Seed paper is an eco-friendly, biodegradable material embedded with seeds that can be planted after use, promoting sustainability. Newspaper for newsprint is traditionally made from wood pulp, primarily designed for mass printing but less environmentally sustainable compared to seed paper.
Table of Comparison
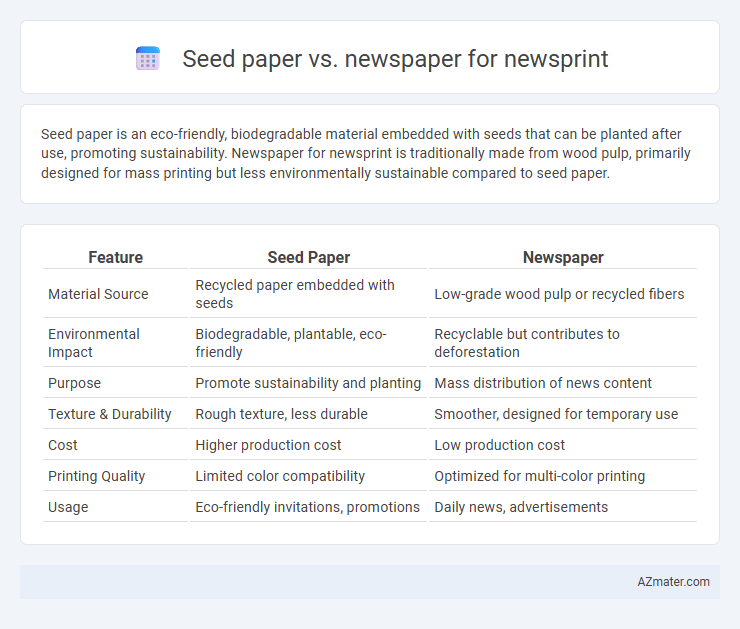
| Feature | Seed Paper | Newspaper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Recycled paper embedded with seeds | Low-grade wood pulp or recycled fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, plantable, eco-friendly | Recyclable but contributes to deforestation |
| Purpose | Promote sustainability and planting | Mass distribution of news content |
| Texture & Durability | Rough texture, less durable | Smoother, designed for temporary use |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Low production cost |
| Printing Quality | Limited color compatibility | Optimized for multi-color printing |
| Usage | Eco-friendly invitations, promotions | Daily news, advertisements |
Introduction to Seed Paper and Newspaper
Seed paper is an innovative eco-friendly material embedded with plant seeds, designed to promote sustainability by allowing users to plant the paper after use, reducing waste and supporting green initiatives. Newspaper, traditionally made from wood pulp and recycled paper fibers, serves as a widely used medium for mass communication and daily news distribution, emphasizing cost-efficiency and recyclability in the newsprint industry. Both materials offer unique environmental benefits but cater to different markets, with seed paper focusing on ecological impact and newspapers prioritizing information dissemination.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Seed paper decomposes naturally and enriches soil by releasing seeds that grow into plants, promoting biodiversity and reducing landfill waste. Newspaper for newsprint, while recyclable, often involves chemical inks and bleaching agents that can strain recycling systems and result in more environmental pollutants. Choosing seed paper over traditional newspaper newsprint significantly lowers the carbon footprint through enhanced biodegradability and ecological contributions.
Production Processes
Seed paper production integrates recycled paper pulp with embedded flower seeds, requiring careful mixing and controlled drying to preserve seed viability, making the process more specialized and environmentally conscious compared to traditional newsprint. Newspaper production relies on high-speed, large-scale mechanical or chemical pulping followed by continuous pressing and drying, optimized for efficiency and cost-effectiveness in mass distribution. The seed paper process emphasizes sustainability and plant growth potential, while newspaper production prioritizes rapid output and print quality for daily information dissemination.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Seed paper consists of biodegradable materials embedded with plant seeds, promoting environmental sustainability by enabling planting after use. Newspaper for newsprint is primarily made from wood pulp or recycled paper fibers, which are recyclable but often involve significant deforestation and chemical processing. Seed paper offers a more sustainable alternative by reducing waste and fostering ecological regeneration, whereas traditional newsprint remains reliant on resource-intensive production methods.
Biodegradability and Recycling
Seed paper offers superior biodegradability compared to traditional newspaper, as it decomposes naturally and supports plant growth by containing embedded seeds. Newspapers are recyclable but often coated with inks and additives that complicate recycling processes and reduce the quality of recycled fibers. Choosing seed paper enhances environmental benefits by minimizing waste and promoting sustainable lifecycle practices in newsprint materials.
Print Quality and Readability
Seed paper offers a unique texture with a slightly rougher surface compared to traditional newspaper, resulting in more vibrant and crisp ink absorption that enhances print quality and color contrast. Newspaper, designed primarily for mass production, tends to have a lower brightness and thinner fibers, which can cause ink to bleed and reduce text sharpness, impacting readability negatively. The higher opacity and sturdiness of seed paper contribute to improved legibility and durability, making it a superior choice for high-quality newsprint applications where visual clarity is essential.
Cost Analysis
Seed paper typically incurs higher costs than traditional newspaper for newsprint due to its unique biodegradable materials and embedded seeds, which increase production expenses. Newspapers benefit from established mass production processes using recycled fibers, significantly lowering raw material and manufacturing costs. When analyzing cost efficiency, newspapers remain the more economical option for large-scale newsprint distribution, while seed paper appeals to niche markets prioritizing sustainability despite its premium price.
Market Adoption and Popularity
Seed paper, made from biodegradable materials embedded with seeds, is gaining traction in niche markets like eco-friendly promotional materials and sustainable packaging but remains limited in mainstream newsprint applications. Traditional newspaper pulp dominates the global newsprint industry due to its cost-effectiveness, high production volume, and established recycling infrastructure, maintaining widespread market adoption. Despite growing environmental awareness, seed paper's higher production costs and slower printability hinder its popularity compared to conventional newspaper for mass newsprint distribution.
Challenges and Limitations
Seed paper for newsprint faces challenges such as limited durability and higher production costs compared to traditional newspaper, impacting large-scale distribution and recycling processes. The biodegradable nature of seed paper reduces its shelf life and print quality, complicating storage and archival efforts. In contrast, newspaper offers established recycling infrastructure but contributes significantly to environmental waste and deforestation concerns.
Future Trends for Newsprint Media
Seed paper presents an innovative alternative to traditional newspaper newsprint by combining sustainability with user engagement, as it can be planted after use, reducing environmental waste. The future trends in newsprint media indicate a shift towards eco-friendly materials amid growing consumer demand for green practices and regulatory pressure to reduce carbon footprints. As digital media continues to dominate, integrating biodegradable seed paper into print news could rejuvenate audience interest while supporting circular economy principles.
Infographic: Seed paper vs Newspaper for Newsprint
 azmater.com
azmater.com