Bluestone offers superior durability and a denser composition compared to limestone, making it ideal for exterior cladding in harsh weather conditions. Limestone provides a softer, more porous surface with natural color variations, suitable for decorative interior cladding and moderate climates.
Table of Comparison
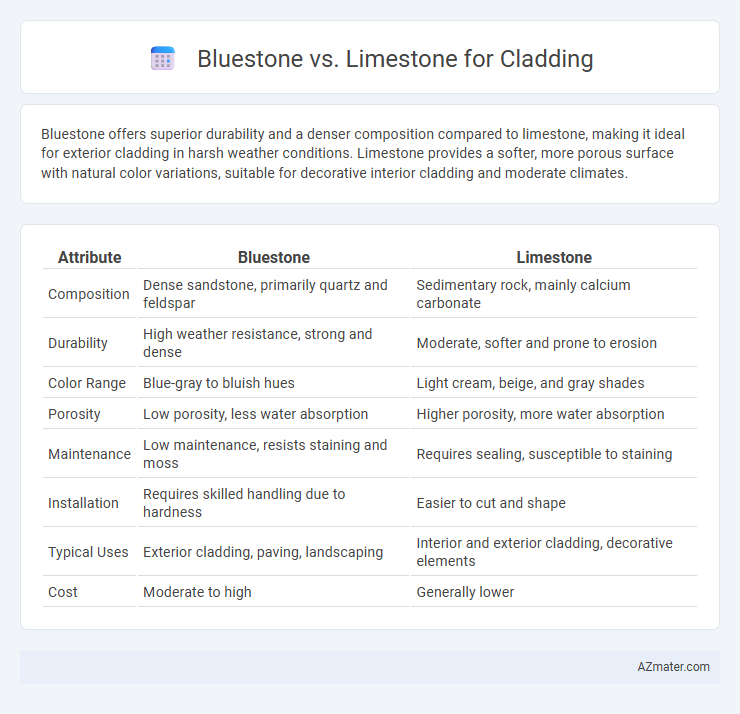
| Attribute | Bluestone | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Dense sandstone, primarily quartz and feldspar | Sedimentary rock, mainly calcium carbonate |
| Durability | High weather resistance, strong and dense | Moderate, softer and prone to erosion |
| Color Range | Blue-gray to bluish hues | Light cream, beige, and gray shades |
| Porosity | Low porosity, less water absorption | Higher porosity, more water absorption |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resists staining and moss | Requires sealing, susceptible to staining |
| Installation | Requires skilled handling due to hardness | Easier to cut and shape |
| Typical Uses | Exterior cladding, paving, landscaping | Interior and exterior cladding, decorative elements |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower |
Introduction: Bluestone vs Limestone for Cladding
Bluestone and limestone are popular choices for cladding due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Bluestone offers a dense, fine-grained texture with natural blue-grey hues, providing a modern, sleek finish ideal for contemporary architecture. Limestone features a softer, porous structure with warmer, earth-toned colors, making it suitable for classic and rustic exterior designs.
Geological Origins and Composition
Bluestone is a dense, fine-grained sandstone primarily composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, formed through sedimentary processes in river and marine environments. Limestone originates from the accumulation of marine organism shells and skeletal fragments, predominantly composed of calcium carbonate, reflecting its biological and chemical sedimentary origins. This fundamental difference in geological formation influences their durability, texture, and suitability for exterior cladding applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Texture
Bluestone offers a rich, deep blue-gray hue with natural variations that create a striking, sophisticated cladding appearance, while limestone provides a softer, cream to beige palette ideal for classic or rustic designs. The texture of bluestone is typically denser and more refined, lending itself to sleek, modern facades, whereas limestone features a porous, matte finish that adds warmth and organic charm. Both materials enhance architectural aesthetics but cater to different design sensibilities and environmental interactions.
Color Variations and Surface Finishes
Bluestone offers rich color variations ranging from deep blues and grays to subtle greens, ideal for creating dynamic facades, while limestone typically showcases warmer tones such as creamy whites, beiges, and soft yellows that provide a classic and elegant appearance. Surface finishes for bluestone include honed, flamed, and tumbled textures, enhancing its natural ruggedness and slip resistance, whereas limestone is often finished as honed or polished, highlighting its smooth, refined surface suitable for sophisticated architectural designs. Both stones provide versatile cladding options, but bluestone's cooler palette and varied textures contrast with limestone's warmer hues and smoother finishes, influencing aesthetic and stylistic choices in building exteriors.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bluestone exhibits superior durability and strength compared to limestone, making it an excellent choice for cladding in areas exposed to harsh weather conditions. Its dense composition provides higher resistance to chipping, cracking, and erosion, ensuring long-lasting performance. Limestone, while aesthetically pleasing, tends to be softer and more porous, requiring additional maintenance to preserve its structural integrity over time.
Weathering and Maintenance Requirements
Bluestone offers superior weathering resistance compared to limestone, with its dense, fine-grained structure providing durability against freeze-thaw cycles and acid rain. Limestone, being more porous and softer, is prone to erosion, staining, and requires frequent sealing to maintain its appearance. Maintenance for bluestone cladding is generally lower, needing only occasional cleaning, while limestone demands regular inspection and protective treatments to prevent surface degradation.
Installation Methods and Versatility
Bluestone offers straightforward installation methods due to its uniform thickness and consistent density, making it ideal for precise panel fitting in cladding applications. Limestone provides greater versatility with its varied textures and colors, allowing for customized designs but often requires specialized cutting and anchoring techniques to accommodate its natural variability. Both materials deliver durable exteriors, but Bluestone's installation efficiency contrasts with Limestone's aesthetic adaptability and installation complexity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bluestone, a dense, durable natural stone, offers superior longevity and lower maintenance, reducing its environmental footprint over time compared to softer limestone, which may require more frequent replacements or repairs. Limestone extraction often involves higher energy consumption and greater carbon emissions due to its more intensive quarrying and processing techniques. Both materials can be sourced locally to minimize transportation emissions, but bluestone's enhanced durability contributes more significantly to sustainable building practices by extending cladding lifespan and decreasing resource depletion.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Bluestone generally has a higher initial cost than limestone due to its durability and unique aesthetic appeal, making it a premium choice for cladding projects. Limestone offers a more budget-friendly option with moderate strength and easier workability, potentially reducing installation expenses. Over time, bluestone's superior resistance to weathering and low maintenance needs provide better long-term value despite higher upfront costs, whereas limestone may incur additional maintenance and potential replacement expenses.
Best Applications: Bluestone or Limestone for Cladding
Bluestone offers superior durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for exterior cladding in regions with harsh climates, while limestone provides a softer, more elegant aesthetic suited to interior or low-impact exterior walls. Bluestone's dense composition resists moisture and staining, ensuring long-lasting performance on building facades exposed to heavy rain or snow. Limestone, with its natural variations and warm tones, is preferred for decorative cladding that enhances architectural character in moderate weather conditions.
Infographic: Bluestone vs Limestone for Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com