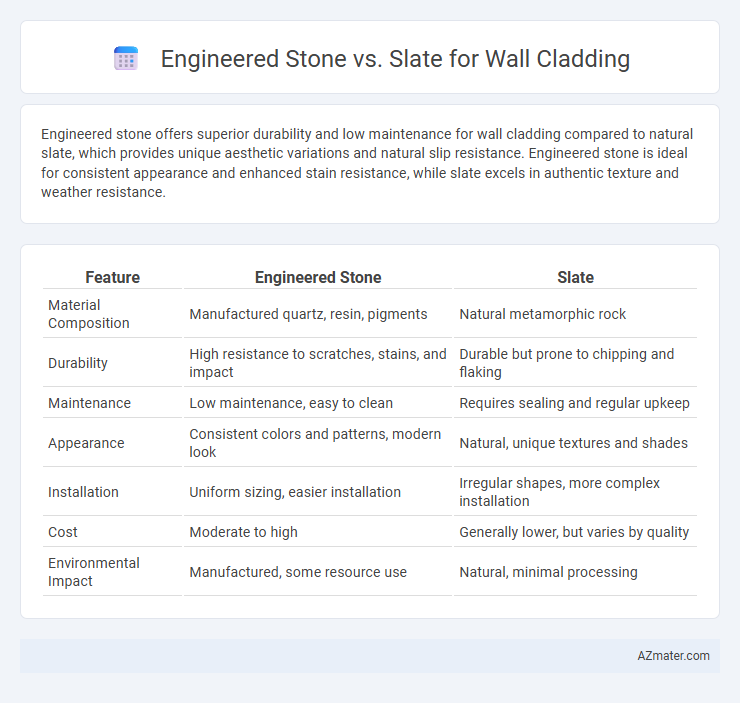
Engineered stone offers superior durability and low maintenance for wall cladding compared to natural slate, which provides unique aesthetic variations and natural slip resistance. Engineered stone is ideal for consistent appearance and enhanced stain resistance, while slate excels in authentic texture and weather resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Engineered Stone | Slate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Manufactured quartz, resin, pigments | Natural metamorphic rock |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches, stains, and impact | Durable but prone to chipping and flaking |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires sealing and regular upkeep |
| Appearance | Consistent colors and patterns, modern look | Natural, unique textures and shades |
| Installation | Uniform sizing, easier installation | Irregular shapes, more complex installation |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower, but varies by quality |
| Environmental Impact | Manufactured, some resource use | Natural, minimal processing |
Introduction to Engineered Stone and Slate for Wall Cladding
Engineered stone for wall cladding offers a versatile and durable option composed of crushed natural stone bound by resin, providing consistent color and pattern with high resistance to stains and impact. Slate, a natural metamorphic rock, is valued for its unique texture and earthy tones, offering a timeless and rustic aesthetic while being highly resistant to weathering and moisture. Selecting between engineered stone and slate depends on desired appearance, maintenance needs, and budget constraints for wall cladding projects.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Engineered stone for wall cladding is composed of crushed natural stone mixed with resins and pigments, creating a durable, uniform material through a polymerization and compression manufacturing process. Slate, on the other hand, is a natural metamorphic rock formed through the compression of shale, split into thin, durable sheets by natural cleavage without additional manufacturing. The engineered stone offers consistent color and texture, while slate provides unique, natural variations due to its geological formation.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Versatility
Engineered stone offers a smoother, more uniform appearance with a wide range of colors and patterns that mimic natural materials, providing extensive design versatility for modern and sleek wall cladding. Slate, with its natural texture and earthy tones, presents a unique, rustic aesthetic that adds depth and character to spaces but has limited color variation. The choice between engineered stone and slate depends on desired visual impact and flexibility in customizing wall cladding designs.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Engineered stone offers superior durability and strength compared to slate, with its composition of quartz and resin providing enhanced resistance to impact, scratches, and stains. Slate, a natural metamorphic rock, has good compressive strength but is more prone to chipping and weathering over time when used in wall cladding. Engineered stone's non-porous surface ensures better long-term performance in both interior and exterior environments, making it a more robust choice for durable wall cladding.
Installation Requirements and Techniques
Engineered stone for wall cladding demands precise substrate preparation and often requires adhesive bonding with mechanical fixing for enhanced stability, accommodating its consistent thickness and weight. Slate installation necessitates careful handling due to its natural variability in thickness and fragility, typically involving mortar beds and mechanical anchors to secure panels and prevent shifting. Understanding the differences in material flexibility and weight distribution is critical for selecting appropriate fasteners and ensuring long-term durability in wall cladding projects.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Engineered stone offers superior stain resistance and requires minimal maintenance compared to slate, which often needs regular sealing to prevent moisture absorption and surface damage. Cleaning engineered stone is simplified by its non-porous surface, allowing the use of mild detergents without risking damage, whereas slate demands specialized stone cleaners to preserve its natural texture and color. The durability of engineered stone reduces the frequency of deep cleanings and repairs, making it a practical choice for low-maintenance wall cladding.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered stone offers a more sustainable option for wall cladding by incorporating recycled materials and reducing quarry extraction, minimizing environmental degradation compared to slate. Slate quarrying involves significant habitat disruption and energy-intensive processes, resulting in higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. Engineered stone's durability and lower maintenance extend its lifespan, enhancing its environmental benefits over the finite and non-renewable nature of natural slate.
Cost Analysis: Engineered Stone vs Slate
Engineered stone typically costs between $40 to $80 per square foot, offering a more budget-friendly option compared to natural slate, which ranges from $60 to $150 per square foot due to its quarrying and transportation expenses. Installation expenses for engineered stone are generally lower because of its uniform thickness and lighter weight, cutting labor time and complexity compared to slate's variable thickness and weight. Maintenance costs also favor engineered stone, as it resists staining and chipping better than slate, reducing long-term expenses.
Popular Applications in Residential and Commercial Projects
Engineered stone is widely favored for residential wall cladding due to its durability, low maintenance, and vast color options, making it ideal for kitchens, bathrooms, and accent walls. Slate excels in commercial projects where a natural, textured aesthetic is desired, often used in lobbies, exterior facades, and feature walls, providing slip resistance and weather durability. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with engineered stone emphasizing design flexibility and slate delivering authentic natural stone appeal.
Pros and Cons Summary for Each Material
Engineered stone offers high durability, resistance to stains and scratches, and a wide range of colors and patterns suitable for wall cladding, but it can be expensive and less natural-looking compared to slate. Slate provides a unique, natural texture with excellent weather resistance and longevity, ideal for outdoor applications, but it can be brittle, prone to chipping, and requires regular maintenance to prevent moss and mildew. Both materials offer distinct aesthetic and functional advantages, with engineered stone favored for uniformity and low upkeep, while slate is preferred for authentic, rustic appeal.
Infographic: Engineered stone vs Slate for Wall cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com