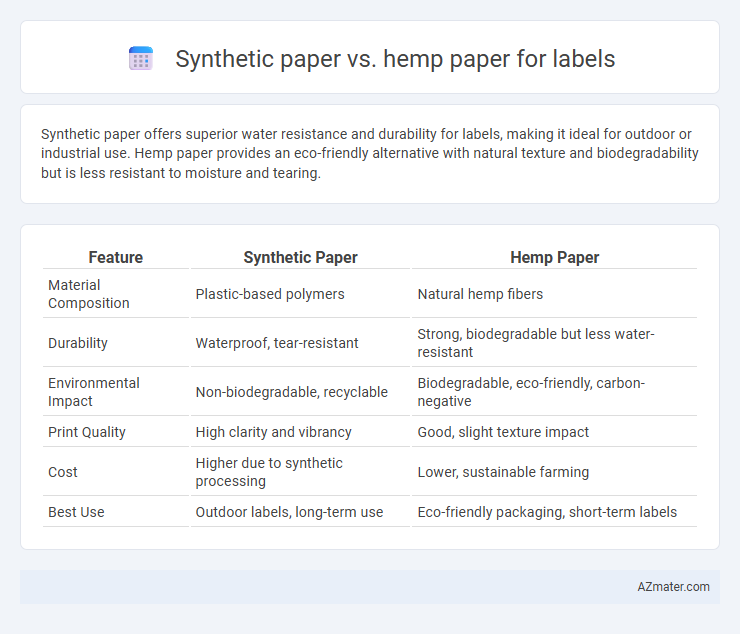
Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance and durability for labels, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial use. Hemp paper provides an eco-friendly alternative with natural texture and biodegradability but is less resistant to moisture and tearing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Hemp Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic-based polymers | Natural hemp fibers |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant | Strong, biodegradable but less water-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Biodegradable, eco-friendly, carbon-negative |
| Print Quality | High clarity and vibrancy | Good, slight texture impact |
| Cost | Higher due to synthetic processing | Lower, sustainable farming |
| Best Use | Outdoor labels, long-term use | Eco-friendly packaging, short-term labels |
Introduction to Synthetic and Hemp Papers
Synthetic paper, made from plastic polymers such as polypropylene, offers waterproof, tear-resistant, and durable properties ideal for high-performance labels. Hemp paper, derived from the fibrous stalks of the hemp plant, provides an eco-friendly, biodegradable alternative with strong fibers and natural texture suitable for sustainable labeling. Both materials serve distinct needs in label production, balancing durability and environmental impact.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Synthetic paper consists mainly of plastic polymers such as polypropylene or polyethylene, providing waterproof and tear-resistant properties ideal for durable labels. Hemp paper is produced from hemp fibers, which are pulped and processed like traditional wood paper but offer greater strength and eco-friendly biodegradability. Manufacturing synthetic paper involves extrusion and calendaring processes to create smooth, opaque sheets, while hemp paper uses mechanical or chemical pulping followed by pressing and drying, resulting in a natural texture suited for sustainable labeling solutions.
Environmental Impact: Synthetic vs Hemp Paper
Synthetic paper, made from petroleum-based plastics, poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and dependence on fossil fuels, resulting in a higher carbon footprint compared to hemp paper. Hemp paper is biodegradable, renewable, and requires fewer pesticides and less water during cultivation, making it a more sustainable option for labels. Choosing hemp paper reduces landfill waste and supports eco-friendly practices in the label industry.
Durability and Performance for Labels
Synthetic paper offers superior durability for labels due to its resistance to water, chemicals, and tearing, ensuring longevity in harsh environments. Hemp paper provides natural strength and eco-friendliness but may lack the waterproof and abrasion-resistant qualities essential for high-performance label applications. For labels requiring extended durability and performance, synthetic paper remains the optimal choice where exposure to moisture and wear is a concern.
Print Quality and Aesthetic Appeal
Synthetic paper offers superior print quality with vibrant colors and sharp details due to its smooth, non-porous surface, making labels highly durable and resistant to water and chemicals. Hemp paper, while eco-friendly and providing a unique, natural texture, tends to absorb ink more, resulting in softer color tones and a rustic, organic aesthetic suitable for artisanal or eco-conscious branding. Choosing between synthetic and hemp paper for labels depends on the desired visual impact, durability requirements, and environmental considerations.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Synthetic paper typically costs more than hemp paper due to its petrochemical-based manufacturing process and durability features. Hemp paper offers a cost-effective alternative, benefiting from renewable resources and increasing agricultural availability, which reduces production expenses over time. Availability of synthetic paper is widespread through industrial suppliers, whereas hemp paper's availability is growing but still limited by regional agricultural production and processing infrastructure.
Biodegradability and Recycling Options
Synthetic paper offers durability and water resistance but poses challenges in biodegradability and is often non-recyclable due to its plastic content. Hemp paper provides superior biodegradability with quick decomposition and is widely accepted in recycling streams, making it an eco-friendly choice for labels. Choosing hemp paper supports sustainable waste management and reduces environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Synthetic paper for labels complies with industry standards such as BS5609 for marine labeling, offering waterproof and chemical-resistant properties essential for regulatory adherence in harsh environments. Hemp paper, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, often lacks certifications like ASTM D6868 for compostability or FDA approval for direct contact, limiting its use in regulated labeling industries. Choosing synthetic paper ensures compliance with stringent safety and durability requirements mandated by sectors like pharmaceuticals and chemical manufacturing.
Applications in Labeling Industries
Synthetic paper offers exceptional durability, water resistance, and tear-proof properties, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial labeling applications requiring longevity and exposure to harsh environments. Hemp paper provides eco-friendly benefits, biodegradability, and a natural texture preferred for organic product packaging and sustainable branding initiatives in the labeling industry. Both materials cater to niche markets, with synthetic paper excelling in performance-critical labels and hemp paper supporting environmentally conscious labeling solutions.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Labels
Synthetic paper offers durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities ideal for labels exposed to harsh conditions, while hemp paper provides an eco-friendly, biodegradable option with a natural texture suited for sustainable branding. Consider synthetic paper for long-lasting labels in outdoor or industrial environments and hemp paper for products emphasizing environmental responsibility and organic appeal. The choice depends on label application, environmental impact priorities, and desired aesthetic.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Hemp paper for Label
 azmater.com
azmater.com