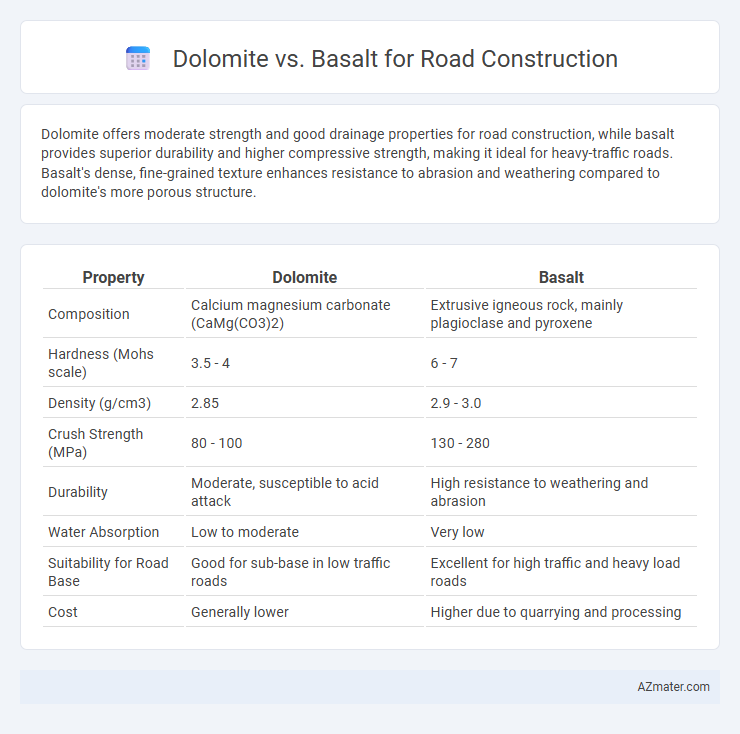
Dolomite offers moderate strength and good drainage properties for road construction, while basalt provides superior durability and higher compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy-traffic roads. Basalt's dense, fine-grained texture enhances resistance to abrasion and weathering compared to dolomite's more porous structure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dolomite | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2) | Extrusive igneous rock, mainly plagioclase and pyroxene |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 3.5 - 4 | 6 - 7 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.85 | 2.9 - 3.0 |
| Crush Strength (MPa) | 80 - 100 | 130 - 280 |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to acid attack | High resistance to weathering and abrasion |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate | Very low |
| Suitability for Road Base | Good for sub-base in low traffic roads | Excellent for high traffic and heavy load roads |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to quarrying and processing |
Introduction to Road Construction Materials
Dolomite and basalt are key materials in road construction, valued for their durability and load-bearing capacity. Basalt, a dense volcanic rock, offers exceptional strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic roadways. Dolomite, a sedimentary carbonate rock, provides good stability and is often used in base layers and asphalt mixes to enhance flexibility and surface quality.
Overview of Dolomite
Dolomite is a sedimentary carbonate rock primarily composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, favored in road construction for its durability and resistance to abrasion. Its high compressive strength and low water absorption make it suitable for base and sub-base layers, providing strong foundational support. Compared to basalt, dolomite offers better chemical stability in alkaline conditions but may have lower skid resistance on surfaces.
Overview of Basalt
Basalt is an igneous rock known for its high compressive strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it an ideal material for road construction. Its dense structure and low porosity contribute to excellent load-bearing capacity and longevity under heavy traffic conditions. Compared to dolomite, basalt offers superior stability and weather resistance, ensuring reliable pavement performance in various climates.
Physical Properties: Dolomite vs Basalt
Dolomite exhibits moderate hardness with a Mohs scale rating of 3.5 to 4, while basalt is significantly harder, ranging between 6 and 7, which makes basalt more resistant to abrasion and wear in road construction. Dolomite has a specific gravity of about 2.84, whereas basalt's specific gravity ranges from 2.8 to 3.0, indicating comparable densities but basalt's finer grain structure enhances compaction and stability. The porosity of dolomite is generally higher, resulting in lower durability compared to basalt, which has low porosity and superior water resistance, critical factors for the longevity of road surfaces under heavy traffic loads.
Durability and Performance in Road Applications
Dolomite offers high compressive strength and good abrasion resistance, making it suitable for surface layers in road construction, but its solubility can affect long-term durability under wet conditions. Basalt provides superior durability due to its dense structure, exceptional resistance to weathering and abrasion, and low water absorption, ensuring enhanced performance in heavy traffic and harsh climates. The choice between dolomite and basalt impacts road lifespan and maintenance costs, with basalt generally outperforming dolomite in durability and structural integrity for road applications.
Cost Comparison: Dolomite and Basalt
Dolomite typically costs less than basalt, making it a more budget-friendly option for road construction projects. Basalt offers superior durability and strength, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses despite its higher initial price. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost is essential to determine the most cost-effective material between dolomite and basalt for specific road construction applications.
Environmental Impact of Dolomite and Basalt
Dolomite and basalt differ in their environmental impact when used in road construction, with basalt generally exhibiting lower carbon emissions due to its natural abundance and minimal processing requirements. Dolomite mining can lead to higher habitat disruption and dust pollution, impacting local air quality and biodiversity. Basalt's greater durability reduces the need for frequent repairs, resulting in less resource consumption and environmental disturbance over the road's lifecycle.
Workability and Processing Differences
Dolomite exhibits easier workability in road construction due to its lower hardness and better machinability compared to basalt, which requires more energy-intensive crushing and grinding processes. Basalt's higher density and strength provide better durability but pose challenges in processing, leading to increased equipment wear and operational costs. Variations in mineral composition also affect binding characteristics, where dolomite's magnesium content improves bonding with asphalt, enhancing pavement integrity.
Case Studies: Dolomite and Basalt in Road Projects
Case studies reveal that basalt's high compressive strength and durability make it ideal for high-traffic road construction, as seen in projects across the Pacific Northwest, where its dense structure improves load-bearing capacity and longevity. Dolomite, exemplified in Southeast Asian road projects, offers excellent skid resistance and improved drainage due to its porous nature but may require stabilization treatments to enhance durability under heavy loads. Comparative reports indicate basalt reduces maintenance costs over time, while dolomite provides cost-effective initial construction with moderate performance in moderate traffic conditions.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Aggregate
Selecting the right aggregate for road construction requires balancing durability, load-bearing capacity, and cost-effectiveness. Dolomite offers moderate strength and good resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for light to medium traffic roads, while basalt provides superior compressive strength and excellent durability for heavy traffic and high-stress conditions. For projects demanding long-lasting performance under heavy loads, basalt is the preferred choice, whereas dolomite suits less demanding environments with budget constraints.
Infographic: Dolomite vs Basalt for Road Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com