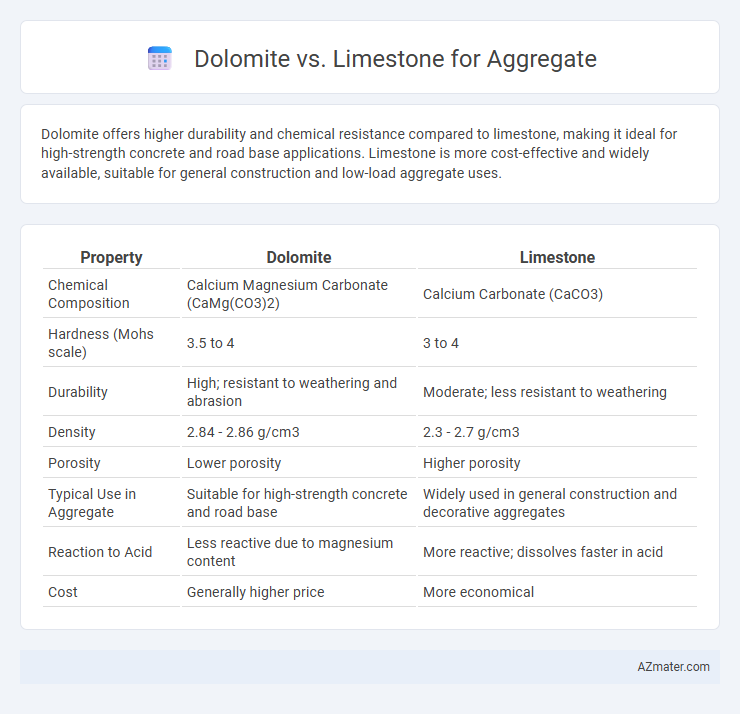
Dolomite offers higher durability and chemical resistance compared to limestone, making it ideal for high-strength concrete and road base applications. Limestone is more cost-effective and widely available, suitable for general construction and low-load aggregate uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dolomite | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Calcium Magnesium Carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2) | Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 3.5 to 4 | 3 to 4 |
| Durability | High; resistant to weathering and abrasion | Moderate; less resistant to weathering |
| Density | 2.84 - 2.86 g/cm3 | 2.3 - 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Porosity | Lower porosity | Higher porosity |
| Typical Use in Aggregate | Suitable for high-strength concrete and road base | Widely used in general construction and decorative aggregates |
| Reaction to Acid | Less reactive due to magnesium content | More reactive; dissolves faster in acid |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More economical |
Overview: Dolomite vs Limestone Aggregate
Dolomite aggregate is composed primarily of calcium magnesium carbonate, offering higher resistance to abrasion and better load-bearing capacity compared to limestone, which consists mainly of calcium carbonate. Limestone aggregate is widely used for construction due to its availability and cost-effectiveness but may be less durable in harsh environments than dolomite. Both materials serve as essential components in road base, concrete, and asphalt production, with dolomite preferred for projects requiring enhanced strength and durability.
Geological Formation and Composition
Dolomite and limestone are sedimentary rocks primarily composed of carbonate minerals, with dolomite rich in the mineral dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) and limestone mainly composed of calcite (CaCO3). Dolomite forms through the chemical alteration of limestone by magnesium-rich fluids, resulting in a denser crystalline structure, while limestone typically originates from marine organisms and accumulates from calcite skeletal fragments. The distinct mineral compositions influence their geological stability and suitability as aggregate materials in construction and industrial applications.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Dolomite and limestone differ significantly in physical and chemical properties, making them suitable for various aggregate applications. Dolomite primarily consists of calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2), offering higher hardness and greater resistance to abrasion compared to limestone, which is primarily calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Limestone tends to have a lower density and may exhibit higher reactivity with acids, while dolomite's magnesium content enhances its durability and reduces susceptibility to chemical weathering in construction uses.
Aggregate Strength and Durability
Dolomite aggregate provides higher strength and better durability compared to limestone due to its crystalline structure and magnesium content. Its resistance to weathering and chemical attacks makes dolomite ideal for heavy-duty construction applications such as road bases and concrete production. Limestone aggregate, while generally softer and less durable, is often preferred for cost-effective projects with moderate strength requirements.
Performance in Concrete and Asphalt
Dolomite offers higher compressive strength and enhanced durability compared to limestone, making it more suitable for high-performance concrete and asphalt mixtures. Limestone aggregates provide better workability and lower alkali reactivity, reducing the risk of alkali-silica reaction (ASR) in concrete structures. In asphalt applications, dolomite's angularity improves interlock and resistance to rutting, while limestone contributes to better asphalt binder adhesion and flexibility.
Environmental Considerations
Dolomite aggregate exhibits lower carbon dioxide emissions during extraction and processing compared to limestone, making it a more sustainable choice for construction projects. Limestone quarrying often results in higher dust generation and greater disturbance to local ecosystems. Both materials require proper management practices to minimize habitat disruption and groundwater contamination, but dolomite's lower acid-reactivity offers enhanced resistance to environmental degradation.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Dolomite aggregate typically costs more than limestone due to its higher density and chemical composition, which can enhance strength and durability in construction projects. Limestone is more widely available and abundant in many regions, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale applications. Supply chain factors and local quarry proximity heavily influence the price and accessibility of both aggregates.
Regional Usage Trends
Dolomite aggregate is predominantly favored in regions with sedimentary basins rich in magnesium carbonate, such as parts of the Midwest and Northeast United States, due to its superior hardness and chemical stability. Limestone aggregate is more commonly utilized in the South and West, where abundant calcite deposits support its widespread use in construction and road base applications. Regional geological availability significantly influences the choice between dolomite and limestone, impacting local infrastructure projects and supply chain logistics.
Suitability for Construction Applications
Dolomite offers higher strength and better resistance to abrasion and chemical weathering compared to limestone, making it more suitable for heavy-duty construction applications like road base and concrete aggregates. Limestone, with its higher calcium carbonate content, is ideal for projects requiring good workability and lower cost, such as cement production and building stone. Both materials are widely used, but the choice depends on specific load-bearing requirements and environmental exposure in construction projects.
Key Takeaways: Choosing the Right Aggregate
Dolomite and limestone serve as essential aggregates in construction, with dolomite offering higher density and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-strength concrete and road base applications. Limestone provides excellent workability and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general construction and asphalt production. Selecting the right aggregate depends on project-specific factors such as durability requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Dolomite vs Limestone for Aggregate
 azmater.com
azmater.com