Uncoated paper offers a smooth, printable surface ideal for lightweight packaging, while cardboard provides superior durability and structural strength for heavy-duty protection. Choosing between uncoated paper and cardboard depends on packaging requirements such as strength, appearance, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
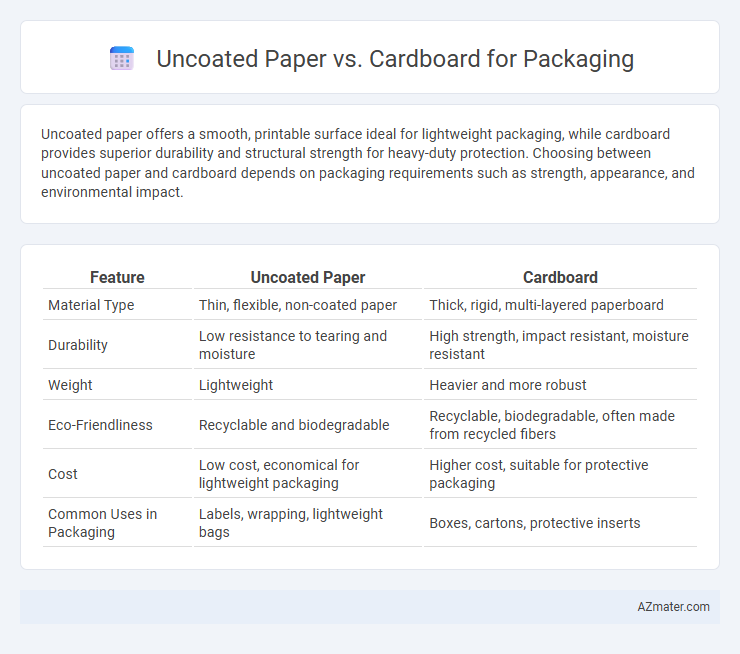
| Feature | Uncoated Paper | Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thin, flexible, non-coated paper | Thick, rigid, multi-layered paperboard |
| Durability | Low resistance to tearing and moisture | High strength, impact resistant, moisture resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and more robust |
| Eco-Friendliness | Recyclable and biodegradable | Recyclable, biodegradable, often made from recycled fibers |
| Cost | Low cost, economical for lightweight packaging | Higher cost, suitable for protective packaging |
| Common Uses in Packaging | Labels, wrapping, lightweight bags | Boxes, cartons, protective inserts |
Introduction to Packaging Materials
Uncoated paper offers a smooth, natural texture ideal for lightweight packaging requiring high print quality and recyclability, while cardboard provides superior strength and durability suited for protecting heavier products during shipping and storage. The choice between uncoated paper and cardboard depends on factors such as product weight, protection needs, environmental impact, and cost efficiency. Both materials play a crucial role in sustainable packaging solutions, emphasizing renewable resources and recyclability in supply chain management.
What is Uncoated Paper?
Uncoated paper is a natural, untreated paper type without any added coatings or finishes, offering a porous surface that absorbs ink easily for high-quality printing. It is commonly used in packaging for its eco-friendly properties, biodegradability, and recyclability, making it ideal for sustainable brands. Unlike cardboard, uncoated paper provides a smooth, tactile feel but less structural strength, often used for wrapping or lightweight packaging applications.
Understanding Cardboard in Packaging
Cardboard in packaging offers superior durability and rigidity compared to uncoated paper, making it ideal for protecting heavier or fragile items during transportation. Its multi-layered structure provides enhanced cushioning and resistance to external impacts, ensuring product safety and maintaining branding integrity. Unlike uncoated paper, cardboard can be easily customized in terms of thickness, finish, and print quality, catering to diverse packaging needs.
Key Differences Between Uncoated Paper and Cardboard
Uncoated paper is thinner, more flexible, and uncoated, making it ideal for printing and lightweight packaging, while cardboard is thicker, rigid, and designed for durability and structural support in packaging. Uncoated paper offers a natural, matte finish that enhances print clarity but lacks the protective strength found in cardboard, which often consists of layers for added sturdiness. Cardboard excels in heavy-duty shipping applications, whereas uncoated paper suits products requiring a more refined aesthetic with moderate protection.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Uncoated paper offers moderate durability and is suitable for lightweight packaging, but it lacks the rigidity and tear resistance of cardboard. Cardboard, especially corrugated types, provides superior strength and durability, making it ideal for protecting heavier or fragile items during shipping and handling. The thickness and fluting in cardboard contribute significantly to its enhanced performance in impact resistance and structural support compared to uncoated paper.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Uncoated paper typically has a lower environmental impact than cardboard due to its minimal processing and higher recyclability, making it more sustainable for short-term packaging needs. Cardboard, while heavier and more resource-intensive to produce, offers enhanced durability and reusability, contributing to longer lifecycle use and reduced waste generation. Sustainable packaging decisions must consider lifecycle assessments, recyclability rates, and resource consumption to optimize environmental benefits between uncoated paper and cardboard.
Print Quality and Design Flexibility
Uncoated paper offers superior print quality with vibrant colors and sharp details, making it ideal for intricate designs and high-resolution images in packaging. Cardboard provides enhanced design flexibility through its sturdier structure, allowing for embossing, debossing, and various finishing techniques that enhance tactile appeal. Selecting between the two depends on balancing the need for detailed graphic presentation with structural durability and creative customization.
Cost Analysis: Uncoated Paper vs Cardboard
Uncoated paper generally offers a lower initial cost compared to cardboard, making it a cost-effective choice for lightweight packaging applications. Cardboard, with its higher durability and structural strength, tends to have a higher upfront expense but reduces product damage rates, potentially lowering overall costs in shipping. When evaluating packaging expenses, it's essential to balance the material cost of uncoated paper or cardboard with factors like protection requirements, shipping volume, and sustainability goals.
Best Uses for Uncoated Paper Packaging
Uncoated paper packaging excels in applications requiring high printability, breathability, and environmental friendliness, making it ideal for food packaging, retail bags, and luxury product wraps. Its porous surface allows for better ink absorption and natural texture, enhancing brand aesthetics while supporting eco-conscious packaging solutions. This material is preferred for lightweight, biodegradable, and recyclable options that emphasize sustainability without compromising visual appeal.
Ideal Applications for Cardboard Packaging
Cardboard packaging is ideal for shipping and storing heavy or fragile items due to its sturdy structure and impact resistance. It excels in e-commerce, food delivery, and electronics packaging where durability and protection against crushing or punctures are critical. Unlike uncoated paper, cardboard provides superior insulation and moisture resistance, making it suitable for cold chain logistics and eco-friendly retail packaging.
Infographic: Uncoated paper vs Cardboard for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com