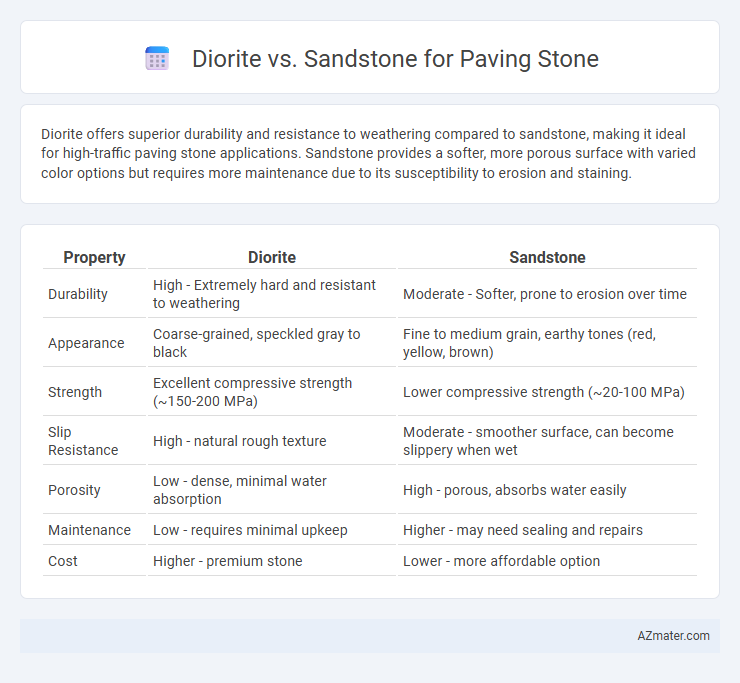
Diorite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic paving stone applications. Sandstone provides a softer, more porous surface with varied color options but requires more maintenance due to its susceptibility to erosion and staining.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Diorite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High - Extremely hard and resistant to weathering | Moderate - Softer, prone to erosion over time |
| Appearance | Coarse-grained, speckled gray to black | Fine to medium grain, earthy tones (red, yellow, brown) |
| Strength | Excellent compressive strength (~150-200 MPa) | Lower compressive strength (~20-100 MPa) |
| Slip Resistance | High - natural rough texture | Moderate - smoother surface, can become slippery when wet |
| Porosity | Low - dense, minimal water absorption | High - porous, absorbs water easily |
| Maintenance | Low - requires minimal upkeep | Higher - may need sealing and repairs |
| Cost | Higher - premium stone | Lower - more affordable option |
Introduction to Diorite and Sandstone Paving Stones
Diorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock known for its durability and striking salt-and-pepper appearance, making it a popular choice for long-lasting paving stones. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, offers a softer texture and a warm, natural aesthetic suitable for decorative paving applications. Both materials provide excellent slip resistance, but diorite's higher hardness makes it more resistant to weathering compared to the typically more porous sandstone.
Geological Formation and Composition
Diorite forms from the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in a coarse-grained igneous rock composed primarily of plagioclase feldspar, biotite, hornblende, and minor amounts of quartz. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock created through the compaction and cementation of sand-sized mineral particles, predominantly quartz and feldspar, deposited by water, wind, or ice. The igneous origin of diorite grants it higher durability and resistance to weathering compared to sandstone, which varies widely in hardness and porosity depending on its sedimentary composition and cementing materials.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetics
Diorite features a coarse-grained texture with a striking speckled pattern of black, white, and gray, offering a bold and modern aesthetic ideal for contemporary outdoor spaces. Sandstone presents a more natural, earthy appearance with warm tones ranging from beige to reddish-brown, providing a rustic and timeless look for traditional or naturalistic paving designs. The choice between Diorite and Sandstone for paving stone emphasizes whether a sleek, dramatic visual or a softer, organic atmosphere is desired in landscape architecture.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Diorite exhibits significantly higher hardness and durability compared to sandstone, making it a superior choice for paving stones in high-traffic areas. Its interlocking crystal structure contributes to exceptional resistance against abrasion, weathering, and impact, which extends the lifespan of paved surfaces. Sandstone, although aesthetically appealing with its natural grain and color variations, tends to be softer and more porous, reducing its performance under heavy load and harsh environmental conditions.
Weather and Climate Resistance
Diorite exhibits exceptional resistance to weathering and harsh climates due to its dense, coarse-grained granular structure that withstands freeze-thaw cycles and moisture penetration effectively. Sandstone, while aesthetically versatile, tends to be more porous and susceptible to erosion in wet or freeze-thaw environments, making it less durable under extreme weather conditions. For paving stones in regions with fluctuating temperatures and heavy precipitation, diorite offers superior longevity and structural integrity over sandstone.
Maintenance and Longevity
Diorite offers superior durability and low maintenance compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic paving applications. Its dense, hard composition resists weathering, staining, and wear, extending the lifespan of driveways or walkways. Sandstone requires more frequent sealing and cleaning due to its porous nature, which makes it susceptible to erosion and discoloration over time.
Installation Process and Workability
Diorite offers exceptional durability and density, making it more challenging to cut and shape during the installation process compared to sandstone, which is softer and easier to work with. Sandstone's workability allows for quicker and more precise customization, reducing labor time and installation complexity. The choice between diorite and sandstone impacts overall project timelines, with sandstone providing greater ease for intricate designs and diorite ensuring long-term wear resistance.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Diorite paving stones are generally more expensive due to their durability and aesthetic appeal, with prices ranging from $5 to $15 per square foot, making them a higher upfront investment compared to sandstone. Sandstone offers a more budget-friendly option, typically costing between $3 and $10 per square foot, while providing natural slip resistance and a warm, earthy color palette that suits various landscaping styles. Cost analysis must also include installation expenses, where sandstone's softer nature often reduces labor costs, whereas diorite's hardness can increase installation time and overall budget.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Diorite offers eco-friendly benefits due to its durability and low maintenance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and conserving natural resources over time. Sandstone, being a natural sedimentary rock, is often sourced sustainably and supports eco-conscious landscaping with its biodegradability and minimal processing requirements. Both materials contribute to sustainable paving options, but diorite's hardness ensures longer lifespan, while sandstone's natural composition enhances environmental compatibility.
Recommended Applications and Final Verdict
Diorite offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it an excellent choice for high-traffic areas such as driveways, patios, and commercial walkways where longevity is crucial. Sandstone, known for its natural slip resistance and aesthetic texture, works well in garden paths, pool surrounds, and decorative paving where visual appeal and safety are priorities. For paving stone applications demanding robust performance and minimal maintenance, diorite is the recommended option, while sandstone suits environments emphasizing natural beauty and moderate use.
Infographic: Diorite vs Sandstone for Paving Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com