Transparent paper offers superior clarity and ink absorption for precise duplication, while carbon paper provides cost-effective multi-copy transfer but often yields smudged or less sharp results. Choosing between them depends on the need for image sharpness versus quantity of duplicates.
Table of Comparison
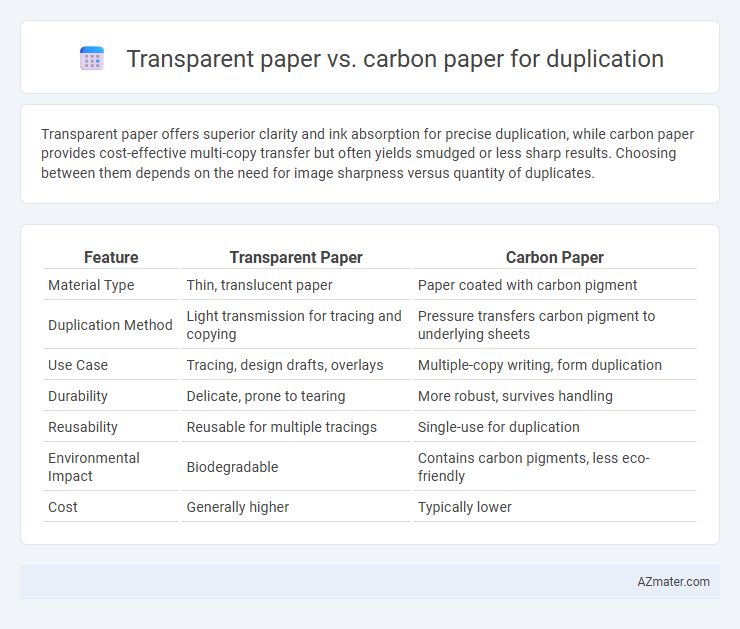
| Feature | Transparent Paper | Carbon Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thin, translucent paper | Paper coated with carbon pigment |
| Duplication Method | Light transmission for tracing and copying | Pressure transfers carbon pigment to underlying sheets |
| Use Case | Tracing, design drafts, overlays | Multiple-copy writing, form duplication |
| Durability | Delicate, prone to tearing | More robust, survives handling |
| Reusability | Reusable for multiple tracings | Single-use for duplication |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable | Contains carbon pigments, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Generally higher | Typically lower |
Introduction to Duplication Methods
Duplication methods historically rely on materials like transparent paper and carbon paper to reproduce text or images efficiently. Transparent paper offers clarity and reusability, making it ideal for tracing and transferring designs, while carbon paper provides immediate, multiple copies by placing it between sheets during writing or typing. Understanding these materials highlights their distinct roles in evolving duplication techniques for administrative, artistic, and industrial applications.
What is Transparent Paper?
Transparent paper, often known as tracing paper, is a lightweight, translucent sheet used for copying drawings or texts by placing it over the original and tracing the content. Unlike carbon paper, which involves a coated layer to transfer ink through pressure, transparent paper offers a clean, reusable surface ideal for precision work and detailed duplication without ink smudges. Its durability and clarity make it suitable for architectural plans, art projects, and design duplications requiring high accuracy and minimal mess.
What is Carbon Paper?
Carbon paper is a thin sheet coated with a layer of dry ink or pigmented material that transfers markings from the top sheet to the underlying paper when pressure is applied, commonly used for making duplicate copies. It excels in quickly producing multiple carbon copies in forms like receipts, invoices, and handwritten notes, providing clear and crisp imprints. Unlike transparent paper, which relies on tracing, carbon paper offers direct and instant duplication through physical contact and pressure.
Key Differences Between Transparent and Carbon Paper
Transparent paper offers clarity and reusability, allowing users to trace original documents without leaving ink residue, whereas carbon paper embeds ink between sheets to produce direct copies. Carbon paper is more effective for multi-copy duplication but can cause smudging and requires replacement after use. Transparent paper excels in precision and archival quality, making it ideal for drafting and artwork reproduction.
Duplication Quality Comparison
Transparent paper offers superior duplication quality compared to carbon paper due to its ability to provide sharper and clearer copies without ink smudging or irregularities. Carbon paper often results in uneven impressions and can leave residual stains on original documents, reducing overall duplication fidelity. For high-precision document replication, transparent paper ensures consistent clarity and professional-grade output crucial in detailed work.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Transparent paper produces less waste because it is often recyclable and biodegradable, reducing environmental pollution compared to carbon paper. Carbon paper contains toxic inks and chemicals that can contaminate soil and water, posing sustainability challenges during disposal. Choosing transparent paper supports eco-friendly duplication practices by minimizing harmful chemical use and enhancing material recyclability.
Ease of Use and Practicality
Transparent paper offers superior ease of use compared to carbon paper as it allows users to see through the sheets, ensuring accurate alignment and reducing errors during duplication. Carbon paper, while effective for creating multiple copies simultaneously, can be messy and requires careful handling to avoid smudging and inconsistent ink transfer. For practical duplication, transparent paper is preferred in environments where precision and tidiness are prioritized, whereas carbon paper remains suitable for quick, multi-copy tasks despite its less clean application process.
Cost and Availability
Transparent paper offers a cost-effective solution for duplication with consistent availability in office supply stores, often priced lower due to its simpler manufacturing process. Carbon paper, while slightly more expensive and less commonly stocked, provides reliable duplicate copies with clear impressions, especially favored for multi-part forms. Both materials remain accessible but transparent paper tends to have broader availability and a lower overall cost, making it preferable for routine duplication tasks.
Best Uses for Transparent Paper
Transparent paper is ideal for tracing and overlay tasks in graphic design, allowing artists to reproduce images accurately without altering the original. Its smooth, translucent surface supports fine detail work and is often used in architectural drawings and technical drafts. Unlike carbon paper, transparent paper offers cleaner duplication with no risk of smudging or ink transfer, making it best suited for precision tasks requiring clarity.
Best Uses for Carbon Paper
Carbon paper excels in duplication tasks requiring fast, multiple-copy creation, such as in handwritten forms, invoices, or receipts. It is ideal for environments where immediate, physical duplicates are necessary without the need for electronic devices. Transparent paper is less effective for duplication as it primarily serves tracing and design purposes rather than producing multiple carbon copies.
Infographic: Transparent paper vs Carbon paper for Duplication
 azmater.com
azmater.com