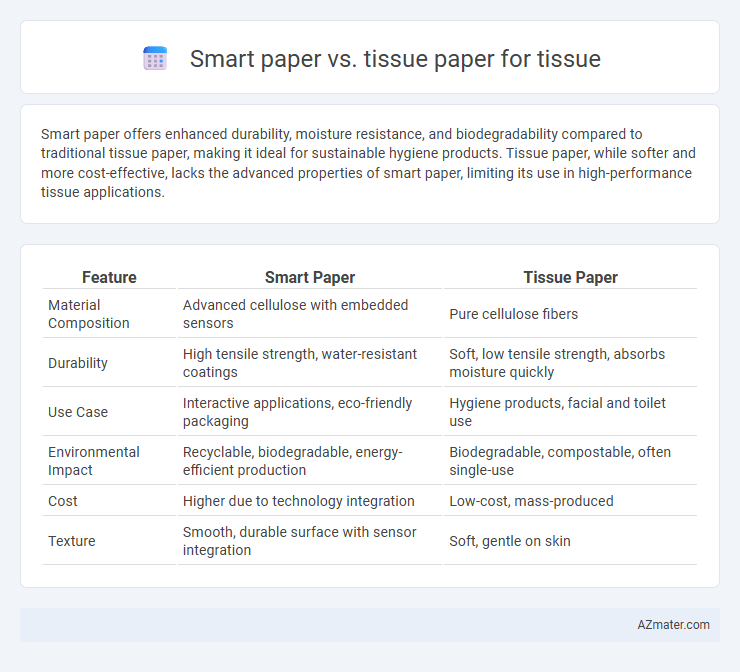
Smart paper offers enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and biodegradability compared to traditional tissue paper, making it ideal for sustainable hygiene products. Tissue paper, while softer and more cost-effective, lacks the advanced properties of smart paper, limiting its use in high-performance tissue applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Paper | Tissue Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced cellulose with embedded sensors | Pure cellulose fibers |
| Durability | High tensile strength, water-resistant coatings | Soft, low tensile strength, absorbs moisture quickly |
| Use Case | Interactive applications, eco-friendly packaging | Hygiene products, facial and toilet use |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, biodegradable, energy-efficient production | Biodegradable, compostable, often single-use |
| Cost | Higher due to technology integration | Low-cost, mass-produced |
| Texture | Smooth, durable surface with sensor integration | Soft, gentle on skin |
Introduction to Smart Paper and Tissue Paper
Smart paper incorporates embedded sensors or electronic components enabling real-time data collection and interactive functionalities, enhancing usability in healthcare and hygiene applications. Tissue paper, typically made from soft, absorbent cellulose fibers, serves primarily for personal hygiene and cleaning purposes with emphasis on softness and disposability. Comparing smart paper's technological integration with tissue paper's traditional absorbency highlights advancements in functionality across tissue products.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Smart paper for tissue products typically incorporates advanced polymers or nano-cellulose fibers, enhancing strength, absorbency, and softness, while traditional tissue paper primarily consists of virgin or recycled cellulose fibers. Manufacturing smart paper involves technology-driven processes such as nano-coating or embedding functional additives, contrasting with the conventional creping and pressing methods used in standard tissue paper production. The composition and manufacturing innovations in smart paper result in superior durability and multifunctional properties compared to conventional tissue, meeting evolving consumer needs.
Absorbency: Smart Paper vs Tissue Paper
Smart paper exhibits superior absorbency compared to traditional tissue paper due to its advanced fiber technology that enhances liquid retention and distribution. Tissue paper typically absorbs moisture quickly but has limited capacity, leading to faster saturation. The optimized structure of smart paper allows for prolonged absorbency and better performance in applications requiring effective moisture management.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Smart paper exhibits superior strength and durability compared to traditional tissue paper due to advanced fiber bonding techniques and higher-quality raw materials. It maintains structural integrity and resists tearing even under wet conditions, making it ideal for prolonged use and demanding applications. Tissue paper, while softer, tends to be less resilient and more prone to disintegration when exposed to moisture or tension.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability Factors
Smart paper is engineered to enhance recyclability and reduce chemical use, making it a more eco-friendly option compared to traditional tissue paper, which often involves more intensive resource consumption and waste generation. Tissue paper typically requires higher water and energy usage in production and generates more landfill waste if not recycled properly. Sustainability factors favor smart paper due to its lower carbon footprint, biodegradable materials, and improved lifecycle management, supporting better environmental outcomes for tissue applications.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Economical?
Smart paper, designed for higher durability and multifunctional use, typically incurs a higher upfront cost compared to traditional tissue paper, which is cheaper but less durable. When analyzing cost-effectiveness, tissue paper offers lower initial expenses, making it more economical for disposable or single-use applications. However, Smart paper's reusability can reduce long-term costs in repeated-use scenarios, potentially balancing or surpassing the initial investment over time.
Hygiene and Health Considerations
Smart paper for tissue applications offers enhanced hygiene through antimicrobial treatments that reduce bacteria and virus transmission on surfaces, significantly improving health safety. Tissue paper, while highly absorbent and soft, may lack these advanced properties, making it less effective in preventing cross-contamination in medical or high-touch environments. Choosing smart paper can contribute to better infection control and overall public health, especially in healthcare settings.
User Experience and Comfort
Smart paper tissue offers enhanced softness and absorbency compared to traditional tissue paper, providing a superior user experience with gentle touch and efficient moisture control. Its innovative fiber structure reduces irritation and increases durability, ensuring comfort during use even for sensitive skin. This advanced material outperforms conventional tissue paper by maintaining strength when wet and delivering a more pleasant, less abrasive feel.
Applications and Usability Scenarios
Smart paper enhances tissue applications by integrating features such as moisture resistance and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for medical and hygiene products. Tissue paper, valued for its softness and absorbency, remains preferred for everyday use in personal care, food service, and cleaning tasks. In environments requiring durability and added functionality, smart paper provides superior usability, while traditional tissue excels in comfort-centric scenarios.
Future Trends in Tissue Paper Technology
Future trends in tissue paper technology emphasize sustainable materials and enhanced functionality, with smart paper integrating sensors and biodegradable composites to provide improved hygiene and environmental benefits. Innovations in nanotechnology and antimicrobial coatings are expected to revolutionize tissue paper, offering superior absorbency, durability, and user safety. The convergence of smart paper with digital health monitoring signals a transformative shift in consumer tissue products, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Infographic: Smart paper vs Tissue paper for Tissue
 azmater.com
azmater.com