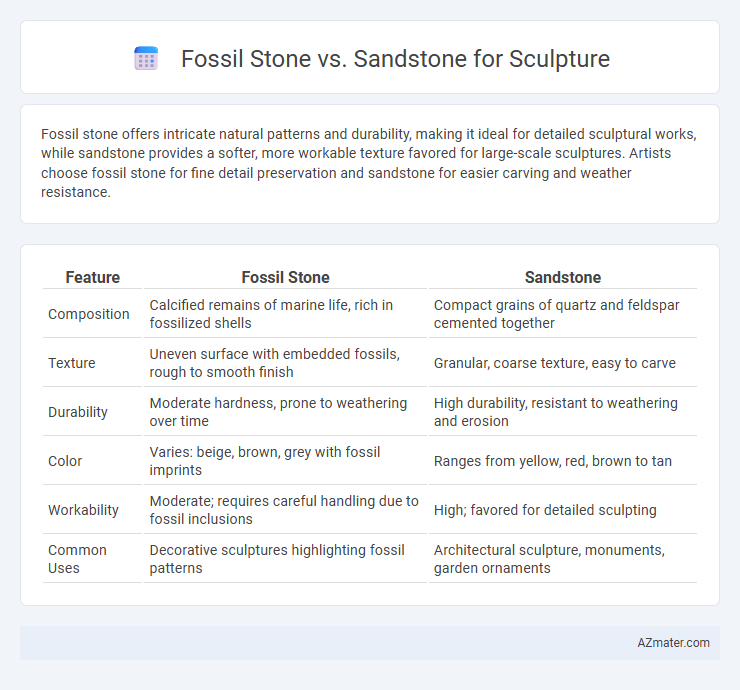
Fossil stone offers intricate natural patterns and durability, making it ideal for detailed sculptural works, while sandstone provides a softer, more workable texture favored for large-scale sculptures. Artists choose fossil stone for fine detail preservation and sandstone for easier carving and weather resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fossil Stone | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcified remains of marine life, rich in fossilized shells | Compact grains of quartz and feldspar cemented together |
| Texture | Uneven surface with embedded fossils, rough to smooth finish | Granular, coarse texture, easy to carve |
| Durability | Moderate hardness, prone to weathering over time | High durability, resistant to weathering and erosion |
| Color | Varies: beige, brown, grey with fossil imprints | Ranges from yellow, red, brown to tan |
| Workability | Moderate; requires careful handling due to fossil inclusions | High; favored for detailed sculpting |
| Common Uses | Decorative sculptures highlighting fossil patterns | Architectural sculpture, monuments, garden ornaments |
Understanding Fossil Stone and Sandstone
Fossil stone, composed primarily of mineralized organic remains, offers unique textures and patterns that enhance the artistic appeal of sculptures, making it a favored choice for detailed and naturalistic works. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock formed from compacted sand grains, provides a softer and more workable medium ideal for large-scale sculptures due to its ease of carving and durability. Understanding the mineral composition, grain size, and weathering properties of fossil stone and sandstone is essential for sculptors to select the best material suited to their artistic vision and environmental conditions.
Geological Formation Differences
Fossil stone, formed from sedimentary deposits rich in preserved organic remains, exhibits a compact, often intricate texture due to mineralization processes over millions of years, making it unique for detailed sculptural work. Sandstone results from cemented sand-sized mineral grains, primarily quartz, deposited in layers through wind or water action, offering a more uniform grain structure but typically less dense than fossil stone. The geological differences impact durability and carving techniques, with fossil stone often providing greater resistance to erosion than the more porous, softer sandstone.
Physical Properties Comparison
Fossil stone exhibits greater hardness and durability compared to sandstone, making it more suitable for intricate sculptural details and long-lasting outdoor installations. Sandstone, characterized by its porous texture and softer composition, offers easier carving but is more susceptible to weathering and erosion over time. The denser mineral matrix of fossil stone enhances resistance to chipping and abrasion, while sandstone's grainier structure allows for varied surface finishes but reduced structural integrity.
Aesthetic Qualities and Appearance
Fossil stone exhibits unique aesthetic qualities characterized by embedded marine fossils and intricate natural patterns, offering a visually captivating and historically rich appearance ideal for detailed sculptural work. Sandstone, conversely, features a more uniform, granular texture with warm earth tones that provide a classic, rustic look, making it suitable for larger, weather-resistant sculptures. The choice between fossil stone and sandstone hinges on the desired artistic expression, with fossil stone emphasizing intricate fossilized details while sandstone prioritizes durability and timeless simplicity.
Workability for Sculptors
Fossil stone offers unique texture and historical depth, but its variable hardness can complicate detailed carving, requiring specialized tools and techniques. Sandstone provides excellent workability with a consistent grain and moderate hardness, making it a favored choice for sculptors seeking smooth finishes and intricate designs. The porosity of sandstone also allows for easier shaping and abrasion compared to fossilized materials, enhancing precision in sculptural work.
Durability and Longevity
Fossil stone offers superior durability and longevity compared to sandstone due to its denser composition and natural mineralization, making it highly resistant to weathering and erosion. Sandstone, while easier to carve and widely used for sculpture, is more porous and susceptible to wear over time, especially in outdoor environments exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Choosing fossil stone ensures a sculpture maintains its structural integrity and fine details for centuries, whereas sandstone may require more maintenance and conservation efforts.
Cost and Availability
Fossil stone tends to be more expensive than sandstone due to its uniqueness and the complexity of quarrying fossilized materials, making it less accessible for large projects. Sandstone is widely available globally, offering a more cost-effective option for sculptors seeking durability and ease of carving. The choice between fossil stone and sandstone largely depends on budget constraints and the desired aesthetic impact of the sculpture.
Historical Uses in Sculpture
Fossil stone has been prized in sculpture for its unique patterns and the historical significance of preserving ancient life forms, often seen in decorative artifacts from the Paleozoic era. Sandstone, with its abundant availability and ease of carving, became a favored material in ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia for monumental sculptures and architectural reliefs. The durability and textural qualities of sandstone allowed artists to create detailed works that have lasted millennia, while fossil stone's rarity made it a symbol of prestige in sculptural art.
Environmental Impact of Quarrying
Quarrying fossil stone for sculpture often results in less environmental degradation compared to sandstone due to the smaller scale and lower extraction volume required, preserving biodiversity and reducing habitat disruption. Sandstone quarrying tends to produce higher dust emissions and greater landscape alteration, causing soil erosion and impacting local water quality. Sustainable practices in fossil stone extraction can further minimize carbon footprint and ecological disturbance relative to conventional sandstone quarry operations.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Sculpture
Fossil stone offers unique textures and embedded natural history, making it ideal for sculptures requiring intricate detail and visual storytelling. Sandstone provides a softer, more workable medium with consistent grain, suitable for larger or more abstract forms demanding smooth finishes. Selecting the right stone depends on the desired durability, level of detail, and the environmental exposure your sculpture will face.
Infographic: Fossil stone vs Sandstone for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com