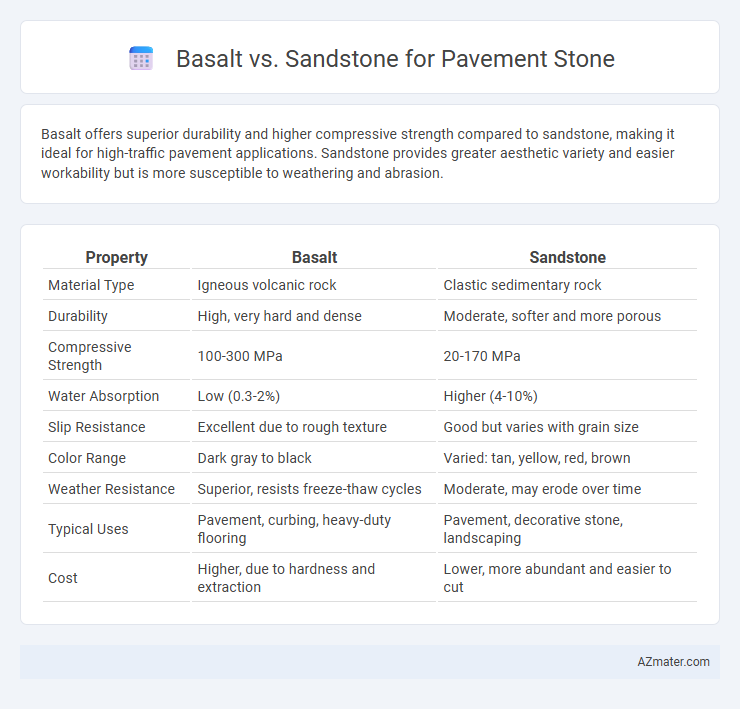
Basalt offers superior durability and higher compressive strength compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic pavement applications. Sandstone provides greater aesthetic variety and easier workability but is more susceptible to weathering and abrasion.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Igneous volcanic rock | Clastic sedimentary rock |
| Durability | High, very hard and dense | Moderate, softer and more porous |
| Compressive Strength | 100-300 MPa | 20-170 MPa |
| Water Absorption | Low (0.3-2%) | Higher (4-10%) |
| Slip Resistance | Excellent due to rough texture | Good but varies with grain size |
| Color Range | Dark gray to black | Varied: tan, yellow, red, brown |
| Weather Resistance | Superior, resists freeze-thaw cycles | Moderate, may erode over time |
| Typical Uses | Pavement, curbing, heavy-duty flooring | Pavement, decorative stone, landscaping |
| Cost | Higher, due to hardness and extraction | Lower, more abundant and easier to cut |
Introduction to Pavement Stones
Basalt and sandstone are commonly used pavement stones, each offering unique properties suited for different applications. Basalt is an igneous rock known for its high durability, dense structure, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for heavy traffic areas. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock, features a softer texture and natural slip resistance, providing an aesthetically pleasing surface with good traction for pedestrian pathways.
Basalt: Properties and Characteristics
Basalt is a dense, fine-grained igneous rock known for its exceptional hardness and durability, making it an ideal choice for pavement stone. Its high compressive strength and low porosity contribute to excellent resistance against abrasion, weathering, and heavy traffic loads. The dark color and uniform texture of basalt also enhance its aesthetic appeal while providing long-lasting performance in both commercial and residential paving projects.
Sandstone: Properties and Characteristics
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of quartz and feldspar, offering excellent durability and weather resistance for pavement applications. Its natural grainy texture provides superior slip resistance, making it ideal for outdoor walkways and patios. The stone's ability to withstand temperature fluctuations and its range of warm earthy colors enhance both functionality and aesthetic appeal in pavement settings.
Durability Comparison: Basalt vs Sandstone
Basalt exhibits superior durability compared to sandstone due to its higher density and igneous origin, making it highly resistant to abrasion, weathering, and heavy traffic wear. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock, generally has lower compressive strength and porosity, which can lead to faster erosion and surface deterioration under harsh environmental conditions. For long-term pavement applications requiring high durability and minimal maintenance, basalt is often the preferred choice over sandstone.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Basalt pavement stones offer a sleek, modern aesthetic with dark gray to black hues that provide a striking contrast in landscape designs. Sandstone presents a warm, earthy palette ranging from creamy beiges to rich reds and browns, enhancing natural and rustic environments. The color variations in sandstone cater to diverse design preferences, while basalt maintains a consistent, uniform appearance favored for minimalist and contemporary styles.
Slip Resistance and Surface Texture
Basalt offers superior slip resistance for pavement stone due to its dense, fine-grained texture, providing a rough surface that minimizes slipping hazards in wet conditions. Sandstone, with its naturally porous and coarse surface, delivers excellent traction but may wear down faster under heavy foot traffic, potentially reducing slip resistance over time. Selecting basalt ensures greater durability and consistent safety on pavements, especially in areas exposed to moisture and heavy use.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Basalt exhibits superior weather resistance compared to sandstone due to its dense, fine-grained structure, which minimizes water absorption and reduces susceptibility to freeze-thaw cycles. Sandstone, while aesthetically appealing, is more porous, making it prone to erosion and deterioration in harsh weather conditions. Consequently, basalt pavers offer enhanced longevity and durability for pavement applications in environments exposed to extreme weather fluctuations.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Basalt pavement stones offer superior durability and require less frequent maintenance compared to sandstone, making them ideal for high-traffic areas with minimal upkeep. Sandstone, being softer, demands careful installation with adequate sealing to prevent erosion and staining, increasing long-term maintenance efforts. Proper jointing and periodic cleaning are essential for both materials to ensure longevity and aesthetic appeal.
Cost Analysis: Basalt vs Sandstone
Basalt pavement stones typically cost more upfront than sandstone due to their higher density and durability, which translates to lower maintenance expenses and longer lifespan in high-traffic applications. Sandstone offers a more affordable initial investment but may incur higher long-term costs from weathering and wear, especially in freeze-thaw climates. Considering lifecycle costing, basalt often provides better value for commercial or heavy-duty paving projects, while sandstone suits budget-conscious residential uses.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Basalt offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements and outdoor spaces exposed to harsh elements. Sandstone, valued for its natural aesthetics and ease of shaping, suits decorative paving in low-traffic areas such as garden paths and patios. For heavy-use applications and longevity, basalt is recommended, while sandstone is preferred for enhancing visual appeal in residential or light-use environments.
Infographic: Basalt vs Sandstone for Pavement Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com