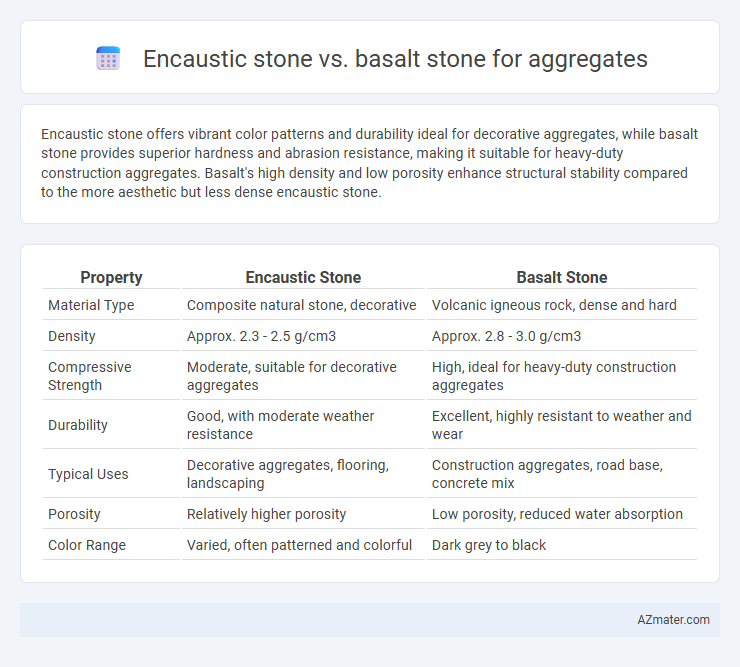
Encaustic stone offers vibrant color patterns and durability ideal for decorative aggregates, while basalt stone provides superior hardness and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty construction aggregates. Basalt's high density and low porosity enhance structural stability compared to the more aesthetic but less dense encaustic stone.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Encaustic Stone | Basalt Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite natural stone, decorative | Volcanic igneous rock, dense and hard |
| Density | Approx. 2.3 - 2.5 g/cm3 | Approx. 2.8 - 3.0 g/cm3 |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate, suitable for decorative aggregates | High, ideal for heavy-duty construction aggregates |
| Durability | Good, with moderate weather resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to weather and wear |
| Typical Uses | Decorative aggregates, flooring, landscaping | Construction aggregates, road base, concrete mix |
| Porosity | Relatively higher porosity | Low porosity, reduced water absorption |
| Color Range | Varied, often patterned and colorful | Dark grey to black |
Introduction to Encaustic Stone and Basalt Stone Aggregates
Encaustic stone aggregates are prized for their vibrant, patterned surfaces derived from ceramic tiles infused with colored clays, offering decorative versatility in landscaping and flooring applications. Basalt stone aggregates, formed from cooled volcanic lava, exhibit exceptional hardness, durability, and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty construction and road base materials. The choice between encaustic and basalt aggregates depends on aesthetic requirements versus structural performance in aggregate use.
Geological Origins and Composition
Encaustic stone, typically derived from sedimentary formations, features a composition rich in silica and feldspar, contributing to its angular shape and durability in aggregates. Basalt stone originates from volcanic activity, characterized by fine-grained, mafic minerals such as pyroxene and plagioclase, offering high density and strength in construction applications. The distinct geological origins result in differences in mineral composition and physical properties, influencing their performance as aggregate materials.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Encaustic stone exhibits higher compressive strength and better wear resistance compared to basalt stone, making it more durable for aggregate applications in heavy-duty construction. Basalt stone offers superior impact resistance and lower water absorption, which enhances its performance in environments prone to moisture and freeze-thaw cycles. Both stones display high density and abrasion resistance, but Encaustic stone's enhanced hardness and durability provide advantages in long-term structural integrity.
Durability and Longevity in Construction
Encaustic stone exhibits high durability due to its dense composition and resistance to weathering, making it an excellent choice for long-lasting aggregates in construction projects exposed to varying environmental conditions. Basalt stone offers superior hardness and exceptional longevity, with strong resistance to abrasion and chemical degradation, which ensures sustained structural integrity in heavy-duty applications. Both stones provide robust performance, but basalt's enhanced durability under mechanical stress positions it as a preferred aggregate in infrastructure requiring maximum lifespan and minimal maintenance.
Color, Texture, and Aesthetic Differences
Encaustic stone aggregates exhibit vibrant, multi-colored patterns with a smooth, polished texture, offering a decorative and artistic appeal suitable for design-focused projects. Basalt stone aggregates feature a uniform dark gray to black color with a rough, coarse texture, providing a more industrial and natural aesthetic. The color vibrancy and intricate patterns of encaustic stones contrast sharply with the solid, muted tones of basalt, influencing their suitability in architectural and landscaping applications.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Encaustic stone aggregates, derived from ceramic-based materials, typically incur higher production costs compared to basalt stone due to complex manufacturing processes and material sourcing. Basalt stone, a naturally occurring igneous rock, offers more economical pricing driven by abundant availability and lower extraction expenses, making it a preferred choice for large-scale construction projects. Economic factors such as transportation, durability, and long-term maintenance also favor basalt, providing better cost-efficiency over the lifecycle of infrastructure developments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Encaustic stone aggregates are often sourced from natural clays and pigments, offering lower environmental impact due to their minimal processing requirements and potential for recycling in construction. Basalt stone aggregates, derived from volcanic rock, provide high durability and strength but extraction involves significant quarrying and energy-intensive crushing processes that contribute to higher carbon emissions. Sustainable practices favor encaustic stone when prioritizing reduced resource consumption and lower embodied energy, while basalt's longevity supports long-term infrastructure resilience in aggregate applications.
Applications in Modern Construction Projects
Encaustic stone offers superior aesthetic appeal and vibrant surface patterns, making it ideal for decorative aggregates in upscale architectural facades and interior landscaping. Basalt stone provides exceptional strength, durability, and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it a preferred aggregate choice for heavy-duty concrete, road base layers, and infrastructure projects requiring long-term performance. Modern construction projects leverage the unique properties of encaustic stones for visual enhancement and basalt stones for structural integrity, optimizing both form and function in aggregate applications.
Performance in Various Climates and Conditions
Encaustic stone, known for its dense and porous structure, offers superior thermal insulation and weather resistance, making it ideal for varied climatic conditions including freeze-thaw cycles. Basalt stone exhibits exceptional durability and high compressive strength, ensuring robust performance under heavy loads and in both wet and dry environments, particularly in harsh climates. When used as aggregates, basalt provides enhanced abrasion resistance while encaustic stone contributes to improved thermal stability and moisture regulation in construction applications.
Choosing the Right Aggregate: Encaustic vs Basalt
Encaustic stone aggregates offer vibrant colors and distinctive patterns, making them ideal for decorative concrete and architectural projects requiring aesthetic appeal. Basalt stone aggregates provide superior strength, durability, and resistance to weathering, making them suitable for heavy-duty construction, road bases, and high-load-bearing applications. Selecting between encaustic and basalt depends on project requirements for visual impact versus structural performance.
Infographic: Encaustic stone vs Basalt stone for Aggregates
 azmater.com
azmater.com