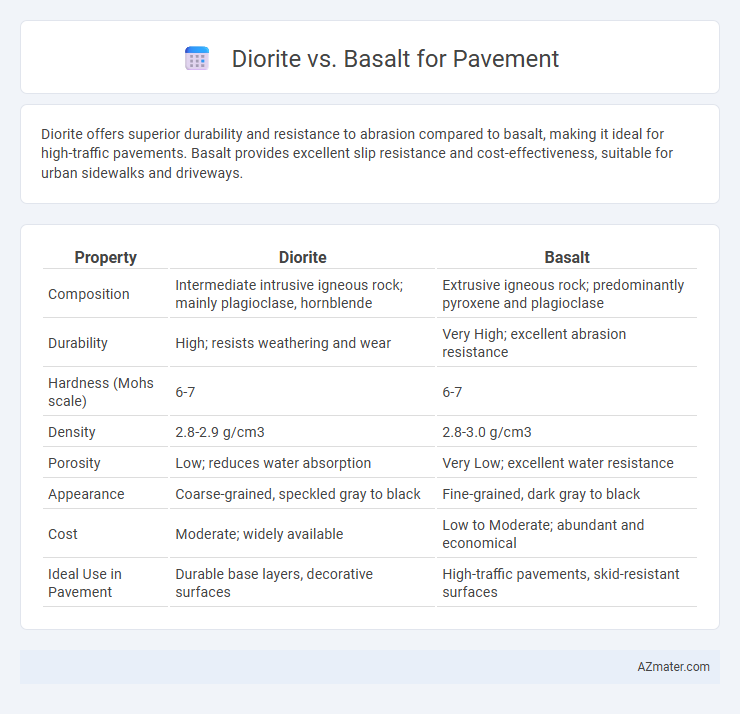
Diorite offers superior durability and resistance to abrasion compared to basalt, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements. Basalt provides excellent slip resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for urban sidewalks and driveways.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Diorite | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Intermediate intrusive igneous rock; mainly plagioclase, hornblende | Extrusive igneous rock; predominantly pyroxene and plagioclase |
| Durability | High; resists weathering and wear | Very High; excellent abrasion resistance |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 6-7 | 6-7 |
| Density | 2.8-2.9 g/cm3 | 2.8-3.0 g/cm3 |
| Porosity | Low; reduces water absorption | Very Low; excellent water resistance |
| Appearance | Coarse-grained, speckled gray to black | Fine-grained, dark gray to black |
| Cost | Moderate; widely available | Low to Moderate; abundant and economical |
| Ideal Use in Pavement | Durable base layers, decorative surfaces | High-traffic pavements, skid-resistant surfaces |
Introduction to Diorite and Basalt
Diorite is a coarse-grained, intrusive igneous rock composed mainly of plagioclase feldspar and amphibole, known for its durability and resistance to weathering, making it a suitable choice for pavement construction. Basalt is a fine-grained, extrusive igneous rock formed from rapid cooling of lava, characterized by its dense, hard structure and excellent load-bearing capacity, often used in high-traffic pavement applications. Both rocks offer strength and longevity, but their mineral composition and formation processes influence their performance and cost in pavement projects.
Geological Formation: Diorite vs Basalt
Diorite forms through the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in coarse-grained, intrusive igneous rock with a composition rich in plagioclase feldspar and hornblende. Basalt originates from rapid cooling of lava at or near the surface, creating a fine-grained, extrusive igneous rock predominantly composed of pyroxene and plagioclase. The contrasting formation processes influence their durability and texture, making diorite typically more coarse and robust, while basalt is denser and more uniform for pavement applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Diorite exhibits higher compressive strength and durability compared to basalt, making it ideal for high-traffic pavement applications requiring long-term wear resistance. Basalt has better thermal resistance and slightly lower porosity, offering enhanced performance in extreme temperature conditions and improved water drainage on pavements. Both stones have excellent toughness, but diorite's coarse-grained texture provides superior skid resistance for safer pedestrian and vehicular movement.
Strength and Durability for Pavement Use
Diorite exhibits exceptional compressive strength, typically ranging from 170 to 220 MPa, making it highly suitable for heavy-duty pavement applications requiring long-lasting durability. Basalt offers comparable strength, generally between 100 to 300 MPa, with superior resistance to abrasion and weathering, enhancing its lifespan in high-traffic areas. Both igneous rocks present excellent durability, but basalt's fine-grained texture provides better wear resistance, making it a preferred choice for pavements exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Abrasion Resistance and Wear Performance
Diorite exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to basalt, making it more suitable for high-traffic pavement applications where durability is critical. Its coarse-grained texture enhances wear performance by resisting surface degradation under heavy loads, whereas basalt, although dense and fine-grained, tends to exhibit faster wear in harsh conditions. Pavement constructed with diorite results in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs due to its enhanced toughness and hardness properties.
Cost Effectiveness in Pavement Projects
Diorite offers a moderate cost advantage over basalt due to its easier quarrying and processing, making it a budget-friendly option for large pavement projects. Basalt, while typically more expensive, provides superior durability and resistance to abrasion, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost, including installation and upkeep, is crucial for selecting the most cost-effective material between diorite and basalt in pavement applications.
Workability and Installation Considerations
Diorite offers excellent workability for pavement installation due to its coarse-grained texture, allowing easier cutting and shaping compared to the fine-grained, denser basalt. Basalt's hardness and durability enhance pavement longevity but may require specialized cutting tools and more labor-intensive installation processes. Choosing between diorite and basalt for pavement depends on balancing ease of installation with long-term durability and maintenance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Diorite and basalt, both igneous rocks, differ in environmental impact and sustainability when used for pavement. Basalt's higher density and durability contribute to longer-lasting pavements, reducing the need for frequent repairs and lowering the overall carbon footprint. Diorite extraction often causes more landscape disruption, whereas basalt's abundant global availability promotes sustainable sourcing practices, making basalt a more eco-friendly choice for pavement applications.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Potential
Diorite offers a unique speckled texture with contrasting black and white mineral grains that enhance pavement aesthetics through natural variegation and visual depth, making it ideal for sophisticated urban designs. Basalt features a consistent dark gray to black color with a fine-grained texture, providing a sleek, modern look that complements minimalist and contemporary landscape architecture. Both stones exhibit excellent durability, but the distinct visual appeal of diorite's mottled surface expands creative possibilities for decorative paving patterns compared to the uniform appearance of basalt.
Best Applications: Choosing Between Diorite and Basalt
Diorite offers superior durability and a distinct coarse texture, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements requiring long-lasting wear resistance. Basalt provides enhanced density and smoothness, better suited for urban sidewalks and driveways where slip resistance and weather resilience are important. Selecting between diorite and basalt depends on specific project needs, with diorite favored for rugged outdoor environments and basalt preferred for refined architectural finishes.
Infographic: Diorite vs Basalt for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com