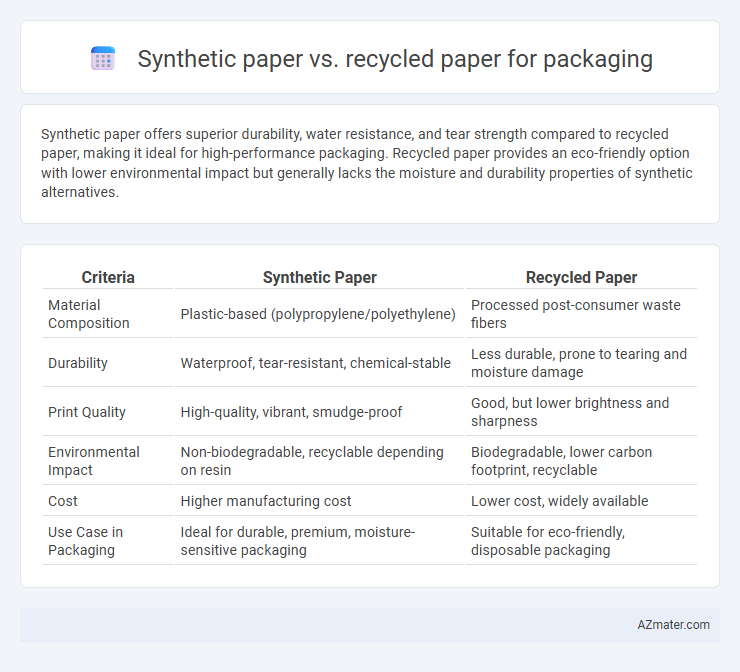
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to recycled paper, making it ideal for high-performance packaging. Recycled paper provides an eco-friendly option with lower environmental impact but generally lacks the moisture and durability properties of synthetic alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Synthetic Paper | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic-based (polypropylene/polyethylene) | Processed post-consumer waste fibers |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant, chemical-stable | Less durable, prone to tearing and moisture damage |
| Print Quality | High-quality, vibrant, smudge-proof | Good, but lower brightness and sharpness |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable depending on resin | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint, recyclable |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Use Case in Packaging | Ideal for durable, premium, moisture-sensitive packaging | Suitable for eco-friendly, disposable packaging |
Understanding Synthetic Paper: Composition and Characteristics
Synthetic paper, primarily composed of polypropylene or polyethylene resins, offers exceptional durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to recycled paper. Its non-porous surface ensures high-quality printability with vibrant colors and sharp images, making it ideal for premium packaging applications. The material's chemical resistance and longevity provide sustainable advantages by reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste.
What is Recycled Paper? Types and Sources
Recycled paper for packaging is produced by reprocessing used paper materials, reducing the demand for virgin resources and minimizing environmental impact. Key types include post-consumer recycled paper, sourced from discarded paper products recovered from consumers, and pre-consumer recycled paper, derived from manufacturing waste and scraps. Common sources span office waste, newspapers, and industrial offcuts, contributing to sustainable packaging solutions by promoting resource efficiency and waste reduction.
Durability and Performance in Packaging Applications
Synthetic paper offers superior durability and resistance to water, tearing, and chemicals, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring long-lasting performance. Recycled paper, while more environmentally friendly, generally lacks the same level of strength and moisture resistance, which can limit its use in demanding packaging environments. Choosing synthetic paper enhances package integrity and shelf life, whereas recycled paper suits less intensive applications with a focus on sustainability.
Environmental Impact: Synthetic Paper vs. Recycled Paper
Synthetic paper, made from plastic resins such as polypropylene, offers durability and water resistance but relies on petroleum-based resources and poses challenges in biodegradability and recycling. Recycled paper, derived from post-consumer waste, reduces deforestation and landfill waste while lowering energy consumption in production, making it a more sustainable option for packaging. Evaluating environmental impact, recycled paper significantly decreases carbon footprint and supports circular economy principles compared to synthetic paper's contribution to microplastic pollution and limited end-of-life recyclability.
Print Quality and Customization Options
Synthetic paper offers superior print quality with vibrant colors and sharp details due to its smooth, non-porous surface, making it ideal for high-end packaging designs. Customization options on synthetic paper are extensive, including various finishes, textures, and enhanced durability features like water and tear resistance. Recycled paper, while eco-friendly, often presents limitations in print sharpness and color vibrancy, with fewer customization possibilities and a rougher texture that can affect detailed designs.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Considerations
Synthetic paper generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to recycled paper due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes. Recycled paper offers cost advantages in large-scale packaging production with lower raw material expenses and ease of sourcing. Over the long term, synthetic paper delivers enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, potentially reducing replacement frequency and waste management costs in specific packaging applications.
Suitability for Food and Pharmaceutical Packaging
Synthetic paper offers superior moisture resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making it highly suitable for food and pharmaceutical packaging where hygiene and barrier properties are critical. Recycled paper, while eco-friendly and cost-effective, may lack the necessary strength and contamination resistance required for sensitive products, often necessitating additional coatings or treatments. Food and pharmaceutical industries prioritize packaging materials that ensure product safety, compliance with regulatory standards, and extended shelf life, areas where synthetic paper generally outperforms recycled paper.
Water Resistance and Weather Tolerance
Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance and weather tolerance compared to recycled paper, making it ideal for packaging exposed to moisture and harsh environmental conditions. Its polymer-based composition prevents water absorption and maintains structural integrity under varying temperatures and humidity levels. Recycled paper, while eco-friendly, tends to absorb water and degrade faster when subjected to wet or extreme weather, limiting its durability for outdoor or moisture-sensitive packaging applications.
End-of-Life: Recyclability and Waste Management
Synthetic paper offers superior durability and waterproof properties, making it less prone to degradation but more challenging to recycle due to its plastic-based composition. Recycled paper, derived from post-consumer fibers, is widely accepted in paper recycling streams and decomposes more readily in composting and landfill environments. Effective waste management requires tailored approaches; synthetic paper benefits from specialized recycling facilities, while recycled paper aligns with conventional paper waste processing systems, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure compatibility for sustainability outcomes.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Packaging Needs
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it ideal for packaging that requires longevity and exposure to harsh conditions. Recycled paper provides an eco-friendly alternative that reduces environmental impact while maintaining adequate strength and printability for most packaging applications. Selecting the right paper depends on balancing factors such as sustainability goals, product protection requirements, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Recycled paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com