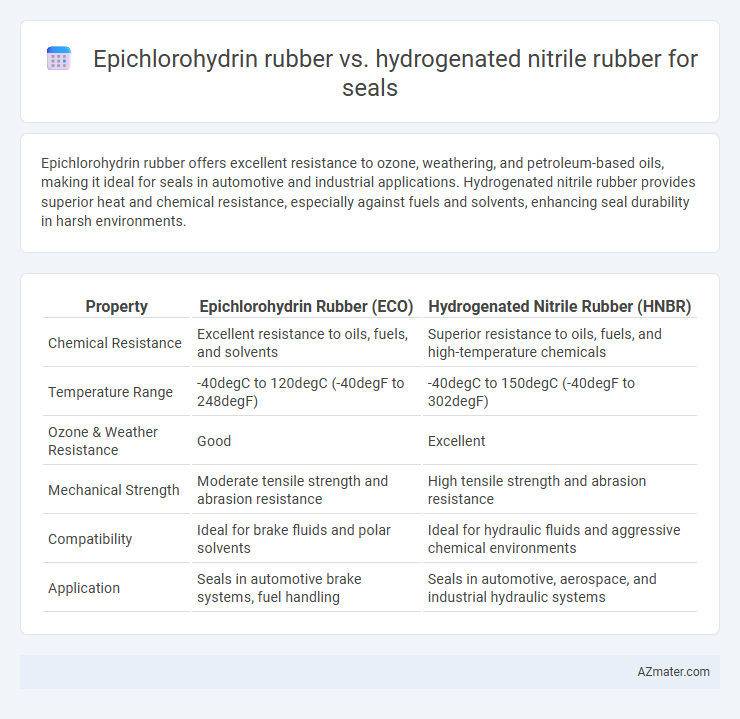
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and petroleum-based oils, making it ideal for seals in automotive and industrial applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides superior heat and chemical resistance, especially against fuels and solvents, enhancing seal durability in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Superior resistance to oils, fuels, and high-temperature chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Compatibility | Ideal for brake fluids and polar solvents | Ideal for hydraulic fluids and aggressive chemical environments |
| Application | Seals in automotive brake systems, fuel handling | Seals in automotive, aerospace, and industrial hydraulic systems |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin Rubber and Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is renowned for its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it ideal for seals in automotive and industrial applications exposed to harsh chemicals and weathering. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, often used in demanding environments such as oil and gas or aerospace sealing solutions. Both materials provide unique advantages in sealing technologies, with ECO excelling in fuel and ozone resistance and HNBR delivering enhanced durability under high temperature and aggressive chemical exposure.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber features a copolymer structure of epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide units, providing excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering due to its polar ether linkages and chlorinated sites. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is derived from nitrile butadiene rubber through hydrogenation, significantly reducing unsaturation and enhancing thermal, chemical, and abrasion resistance by stabilizing the rubber backbone. The main compositional difference lies in Epichlorohydrin's ether and chlorinated groups versus HNBR's saturated hydrocarbon and nitrile groups, dictating their performance in sealing applications exposed to harsh chemical or thermal environments.
Key Performance Properties for Seal Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and ozone, with superior flexibility at low temperatures, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh chemical environments and wide temperature ranges. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits exceptional heat resistance, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, ensuring durability in high-temperature and high-pressure sealing applications. Both materials deliver strong compression set resistance, but ECO excels in fuel permeability while HNBR outperforms in mechanical wear and thermal stability for dynamic seals.
Temperature Resistance: Epichlorohydrin vs. Hydrogenated Nitrile
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent heat resistance with a continuous operating temperature range of -40degC to 130degC, making it suitable for sealing applications exposed to moderate heat and ozone. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) surpasses this with a wider temperature tolerance, effectively sealing between -40degC and 165degC, providing superior resistance to high temperatures and aging. For dynamic seals in harsh thermal environments, HNBR is preferred due to its enhanced thermal stability and durability compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for seals exposed to automotive and industrial oils. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance, particularly against hydrocarbons, acids, and alkalis, with higher thermal stability up to 150degC. While Epichlorohydrin excels in fuel and oil resistance, HNBR is preferred for seals requiring durability in aggressive chemical environments and elevated temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior oil resistance and moderate mechanical strength, making it suitable for seals exposed to hydrocarbon environments but with limited abrasion resistance. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates enhanced mechanical strength and durability due to its saturated polymer backbone, providing excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and aggressive chemicals. The higher tensile strength and improved wear resistance of HNBR seals result in longer service life and better performance under dynamic and high-stress conditions compared to epichlorohydrin rubber.
Ozone and Weathering Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers moderate ozone resistance but can degrade under prolonged exposure to harsh weather conditions, limiting its use in outdoor seal applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates superior ozone and weathering resistance due to its saturated polymer backbone, making it ideal for seals exposed to extreme environmental factors. The enhanced durability of HNBR contributes to longer service life and reliability in automotive, industrial, and oilfield sealing applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and flexibility, often resulting in lower long-term maintenance costs, but it tends to be pricier and less widely available than hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). HNBR provides excellent thermal and chemical resistance at a generally lower cost with broader market availability, making it a popular choice for cost-efficient sealing solutions. Companies prioritize HNBR for large-scale seals due to its balance of performance, affordability, and supply chain reliability.
Typical Seal Industry Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) excels in automotive and fuel system seals due to its superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is preferred in high-temperature sealing applications such as oilfield equipment and hydraulic seals, offering excellent abrasion resistance and chemical stability in harsh environments. Both materials serve critical roles in sealing technologies, with ECO dominating in fuel handling systems and HNBR leading in dynamic mechanical seals and high-pressure applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Seal Needs
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and oil, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh environments and fuel systems. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior mechanical properties, heat resistance up to 150degC, and enhanced wear resistance, suitable for dynamic sealing applications in automotive and industrial settings. Selecting the right rubber depends on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements to ensure optimal seal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com