Basalt offers superior durability, weather resistance, and thermal insulation for wall cladding compared to tuff, which is softer and more porous but provides better natural insulation and ease of carving. Choosing basalt ensures enhanced structural strength and longevity, while tuff is preferred for decorative and lightweight applications.
Table of Comparison
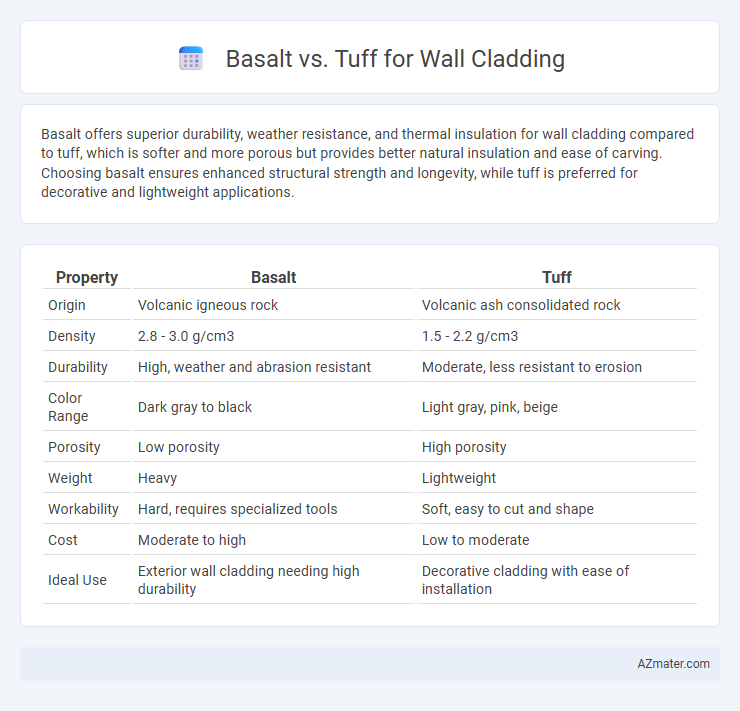
| Property | Basalt | Tuff |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Volcanic igneous rock | Volcanic ash consolidated rock |
| Density | 2.8 - 3.0 g/cm3 | 1.5 - 2.2 g/cm3 |
| Durability | High, weather and abrasion resistant | Moderate, less resistant to erosion |
| Color Range | Dark gray to black | Light gray, pink, beige |
| Porosity | Low porosity | High porosity |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Workability | Hard, requires specialized tools | Soft, easy to cut and shape |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Ideal Use | Exterior wall cladding needing high durability | Decorative cladding with ease of installation |
Introduction to Basalt and Tuff Wall Cladding
Basalt wall cladding is renowned for its durability, natural dark color, and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for modern architectural facades. Tuff wall cladding, derived from volcanic ash, offers lightweight and porous characteristics with excellent insulation properties, often used in both interior and exterior applications. Both materials provide unique textures and aesthetic appeal, with basalt emphasizing strength and tuff highlighting versatility in design.
Geological Origins: Basalt vs Tuff
Basalt originates from rapidly cooled lava flows, forming a dense, fine-grained igneous rock characterized by its durability and dark coloration. Tuff is a volcanic sedimentary rock composed of consolidated volcanic ash and fragmented materials deposited from explosive eruptions, resulting in a softer texture with varying porosity. The geological origins influence their structural properties and aesthetic appeal, with basalt offering greater strength for wall cladding, while tuff provides lighter weight and a more textured surface.
Physical Properties Comparison
Basalt exhibits superior density and compressive strength compared to tuff, making it highly durable and resistant to weathering in wall cladding applications. Tuff, being more porous and lightweight, offers better thermal insulation but is less resistant to abrasion and moisture penetration. The choice between basalt and tuff for cladding depends on balancing structural durability with insulation needs based on their contrasting physical properties.
Aesthetic Appeal and Surface Finishes
Basalt offers a sleek, dark-colored aesthetic with a fine-grained texture that provides a modern and minimalist look, while tuff displays a more porous, varied surface with natural earthy tones ranging from beige to light brown, adding rustic charm to wall cladding. Basalt's dense composition allows for smooth, honed, or polished finishes that enhance its glossy appearance, whereas tuff often features rough, matte, or split-face finishes emphasizing its natural ruggedness. The choice between basalt and tuff for cladding hinges on the desired visual impact, with basalt suited for contemporary designs and tuff preferred for organic, textured surfaces.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Basalt exhibits superior durability and weather resistance compared to tuff, making it ideal for wall cladding in harsh climates. Its dense, fine-grained structure resists erosion, moisture absorption, and thermal stress, ensuring long-lasting performance. Tuff, a porous volcanic rock, tends to be more susceptible to weathering and requires protective treatments to enhance its lifespan on exterior walls.
Installation Techniques and Challenges
Basalt wall cladding installation requires precise cutting and drilling due to its high density and hardness, often necessitating diamond-tipped tools and skilled labor to ensure secure anchoring and alignment. Tuff, being softer and more porous, allows for easier shaping and handling but demands careful waterproofing and sealing to prevent moisture penetration and durability issues over time. Both materials pose challenges in weight management and substrate preparation, with basalt needing robust support structures and tuff requiring protection against weathering effects.
Maintenance and Longevity
Basalt offers superior durability and low maintenance for wall cladding due to its dense, hard-wearing composition resistant to weathering and erosion. Tuff, being a softer volcanic rock, requires more frequent upkeep, including sealing and cleaning to prevent deterioration and staining over time. Basalt's longevity outperforms tuff, making it a cost-effective and sturdy choice for long-term exterior cladding solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt for wall cladding offers superior sustainability due to its natural abundance, durability, and low maintenance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and resource consumption. Tuff, being a lightweight volcanic rock, provides good thermal insulation but has a higher environmental impact during extraction due to its softer nature and increased susceptibility to erosion. Choosing basalt enhances environmental performance through its longer lifespan and resistance to weathering, contributing to a lower carbon footprint in building projects.
Cost Analysis: Basalt vs Tuff
Basalt wall cladding typically incurs higher costs due to its durability and dense composition, which require more intensive quarrying and processing. Tuff, being a softer volcanic rock, is generally more affordable and easier to cut, leading to lower material and labor expenses. When comparing cost-effectiveness for wall cladding, tuff offers budget-friendly options but may require more maintenance over time compared to the long-lasting basalt.
Best Applications and Design Recommendations
Basalt offers exceptional durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for exterior wall cladding in commercial and high-traffic residential buildings where longevity is paramount. Tuff's lightweight and porous nature provide excellent thermal insulation, recommended for interior feature walls or facades in temperate climates requiring moderate weather protection. For design, basalt's dark, uniform texture suits modern minimalist aesthetics, while tuff's varied hues and rough surface enhance rustic or naturalistic architectural styles.
Infographic: Basalt vs Tuff for Wall Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com