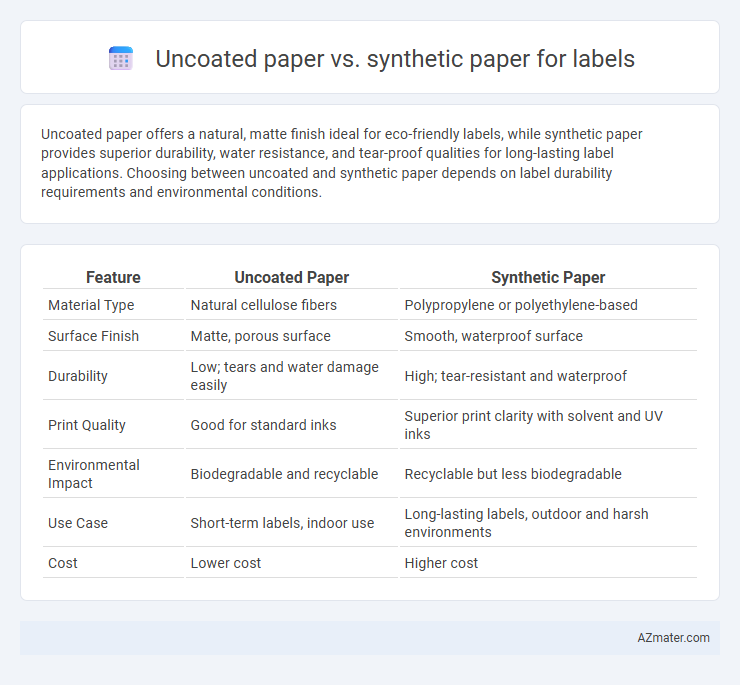
Uncoated paper offers a natural, matte finish ideal for eco-friendly labels, while synthetic paper provides superior durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities for long-lasting label applications. Choosing between uncoated and synthetic paper depends on label durability requirements and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Uncoated Paper | Synthetic Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural cellulose fibers | Polypropylene or polyethylene-based |
| Surface Finish | Matte, porous surface | Smooth, waterproof surface |
| Durability | Low; tears and water damage easily | High; tear-resistant and waterproof |
| Print Quality | Good for standard inks | Superior print clarity with solvent and UV inks |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and recyclable | Recyclable but less biodegradable |
| Use Case | Short-term labels, indoor use | Long-lasting labels, outdoor and harsh environments |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Label Materials: Uncoated vs Synthetic Paper
Uncoated paper labels offer a natural, porous surface ideal for writing and printing with standard inks, providing excellent ink absorption and a matte finish that enhances readability and customization. Synthetic paper labels, made from durable plastic materials like polypropylene or polyethylene, deliver superior resistance to water, chemicals, and tearing, ensuring longevity in harsh environments. Choosing between uncoated and synthetic paper for labels depends on the application requirements, such as durability, print quality, and environmental exposure.
Composition and Characteristics of Uncoated Paper
Uncoated paper for labels is primarily composed of natural fibers such as wood pulp, resulting in a porous surface with a matte finish that readily absorbs ink, providing excellent printability and a natural look. This paper type lacks a plastic or synthetic coating, making it more environmentally friendly and biodegradable compared to synthetic paper, which consists of plastic resins like polypropylene or polyethylene, offering superior water resistance and durability. Uncoated paper's breathability and softness make it ideal for applications requiring writable surfaces and a classic, tactile label appearance.
What is Synthetic Paper? Key Features and Properties
Synthetic paper is a durable, tear-resistant material made from plastic polymers like polypropylene or polyethylene, designed to mimic the appearance and feel of traditional paper while offering superior strength and water resistance. Key features include exceptional waterproof and weatherproof qualities, chemical resistance, and high printability through various printing methods. Its properties make synthetic paper ideal for labels requiring longevity in harsh environments, such as outdoor, industrial, or food labeling applications.
Print Quality: Uncoated Paper vs Synthetic Paper Labels
Uncoated paper labels offer a natural texture that enhances ink absorption, resulting in vibrant, sharp print quality ideal for detailed text and images. Synthetic paper labels provide superior durability with resistance to water, chemicals, and tearing, maintaining high print clarity even in harsh environments. Both materials support high-resolution printing, but synthetic paper excels in preserving print quality over time and exposure.
Durability and Resistance: Which Label Material Lasts Longer?
Uncoated paper labels offer a natural, eco-friendly option but tend to absorb moisture and show wear over time, reducing durability compared to synthetic paper labels. Synthetic paper, made from plastic resins like polypropylene or polyethylene, provides superior water resistance, tear resistance, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for labels exposed to harsh environments or outdoor conditions. For long-lasting applications, synthetic paper labels outperform uncoated paper by maintaining clarity and adhesion, ensuring durability in demanding settings.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Uncoated and Synthetic Paper
Uncoated paper is biodegradable and often made from recycled fibers, reducing landfill waste and promoting a lower carbon footprint in label production. Synthetic paper, composed of plastic polymers such as polypropylene, offers durability and water resistance but challenges sustainability due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential microplastic pollution. Choosing uncoated paper enhances eco-friendliness through compostability, while synthetic paper requires recycling programs to mitigate environmental impact in labeling applications.
Cost Comparison: Uncoated Paper vs Synthetic Paper Labels
Uncoated paper labels typically offer lower initial costs, making them a budget-friendly choice for short-term or low-moisture applications. Synthetic paper labels, while more expensive upfront, provide enhanced durability, resistance to water, chemicals, and tearing, which can reduce replacement and reprinting costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including label longevity and environmental exposure, is crucial when choosing between uncoated paper and synthetic paper labels.
Application Suitability: Industry Uses for Each Label Material
Uncoated paper labels excel in applications requiring eco-friendly, cost-effective solutions often used in food packaging, shipping, and retail due to their recyclability and ease of writing on. Synthetic paper labels provide superior durability, water resistance, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for industrial, pharmaceutical, outdoor, and chemical product labeling where longevity and exposure to harsh conditions are critical. The choice between uncoated and synthetic paper labels depends heavily on the environment and durability needs of the specific industry application.
Adhesion and Finishing Options for Labels
Uncoated paper labels offer excellent ink absorption and strong adhesion with standard adhesives, making them ideal for applications requiring easy writing and printing flexibility. Synthetic paper labels provide superior durability, water resistance, and chemical resistance, ensuring long-lasting adhesion on various surfaces, including plastic and metal, while supporting advanced finishing options such as varnishing, lamination, and thermal transfer printing. Choosing between uncoated and synthetic paper depends on the label's exposure conditions and the required finishing techniques for durability and visual appeal.
Choosing the Right Label Material: Factors to Consider
Selecting between uncoated paper and synthetic paper for labels hinges on factors like durability, moisture resistance, and printing quality; synthetic paper offers superior water and tear resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or harsh environments. Uncoated paper excels in eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness, suitable for indoor applications with less exposure to wear or moisture. Consider the label's intended use, budget constraints, and environmental impact to determine the optimal material, ensuring longevity and print clarity.
Infographic: Uncoated paper vs Synthetic paper for Label
 azmater.com
azmater.com