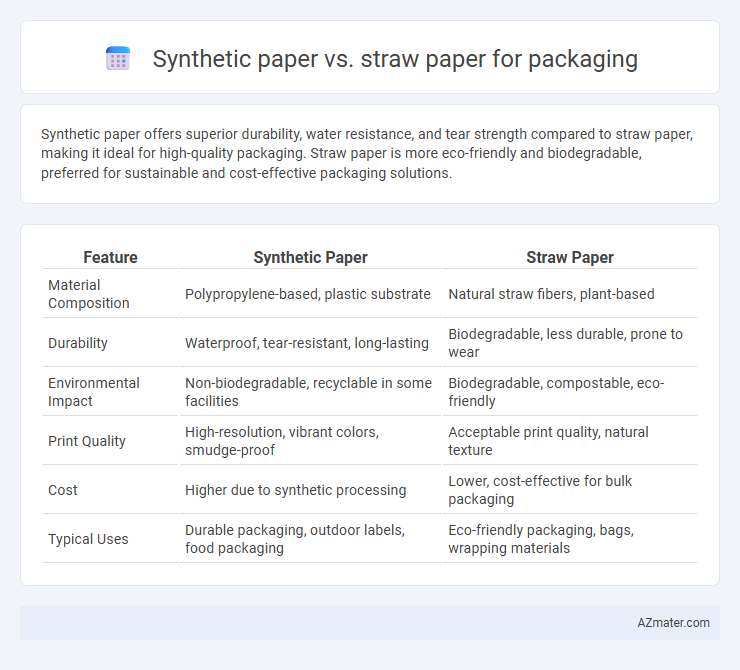
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to straw paper, making it ideal for high-quality packaging. Straw paper is more eco-friendly and biodegradable, preferred for sustainable and cost-effective packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Straw Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polypropylene-based, plastic substrate | Natural straw fibers, plant-based |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant, long-lasting | Biodegradable, less durable, prone to wear |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable in some facilities | Biodegradable, compostable, eco-friendly |
| Print Quality | High-resolution, vibrant colors, smudge-proof | Acceptable print quality, natural texture |
| Cost | Higher due to synthetic processing | Lower, cost-effective for bulk packaging |
| Typical Uses | Durable packaging, outdoor labels, food packaging | Eco-friendly packaging, bags, wrapping materials |
Introduction to Synthetic Paper and Straw Paper
Synthetic paper, made from polypropylene or polyethylene, offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear-resistance compared to traditional paper. Straw paper, derived from agricultural waste like wheat or rice straw, provides an eco-friendly alternative with a lower environmental footprint through recycling natural fibers. Both materials serve distinct roles in packaging, balancing sustainability and performance based on specific application needs.
Material Composition and Production Processes
Synthetic paper is made from plastic resins such as polypropylene or polyethylene, offering water resistance, tear durability, and chemical stability, while straw paper is produced from agricultural waste fibers like wheat or rice straw, making it biodegradable and eco-friendly. The production of synthetic paper involves extrusion, calendaring, and coating processes that create a smooth, durable surface suitable for printing, whereas straw paper manufacturing includes pulping, pressing, and drying of natural fibers to form a more textured, biodegradable sheet. These material compositions and processes result in synthetic paper being more durable and moisture-resistant, while straw paper emphasizes sustainability and compostability in packaging applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic paper, made from polypropylene, offers durability and water resistance but poses challenges in biodegradability and recycling, leading to environmental concerns. Straw paper, produced from agricultural waste like wheat or rice straw, provides a sustainable alternative by utilizing renewable resources and reducing reliance on wood pulp. Despite lower durability, straw paper's compostability and lower carbon footprint enhance its appeal for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Synthetic paper outperforms straw paper in durability and strength, offering superior resistance to tearing, water, and chemicals, making it ideal for robust packaging needs. Straw paper, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, tends to be weaker and less resistant to moisture, limiting its use in heavy-duty or long-lasting packaging applications. Brands prioritizing longevity and protection often prefer synthetic paper due to its enhanced mechanical properties and consistent performance under stress.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Synthetic paper offers superior water and moisture resistance compared to straw paper, making it ideal for packaging applications exposed to humid or wet environments. Its polymer-based composition prevents water absorption, maintaining structural integrity and print quality under moisture stress. Straw paper, derived from natural fibers, tends to absorb water, leading to potential weakening and degradation in packaging performance.
Printing and Customization Capabilities
Synthetic paper offers superior printing quality with excellent ink adhesion and vibrant color reproduction, making it ideal for high-resolution graphics and detailed designs on packaging. Straw paper, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, often poses challenges in achieving consistent print clarity and color intensity due to its rough texture and fibrous composition. Customization on synthetic paper is more versatile, supporting advanced printing techniques like UV and digital printing, whereas straw paper is limited to basic printing methods and may require special treatments to enhance print durability.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Synthetic paper, composed of polypropylene or polyethylene, offers superior durability and water resistance for packaging but incurs higher initial costs compared to straw paper derived from agricultural waste. Straw paper presents an economically feasible option due to its lower raw material and production expenses, promoting sustainability with biodegradable attributes ideal for cost-sensitive packaging solutions. Evaluating long-term benefits, synthetic paper's recyclability and extended lifecycle may offset upfront costs, while straw paper aligns with eco-friendly market trends and budget constraints.
Biodegradability and Recycling Options
Synthetic paper offers high durability and water resistance but poses challenges in biodegradability, as it is typically made from polypropylene, a non-biodegradable plastic. Straw paper, derived from agricultural waste like wheat or rice straw, is biodegradable and compostable, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging. While synthetic paper can be recycled in plastic streams, straw paper is more easily recyclable within conventional paper recycling systems, enhancing its environmental sustainability.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance, tear strength, and durability, making it ideal for packaging in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals industries where moisture and handling are critical concerns. Straw paper, derived from agricultural byproducts, provides an eco-friendly alternative widely used for sustainable packaging solutions in retail, gift wrapping, and biodegradable food containers. Both materials cater to different industrial needs, with synthetic paper suited for high-performance and long-lasting packaging, while straw paper supports environmentally conscious brands prioritizing recyclability and waste reduction.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and print quality, leading to positive consumer perception in premium packaging markets. Straw paper appeals to eco-conscious consumers due to its natural, biodegradable properties and sustainable sourcing, aligning with growing environmental trends. Market trends indicate increasing demand for sustainable materials, positioning straw paper favorably, while synthetic paper remains preferred for high-end, long-lasting packaging solutions.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Straw paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com