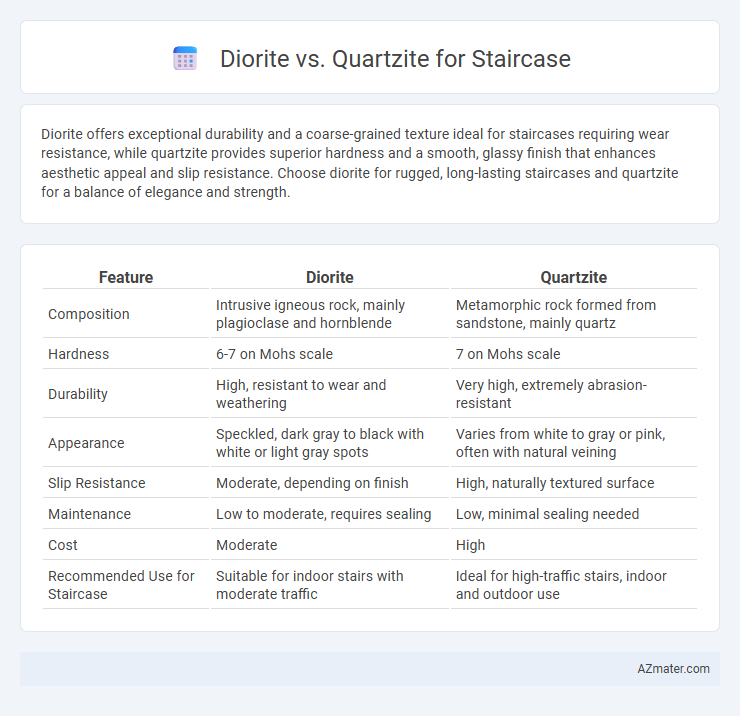
Diorite offers exceptional durability and a coarse-grained texture ideal for staircases requiring wear resistance, while quartzite provides superior hardness and a smooth, glassy finish that enhances aesthetic appeal and slip resistance. Choose diorite for rugged, long-lasting staircases and quartzite for a balance of elegance and strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Diorite | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Intrusive igneous rock, mainly plagioclase and hornblende | Metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, mainly quartz |
| Hardness | 6-7 on Mohs scale | 7 on Mohs scale |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear and weathering | Very high, extremely abrasion-resistant |
| Appearance | Speckled, dark gray to black with white or light gray spots | Varies from white to gray or pink, often with natural veining |
| Slip Resistance | Moderate, depending on finish | High, naturally textured surface |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate, requires sealing | Low, minimal sealing needed |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Recommended Use for Staircase | Suitable for indoor stairs with moderate traffic | Ideal for high-traffic stairs, indoor and outdoor use |
Introduction to Diorite and Quartzite
Diorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock characterized by its durability and speckled black-and-white appearance, making it a practical choice for staircase surfaces requiring strong wear resistance. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, is renowned for its hardness, high quartz content, and resistance to abrasion, offering a sleek, glossy finish ideal for staircases in high-traffic areas. Both materials provide exceptional strength and aesthetic appeal, with quartzite often preferred for its enhanced color variations and polished look, while diorite excels in toughness and cost-effectiveness.
Geological Formation and Composition
Diorite, an intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth's surface, consists mainly of plagioclase feldspar with biotite, hornblende, or other dark minerals, giving it a coarse-grained texture ideal for durable staircases. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock resulting from the recrystallization of quartz-rich sandstone under intense heat and pressure, is composed predominantly of quartz crystals tightly fused together, providing exceptional hardness and resistance to abrasion. The contrasting geological formation--igneous solidification for diorite versus metamorphic transformation for quartzite--results in distinct compositional strengths, influencing their suitability and aesthetic appeal in staircase applications.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetics
Diorite offers a striking contrast with its salt-and-pepper pattern, featuring black, white, and gray mineral grains that create a bold, speckled appearance ideal for modern staircases. Quartzite provides a more uniform and luminous aesthetic, often showcasing subtle veining and a smooth, glassy finish that enhances natural light and adds a luxurious touch to interior designs. Both stones are highly durable, but Diorite's distinctive, granular texture makes it a standout choice for dynamic visual statements, while Quartzite delivers elegant sophistication with its refined surface.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Diorite offers exceptional durability and strength due to its coarse-grained, igneous composition, making it highly resistant to wear, scratches, and heavy foot traffic on staircases. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, boasts superior hardness and density, providing excellent resistance to abrasion and impact, which is ideal for high-traffic staircase applications. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but quartzite's higher quartz content generally makes it slightly stronger and more scratch-resistant than diorite.
Slip Resistance and Surface Texture
Diorite's coarse-grained texture provides excellent slip resistance, making it a safer choice for staircase surfaces, especially in wet or high-traffic areas. Quartzite, with its naturally smooth and glassy finish, offers moderate slip resistance but can be enhanced through honing or sandblasting to improve traction. Both stones are durable, but the rough surface of diorite ensures a more secure footing compared to the typically sleek surface of quartzite.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Diorite requires moderate maintenance with periodic sealing to prevent staining and enhance durability, and regular cleaning using mild soap and water to avoid surface damage. Quartzite offers high resistance to scratches and stains, making it easier to maintain; it benefits from occasional sealing and can be cleaned with gentle, pH-neutral cleansers to preserve its natural shine. Both materials demand avoiding harsh chemicals and abrasive tools to sustain their appearance on staircases.
Installation Challenges and Considerations
Diorite's hardness and dense composition make cutting and shaping for staircase installation more labor-intensive, requiring specialized tools and skilled labor to achieve precise fitting. Quartzite, while also durable, offers slightly easier workability but demands careful sealing due to its natural porosity to prevent staining and wear in high-traffic staircases. Both materials require proper substrate preparation and anchoring methods to ensure long-term stability and safety in stair applications.
Cost Analysis: Diorite vs Quartzite
Diorite offers a more affordable option for staircases compared to quartzite, with prices typically ranging from $30 to $60 per square foot, while quartzite costs between $50 and $150 per square foot depending on quality and origin. Quartzite's higher price reflects its superior hardness, durability, and resistance to scratching, making it ideal for heavy traffic areas such as staircases. Budget-conscious projects often choose diorite for cost savings without significantly compromising aesthetic appeal or structural integrity.
Best Applications for Staircases
Diorite offers exceptional durability and a unique speckled appearance, making it ideal for high-traffic staircases that require both strength and aesthetic appeal. Quartzite provides superior resistance to abrasion and staining, with a more polished finish suitable for modern, elegant stair designs. Both materials excel in slip resistance when properly finished, ensuring safety for indoor and outdoor staircase applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Stone for Your Stairs
Diorite offers exceptional durability and a speckled, coarse-grained appearance ideal for high-traffic staircases, while quartzite provides a harder, more scratch-resistant surface with elegant veining patterns suitable for luxurious designs. Both stones are highly resistant to wear and heat, but quartzite's natural quartz composition ensures superior hardness, minimizing maintenance over time. Select diorite for robust, traditional aesthetics and quartzite for a blend of strength with refined, designer appeal in your staircase.
Infographic: Diorite vs Quartzite for Staircase
 azmater.com
azmater.com