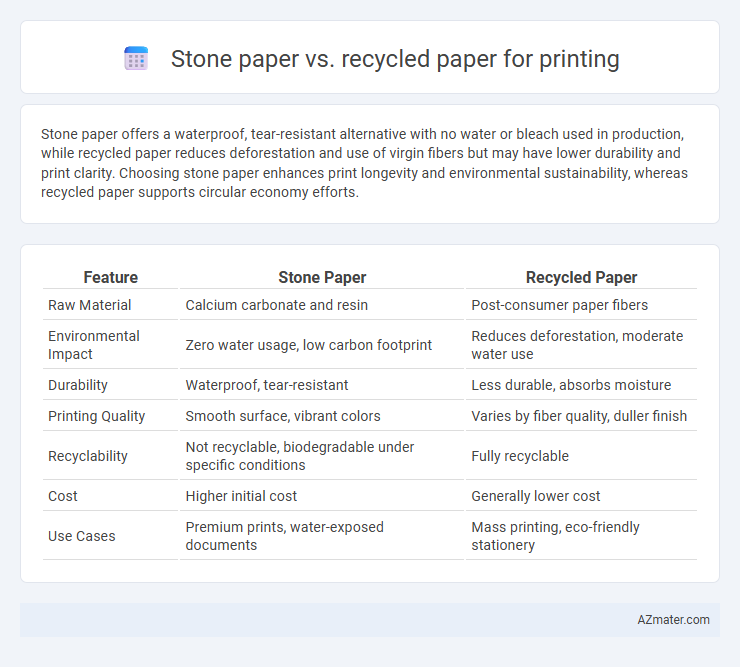
Stone paper offers a waterproof, tear-resistant alternative with no water or bleach used in production, while recycled paper reduces deforestation and use of virgin fibers but may have lower durability and print clarity. Choosing stone paper enhances print longevity and environmental sustainability, whereas recycled paper supports circular economy efforts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stone Paper | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Calcium carbonate and resin | Post-consumer paper fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Zero water usage, low carbon footprint | Reduces deforestation, moderate water use |
| Durability | Waterproof, tear-resistant | Less durable, absorbs moisture |
| Printing Quality | Smooth surface, vibrant colors | Varies by fiber quality, duller finish |
| Recyclability | Not recyclable, biodegradable under specific conditions | Fully recyclable |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Generally lower cost |
| Use Cases | Premium prints, water-exposed documents | Mass printing, eco-friendly stationery |
Introduction to Stone Paper and Recycled Paper
Stone paper is a synthetic paper made from calcium carbonate and non-toxic resins, offering a waterproof, tear-resistant alternative to traditional wood pulp paper, while recycled paper is produced from reclaimed fibers, reducing deforestation and lowering environmental impact. Stone paper provides a smoother print surface with reduced ink absorption, improving print clarity, whereas recycled paper contributes to waste reduction and conserves energy during production. Both materials serve unique environmental and functional roles in sustainable printing, with stone paper excelling in durability and recycled paper emphasizing resource conservation.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Stone paper is primarily composed of calcium carbonate bonded with a non-toxic resin, eliminating the need for water and wood pulp in its manufacturing process. Recycled paper is made from post-consumer or post-industrial paper waste that undergoes pulping, de-inking, and reprocessing to create new sheets. The manufacturing of stone paper results in smoother, tear-resistant sheets, while recycled paper retains fibers from the original wood pulp, impacting texture and environmental footprint.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Stone paper, made from calcium carbonate and non-toxic resin, significantly reduces water and energy use compared to recycled paper, which relies on water-intensive pulping processes. Unlike recycled paper that requires bleaching and chemical treatments, stone paper production generates minimal waste and avoids harmful emissions, lowering its overall carbon footprint. However, stone paper is not biodegradable but is photodegradable, while recycled paper is biodegradable, making each product's environmental impact context-dependent.
Printing Quality and Performance
Stone paper offers smoother, waterproof surfaces that enhance ink vibrancy and reduce bleeding, resulting in sharper, high-quality prints ideal for vivid graphics and photos. Recycled paper tends to have a rougher texture and variable fiber quality that may cause ink absorption inconsistencies, leading to less precise details and occasional smudging. In terms of durability, stone paper outperforms recycled paper by resisting tearing and moisture, making it a superior choice for long-lasting printed materials.
Durability and Water Resistance
Stone paper offers superior durability and water resistance compared to recycled paper, making it ideal for printing materials exposed to moisture or heavy handling. Its composition of calcium carbonate bonded with non-toxic resins creates a tear-resistant, waterproof surface that prevents ink smudging and degradation over time. Recycled paper, while environmentally friendly, generally lacks the robustness and moisture resistance of stone paper, leading to faster wear and potential damage in humid conditions.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Stone paper generally incurs higher production costs due to its novel manufacturing process involving calcium carbonate and resin, leading to a retail price 20-30% above recycled paper. Recycled paper benefits from established supply chains and economies of scale, making it more widely available and cost-effective for large-scale printing applications. Market availability favors recycled paper with extensive global distribution, whereas stone paper remains niche, primarily used in specialty printing markets where durability and water resistance justify the premium expense.
Compatibility with Printing Technologies
Stone paper demonstrates exceptional compatibility with various printing technologies, including inkjet, laser, and offset printing, due to its smooth, non-porous surface that ensures vibrant color reproduction and sharp images. Recycled paper, while generally compatible with most printers, may present challenges such as inconsistent texture and absorbency that can affect print quality and cause paper jams in high-speed printers. Selecting stone paper enhances print durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for high-quality marketing materials, whereas recycled paper prioritizes sustainability with moderate print performance.
Recyclability and End-of-Life Disposal
Stone paper, made from calcium carbonate bonded with non-toxic resin, is water-resistant and durable but not widely recyclable through traditional paper recycling systems due to its plastic content. Recycled paper, derived from post-consumer waste, maintains compatibility with conventional recycling streams and decomposes more efficiently in industrial composting facilities. End-of-life disposal for recycled paper significantly reduces landfill impact and supports circular economy initiatives, whereas stone paper requires specialized disposal methods to avoid environmental persistence.
Applications in Printing Industries
Stone paper offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-quality prints, outdoor posters, and packaging that require longevity. Recycled paper provides an eco-friendly option preferred in mass printing tasks such as newspapers, brochures, and office documents, aligning with sustainability goals. Both materials serve distinct printing industry needs: stone paper enhances product aesthetics and resilience, while recycled paper emphasizes environmental impact reduction.
Future Trends and Innovations
Stone paper, made from calcium carbonate and non-toxic resin, offers waterproof and tear-resistant qualities that reduce environmental impact by eliminating the need for water and bleaching in production. Innovations in biodegradable coatings and enhanced printing technologies promise improved compatibility with high-speed printers, positioning stone paper as a sustainable alternative to recycled paper, which relies on fiber recovery and often involves chemical processing. Future trends include hybrid materials combining stone paper's durability with recycled fibers, aiming to optimize cost, print quality, and ecological benefits in the printing industry.
Infographic: Stone paper vs Recycled paper for Printing
 azmater.com
azmater.com