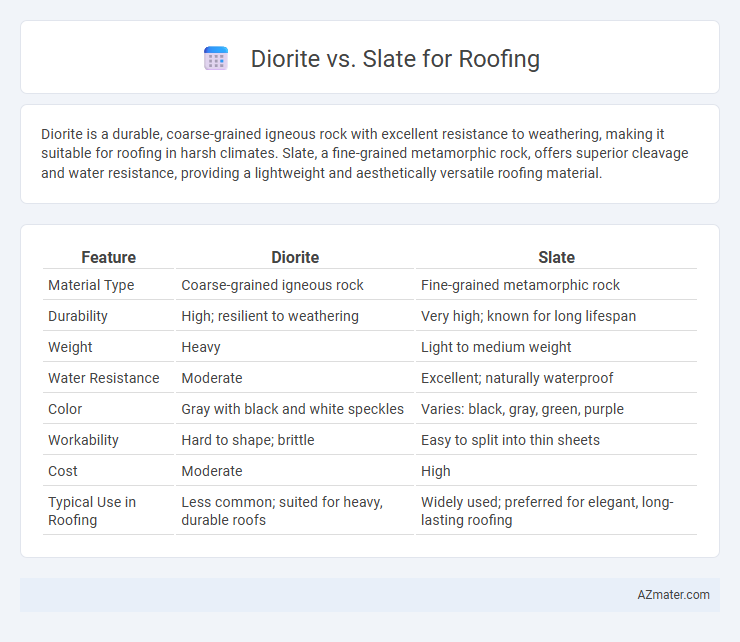
Diorite is a durable, coarse-grained igneous rock with excellent resistance to weathering, making it suitable for roofing in harsh climates. Slate, a fine-grained metamorphic rock, offers superior cleavage and water resistance, providing a lightweight and aesthetically versatile roofing material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Diorite | Slate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Coarse-grained igneous rock | Fine-grained metamorphic rock |
| Durability | High; resilient to weathering | Very high; known for long lifespan |
| Weight | Heavy | Light to medium weight |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | Excellent; naturally waterproof |
| Color | Gray with black and white speckles | Varies: black, gray, green, purple |
| Workability | Hard to shape; brittle | Easy to split into thin sheets |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Typical Use in Roofing | Less common; suited for heavy, durable roofs | Widely used; preferred for elegant, long-lasting roofing |
Introduction to Diorite and Slate as Roofing Materials
Diorite and slate are durable roofing materials known for their natural stone properties and long-lasting performance. Diorite, an igneous rock with a coarse-grained texture, offers high resistance to weathering and structural strength, making it suitable for roofing applications requiring robustness. Slate, a metamorphic rock renowned for its fine grain and split-resistant characteristics, provides excellent water resistance and a sleek, classic appearance ideal for traditional and modern roofing designs.
Geological Formation and Composition
Diorite is an intrusive igneous rock formed from slow cooling magma beneath the Earth's surface, composed mainly of plagioclase feldspar, biotite, hornblende, and quartz, providing durability and coarse-grained texture ideal for roofing. Slate, a metamorphic rock derived from shale through low-grade regional metamorphism, primarily consists of aligned clay minerals and quartz, offering excellent cleavage and water resistance for roofing tiles. The dense, foliated structure of slate contrasts with the granular, interlocking crystal structure of diorite, influencing their performance and aesthetic in roofing applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance Comparison
Diorite offers superior durability due to its coarse-grained igneous structure, making it highly resistant to wear and impact, while slate's fine-grained metamorphic composition provides exceptional weather resistance with natural water-shedding properties and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles. Slate typically exhibits longer lifespan in roofing applications, often exceeding 100 years, whereas diorite's durability is exceptional but less commonly used for roofing, limiting comparative lifespan data. Both materials resist fire and UV damage, but slate excels in maintaining structural integrity under harsh weather conditions, making it a preferred choice for roofing in regions with variable climates.
Weight and Structural Impacts
Diorite roofing is heavier than slate, typically weighing around 150-170 pounds per square foot compared to slate's 80-150 pounds per square foot. This significant difference in weight requires stronger structural support for diorite roofs, potentially increasing construction costs and engineering complexity. Slate's lighter weight allows for more flexible applications and reduced stress on building frameworks, making it a preferred choice for both aesthetic appeal and structural efficiency.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Diorite roofing offers a unique aesthetic appeal with its coarse-grained texture and predominantly gray to black hues, delivering a bold, natural look that complements contemporary and rustic architecture. Slate roofing is prized for its smooth, fine-grained surface and wide color range spanning from deep gray, blue, green, to purple, providing versatile options for elegant, classic designs. Both materials showcase durability, but the choice between diorite and slate hinges on desired texture and specific color palette preferences for enhancing roof visual impact.
Installation Processes and Techniques
Diorite roofing requires precise cutting and anchoring techniques due to its coarse-grained texture and high density, ensuring stability and longevity in harsh weather. Slate installation involves thinner, more uniform slabs that are easier to layer, using specialized hooks and nails to prevent cracking while providing excellent water resistance. Both materials demand experienced craftsmanship to optimize performance, with Diorite offering superior durability and Slate preferred for its aesthetic elegance and easier handling.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Diorite roofing offers exceptional durability with low maintenance requirements, as its dense crystalline structure resists weathering and erosion over time. Slate roofing, known for its natural cleavage properties, requires periodic inspection for broken or slipped tiles but boasts a lifespan exceeding 100 years when properly maintained. Both materials provide excellent longevity, but diorite's hardness results in fewer repairs, while slate's aesthetic appeal often necessitates specialized upkeep to preserve its appearance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Diorite and slate differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for roofing, with diorite being a more abundant igneous rock that requires less energy-intensive extraction compared to slate's metamorphic formation. Slate offers exceptional longevity, often lasting over a century with minimal maintenance, which reduces the need for frequent replacement and associated environmental costs. However, diorite's availability and lower quarrying impact make it a more sustainable choice in regions where conservation of natural resources and reduced carbon footprint are priorities.
Cost Analysis: Diorite vs Slate Roofing
Diorite roofing typically offers a more affordable alternative to slate, with installation costs averaging 20-30% lower due to the stone's availability and easier handling. Slate roofing, renowned for its durability and aesthetic appeal, demands higher upfront investment, with prices often driven by the rarity of high-quality slate and skilled labor requirements. Long-term maintenance expenses tend to be lower for slate, potentially offsetting its initial cost difference over the lifespan of the roof.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Roofing Material
Diorite offers exceptional durability and a unique aesthetic with its coarse-grained texture, making it ideal for long-lasting roofing solutions in harsh climates. Slate, renowned for its fine-grain structure and natural water resistance, provides superior weatherproofing and a classic, elegant appearance favored in historic and upscale architecture. Selecting between Diorite and Slate depends on balancing the need for durability, cost-effectiveness, and desired visual appeal to ensure optimal roofing performance and longevity.
Infographic: Diorite vs Slate for Roofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com