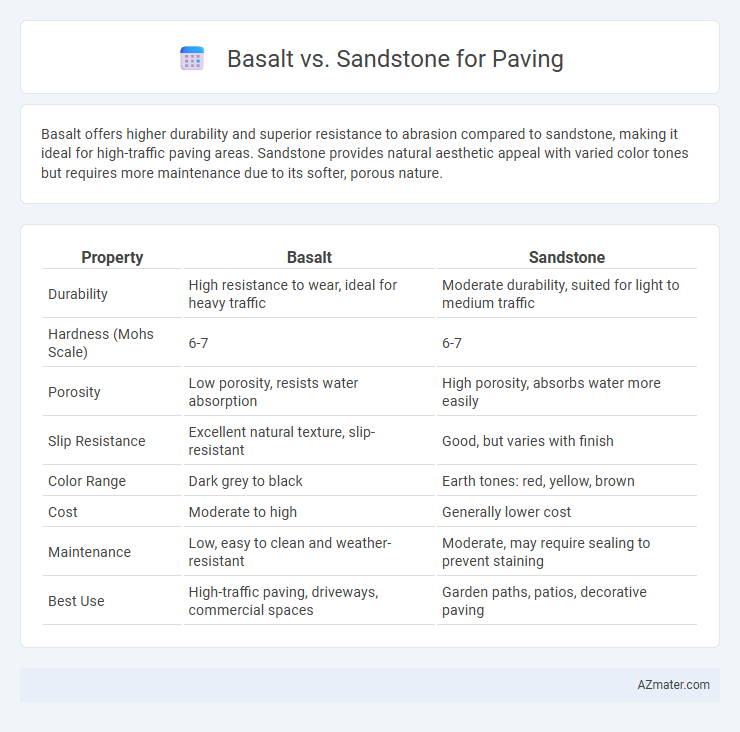
Basalt offers higher durability and superior resistance to abrasion compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic paving areas. Sandstone provides natural aesthetic appeal with varied color tones but requires more maintenance due to its softer, porous nature.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear, ideal for heavy traffic | Moderate durability, suited for light to medium traffic |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 6-7 | 6-7 |
| Porosity | Low porosity, resists water absorption | High porosity, absorbs water more easily |
| Slip Resistance | Excellent natural texture, slip-resistant | Good, but varies with finish |
| Color Range | Dark grey to black | Earth tones: red, yellow, brown |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower cost |
| Maintenance | Low, easy to clean and weather-resistant | Moderate, may require sealing to prevent staining |
| Best Use | High-traffic paving, driveways, commercial spaces | Garden paths, patios, decorative paving |
Introduction to Basalt and Sandstone Paving
Basalt paving offers exceptional durability and a dense, fine-grained texture ideal for high-traffic areas, thanks to its volcanic origin and natural hardness. Sandstone paving, derived from sedimentary rock, features a softer, porous structure that provides natural slip resistance and a warm, earthy aesthetic suitable for gardens and patios. Both materials vary in color and texture, making them versatile options for different paving applications.
Composition and Geological Origins
Basalt, a fine-grained igneous rock formed from rapid cooling of lava, is rich in iron and magnesium minerals, giving it a dense, durable structure ideal for high-traffic paving. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of compacted quartz and feldspar grains, originates from ancient sand deposits cemented over time, resulting in a porous texture that absorbs water more readily. The geological origins influence their physical properties, with basalt's volcanic ancestry providing superior hardness and weather resistance compared to sandstone's sedimentary formation.
Visual Appeal and Aesthetics
Basalt offers a sleek, dark, and uniform appearance that enhances modern and minimalist paving designs, while sandstone provides warm, earthy tones with natural variations that complement rustic and traditional aesthetics. The fine-grained texture of basalt results in a smooth, polished finish that resists staining, whereas sandstone's porous surface can develop a charming patina over time, adding character to outdoor spaces. Both materials offer distinct visual appeals, with basalt emphasizing elegance and sophistication and sandstone highlighting natural beauty and warmth.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Basalt exhibits superior durability and strength compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic paving applications due to its dense, fine-grained structure and high compressive strength, often exceeding 200 MPa. Sandstone, while aesthetically pleasing with its varied textures and colors, typically has lower durability and is more prone to weathering and erosion, with compressive strength ranging between 20-170 MPa depending on the type. Basalt's resistance to abrasion and freeze-thaw cycles outperforms sandstone, ensuring longer-lasting pavements in harsh environmental conditions.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Basalt offers superior weather resistance compared to sandstone, as its dense, fine-grained structure minimizes water absorption, reducing the risk of cracking and erosion in freeze-thaw cycles. Sandstone, being more porous, tends to wear down faster in harsh weather conditions, especially in areas with heavy rainfall or temperature fluctuations. Consequently, basalt provides greater longevity for paving applications, making it a preferred choice for durable outdoor surfaces exposed to variable climates.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Basalt paving requires professional installation due to its hardness and density, demanding specialized cutting tools and precise leveling techniques to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal. Sandstone, being softer and more porous, is easier to cut and lay, allowing for quicker installation but necessitates thorough sealing to prevent staining and erosion. Regular maintenance for basalt includes minimal cleaning and resealing every few years, while sandstone demands more frequent sealing and protection from weathering to maintain its appearance and structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Basalt vs Sandstone
Basalt typically costs more than sandstone due to its higher density and durability, making it a long-term investment for paving projects. Sandstone is generally more affordable and easier to source, but may require more maintenance and replacements over time, increasing overall expenses. Choosing between basalt and sandstone depends on balancing upfront material costs with longevity and upkeep considerations.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Basalt outperforms sandstone in eco-friendliness due to its natural abundance and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering environmental impact. Sandstone, while aesthetically pleasing and more porous, requires more maintenance and is less resistant to weathering, which can lead to increased resource consumption over time. Choosing basalt for paving supports sustainability through its long lifespan and minimal environmental degradation during quarrying and processing.
Popular Applications in Landscaping
Basalt's durability and dense composition make it ideal for high-traffic paving areas such as driveways, patios, and walkways, providing a sleek, modern appearance with excellent weather resistance. Sandstone's porous texture and warm, earthy tones are popular in garden paths, pool surrounds, and patio spaces where a natural, rustic aesthetic is desired, though it requires more maintenance to prevent staining and erosion. Both materials are favored in landscaping for their distinct visual appeal and functional benefits, with basalt preferred for strength and longevity, while sandstone is chosen for its versatility and organic charm.
Choosing the Best Stone for Your Project
Basalt offers exceptional durability and a sleek, dark finish ideal for high-traffic paving areas, while sandstone provides a warmer, more natural aesthetic with varied color options but requires more maintenance due to its porous nature. Consider basalt for projects demanding strength and low upkeep, especially in commercial or heavily used spaces, whereas sandstone suits residential settings where visual appeal and texture are prioritized. Evaluating factors like climate exposure, foot traffic, and budget will help determine the best paving stone choice for your specific project needs.
Infographic: Basalt vs Sandstone for Paving
 azmater.com
azmater.com