Basalt offers exceptional durability and natural thermal insulation for wall applications, while quartzite provides superior hardness and aesthetic appeal with its unique mineral patterns. Choosing basalt enhances structural strength and energy efficiency, whereas quartzite complements design with its vibrant colors and polished finish.
Table of Comparison
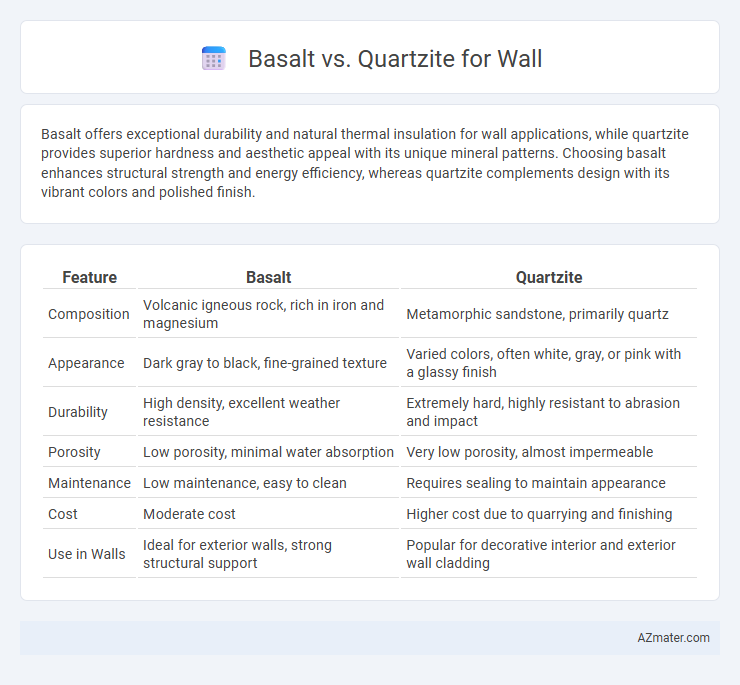
| Feature | Basalt | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Volcanic igneous rock, rich in iron and magnesium | Metamorphic sandstone, primarily quartz |
| Appearance | Dark gray to black, fine-grained texture | Varied colors, often white, gray, or pink with a glassy finish |
| Durability | High density, excellent weather resistance | Extremely hard, highly resistant to abrasion and impact |
| Porosity | Low porosity, minimal water absorption | Very low porosity, almost impermeable |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires sealing to maintain appearance |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to quarrying and finishing |
| Use in Walls | Ideal for exterior walls, strong structural support | Popular for decorative interior and exterior wall cladding |
Introduction to Basalt and Quartzite as Wall Materials
Basalt is a dense, volcanic igneous rock known for its durability and dark, fine-grained texture, making it a popular choice for exterior and interior wall cladding. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, features a hard, glassy surface with a natural gloss and excellent resistance to weathering, ideal for both decorative and structural wall applications. Both materials offer unique aesthetic appeal and long-lasting performance, with basalt providing superior strength and quartzite delivering vibrant color variations and natural sheen.
Formation and Geological Background
Basalt forms from rapidly cooled lava, resulting in fine-grained volcanic rock commonly found at tectonic plate boundaries and oceanic crust. Quartzite originates from the metamorphism of quartz-rich sandstone under intense heat and pressure, typically within continental collision zones. Their distinct geological histories influence their texture and durability, with basalt being fine-grained and dense, while quartzite exhibits a coarse, interlocking crystalline structure.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Basalt exhibits exceptional compressive strength and hardness, making it highly resistant to weathering and abrasion, ideal for wall applications requiring longevity. Quartzite offers superior durability with high quartz content, providing excellent resistance to scratches, heat, and chemical exposure, ensuring a robust and low-maintenance wall surface. Both stones maintain structural integrity under extreme environmental conditions, but basalt's denser composition delivers enhanced impact resistance compared to quartzite.
Aesthetic Differences: Colors and Textures
Basalt walls feature deep, rich tones ranging from dark gray to almost black, offering a smooth, fine-grained texture that creates a sleek, modern aesthetic. Quartzite exhibits a broader color spectrum, including whites, pinks, and blues, with a naturally rough or crystalline texture that adds visual depth and organic appeal. The choice between basalt and quartzite significantly influences a wall's character, with basalt providing a minimalist, uniform look and quartzite delivering dynamic, varied visual interest.
Installation and Workability
Basalt offers excellent durability and is relatively easier to cut and shape during installation, making it suitable for dimensional wall cladding projects requiring precise fitting. Quartzite, being harder and more brittle, demands advanced tools and expertise to prevent fracturing but provides a polished, natural stone finish ideal for decorative wall applications. Installation of basalt typically requires standard masonry adhesives, while quartzite may necessitate specialized anchoring systems to ensure long-term stability.
Maintenance Requirements
Basalt walls require low maintenance due to their dense, non-porous nature, which resists staining and weathering. Quartzite, while also durable, demands more frequent sealing to prevent moisture penetration and surface damage. Routine cleaning with mild detergents preserves quartzite's appearance, whereas basalt's natural hardness reduces the need for intensive upkeep.
Cost Comparison
Basalt typically costs less than quartzite for wall installations due to its abundant availability and easier quarrying process, with prices averaging $5 to $15 per square foot compared to quartzite's $10 to $30. Quartzite, being a harder and more durable natural stone, incurs higher costs in extraction and fabrication, influencing its premium price range. Project budgets often favor basalt for cost-effective wall cladding, while quartzite suits applications requiring superior hardness and aesthetic appeal despite the higher investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt and quartzite differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for wall applications; basalt is a volcanic rock that offers low-energy extraction and high durability, reducing maintenance and replacement needs over time. Quartzite, being a metamorphic rock, typically requires more intensive mining and processing, resulting in higher carbon emissions but provides superior hardness and weather resistance, which can extend the lifespan of walls. Both materials are recyclable and natural, but basalt's abundance and lower processing energy often make it a more sustainable choice in eco-conscious construction projects.
Best Applications for Basalt vs Quartzite on Walls
Basalt is ideal for exterior walls and cladding due to its exceptional durability, weather resistance, and natural dark coloration that enhances modern architectural designs. Quartzite's high hardness and appealing variety of light to medium tones make it perfect for interior feature walls, fireplaces, and accent walls where aesthetic appeal and scratch resistance are paramount. Both stones offer superior strength, but basalt excels in harsh outdoor environments while quartzite provides a refined, elegant appearance suited for indoor decorative applications.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Wall Project
Basalt offers exceptional durability and a sleek, dark appearance, making it ideal for modern wall designs requiring strong resistance to weathering and wear. Quartzite features a unique, natural grain with a wide color range, providing an elegant and visually striking finish that can enhance both exterior and interior walls. Selecting between basalt and quartzite depends on the desired aesthetic, environmental conditions, and maintenance preferences for your wall project.
Infographic: Basalt vs Quartzite for Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com