due to its unique, intricate patterns and limited availability, often priced between $15 and $30 per square foot. Travertine offers a more budget-friendly option, ranging from $10 to $25 per square foot, with consistent textures and easier sourcing contributing to lower installation expenses. Budget considerations should factor in not only material costs but also maintenance and longevity, where fossil stone's durability might justify its initial premium over travertine in high-end projects.
Best Applications for Wall Cladding
Fossil stone offers a unique, textured look with embedded ancient shell or coral patterns, ideal for feature walls in living rooms or commercial spaces seeking a natural, historical aesthetic. Travertine provides a smooth, porous surface with warm earthy tones, making it perfect for both interior and exterior wall cladding in bathrooms, kitchens, and facades that require a timeless, Mediterranean appeal. Both stones withstand weather elements well, but fossil stone is preferred for bold, decorative accents, while travertine excels in creating elegant, uniform wall surfaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fossil stone and travertine differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for wall cladding, with fossil stone often sourced from quarries that may disrupt prehistoric fossil sites, raising concerns about ecological preservation. Travertine, a carbonate rock formed in mineral springs, typically involves less destructive extraction but demands substantial energy for processing and transportation, influencing its carbon footprint. Selecting travertine from local quarries with certified sustainable practices can enhance eco-friendliness, whereas fossil stone requires careful consideration of its origin and quarrying methods to minimize environmental harm.
Infographic: Fossil stone vs Travertine for Wall Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com