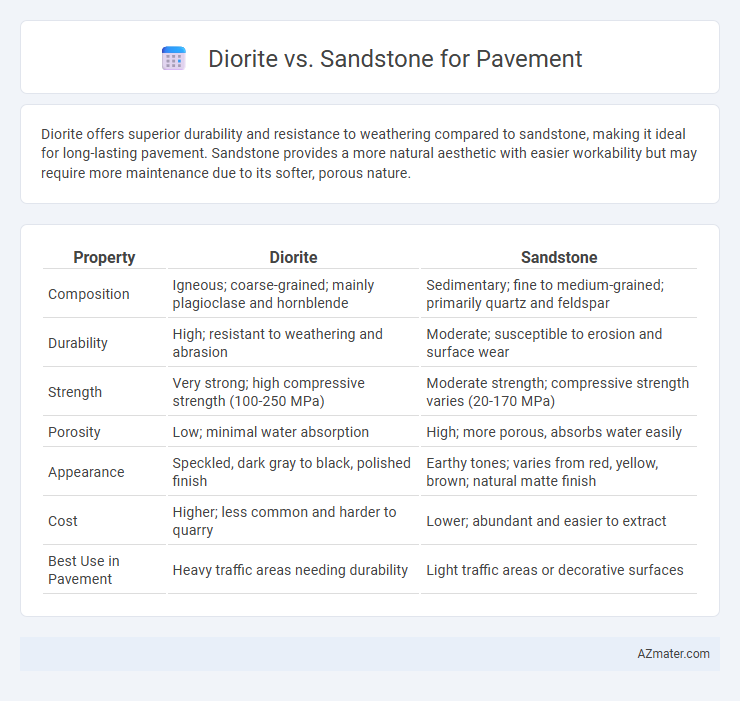
Diorite offers superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to sandstone, making it ideal for long-lasting pavement. Sandstone provides a more natural aesthetic with easier workability but may require more maintenance due to its softer, porous nature.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Diorite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Igneous; coarse-grained; mainly plagioclase and hornblende | Sedimentary; fine to medium-grained; primarily quartz and feldspar |
| Durability | High; resistant to weathering and abrasion | Moderate; susceptible to erosion and surface wear |
| Strength | Very strong; high compressive strength (100-250 MPa) | Moderate strength; compressive strength varies (20-170 MPa) |
| Porosity | Low; minimal water absorption | High; more porous, absorbs water easily |
| Appearance | Speckled, dark gray to black, polished finish | Earthy tones; varies from red, yellow, brown; natural matte finish |
| Cost | Higher; less common and harder to quarry | Lower; abundant and easier to extract |
| Best Use in Pavement | Heavy traffic areas needing durability | Light traffic areas or decorative surfaces |
Introduction to Diorite and Sandstone
Diorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock characterized by its durability and speckled appearance, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements requiring long-lasting materials. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of quartz and feldspar, offers a softer texture and natural aesthetic suitable for decorative and low-traffic paving areas. Both stones provide unique structural properties and visual appeal, with diorite excelling in strength and sandstone favored for its workability and warm tones.
Geological Formation and Composition
Diorite, an igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth's surface, consists primarily of plagioclase feldspar, biotite, hornblende, and minor quartz, providing high durability and resistance to weathering for pavement applications. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles or rock fragments, predominantly quartz and feldspar, cemented together by silica, calcium carbonate, or iron oxide, resulting in varying porosity and strength depending on its formation environment. The crystalline texture and compact nature of diorite offer superior load-bearing capacity compared to the often more porous and softer sandstone, influencing long-term performance in pavement construction.
Physical Properties Comparison
Diorite exhibits higher hardness and greater density compared to sandstone, making it more resistant to abrasion and suitable for high-traffic pavement areas. Sandstone, characterized by its porous structure and lower compressive strength, offers better flexibility but may require more maintenance due to weathering and wear. The choice between diorite and sandstone for pavement depends on balancing durability with aesthetic requirements and environmental exposure.
Strength and Durability
Diorite exhibits significantly higher compressive strength, typically ranging from 150 to 200 MPa, compared to sandstone's average of 40 to 100 MPa, making diorite more suitable for high-traffic pavement areas. The dense, interlocking crystal structure of diorite enhances its durability and resistance to weathering, whereas sandstone's porous nature can lead to quicker degradation under freeze-thaw cycles. For long-term pavement applications where load-bearing capacity and minimal maintenance are critical, diorite provides superior performance and lifespan compared to sandstone.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Options
Diorite offers a bold, speckled appearance with a mix of black, white, and gray tones, creating a striking, modern aesthetic for pavement. Sandstone provides a warm, natural palette ranging from soft beige to rich reds and browns, ideal for achieving a rustic or earthy look. Both materials offer versatile color options, but diorite's unique granular texture contrasts sharply with sandstone's smooth, layered finish, influencing the overall visual impact of paved surfaces.
Slip Resistance and Surface Texture
Diorite offers superior slip resistance for pavement applications due to its coarse-grained texture and interlocking mineral crystals, which create a naturally rough surface ideal for safety in wet conditions. Sandstone, with its finer grains and sedimentary layering, generally provides moderate slip resistance but can become smoother and more slippery when polished or worn over time. Selecting diorite ensures enhanced durability and grip on pavements, making it preferable in high-traffic or moisture-prone areas compared to sandstone's more decorative but less slip-resistant surface.
Weathering and Maintenance Requirements
Diorite offers superior resistance to weathering compared to sandstone due to its dense, coarse-grained igneous composition, making it less prone to erosion and chemical breakdown. Sandstone, being a sedimentary rock with a porous structure, tends to absorb water, leading to faster weathering and surface degradation under freeze-thaw cycles. Maintenance for diorite pavement is minimal, requiring less frequent sealing or repair, whereas sandstone pavements demand regular sealing and vigilance to prevent moisture infiltration and surface wear.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Diorite typically commands a higher price than sandstone due to its durability and density, resulting in increased transportation and installation costs. Sandstone is more widely available in many regions, making it a cost-effective option for pavement projects, especially where local quarries supply it in abundance. The choice between diorite and sandstone largely depends on budget constraints and regional availability, with sandstone offering more economical solutions for large-scale installations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Diorite offers greater durability and requires less maintenance than sandstone, reducing long-term environmental impact through fewer replacements and repairs. Sandstone, being a natural sedimentary rock, typically has lower embodied energy in extraction but may weather faster, increasing lifecycle resource consumption. Choosing diorite for pavement aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing resource depletion and extending pavement lifespan, while sandstone's environmental footprint depends heavily on local sourcing and durability considerations.
Best Applications for Pavement
Diorite offers exceptional durability and a high resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements in urban areas and industrial zones. Sandstone's natural porosity and aesthetic appeal suit it best for decorative walkways, garden paths, and low-traffic residential pavements. Both materials provide distinct advantages, with diorite excelling in strength and sandstone favored for visual texture and slip resistance.
Infographic: Diorite vs Sandstone for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com