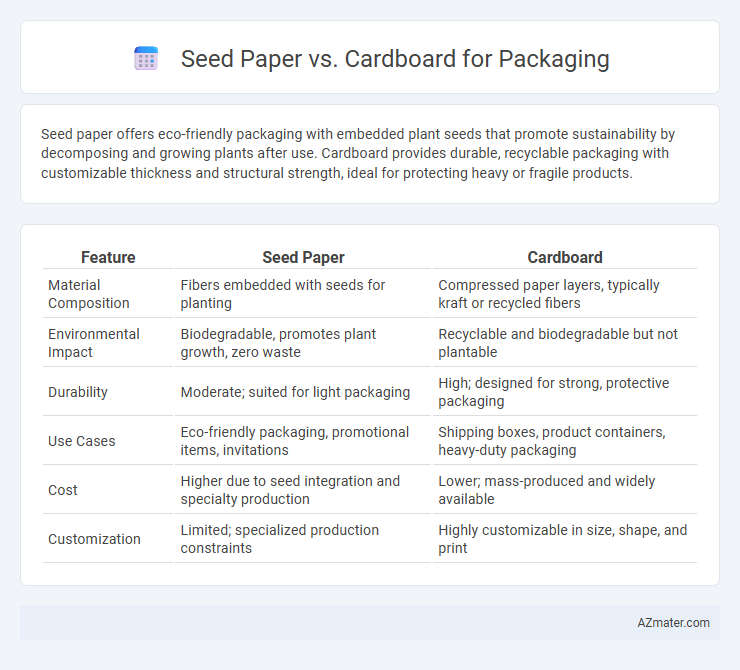
Seed paper offers eco-friendly packaging with embedded plant seeds that promote sustainability by decomposing and growing plants after use. Cardboard provides durable, recyclable packaging with customizable thickness and structural strength, ideal for protecting heavy or fragile products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Seed Paper | Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fibers embedded with seeds for planting | Compressed paper layers, typically kraft or recycled fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, promotes plant growth, zero waste | Recyclable and biodegradable but not plantable |
| Durability | Moderate; suited for light packaging | High; designed for strong, protective packaging |
| Use Cases | Eco-friendly packaging, promotional items, invitations | Shipping boxes, product containers, heavy-duty packaging |
| Cost | Higher due to seed integration and specialty production | Lower; mass-produced and widely available |
| Customization | Limited; specialized production constraints | Highly customizable in size, shape, and print |
Introduction: Seed Paper vs Cardboard Packaging
Seed paper packaging integrates biodegradable paper embedded with seeds that sprout when planted, offering an eco-friendly, sustainable alternative to traditional materials. Cardboard packaging, a widely used material made from recycled paper fibers, provides sturdy protection and recyclability but lacks the regenerative benefits of seed paper. Choosing between seed paper and cardboard involves balancing environmental impact, durability, and marketing appeal in sustainable packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Seed paper packaging decomposes naturally in soil, promoting plant growth by embedding seeds, which significantly reduces landfill waste and supports biodiversity. Cardboard packaging, while recyclable and biodegradable, typically requires more energy and water for production and contributes to deforestation if not sourced sustainably. Choosing seed paper over cardboard minimizes carbon footprint and enhances circular economy principles by combining packaging with ecological regeneration.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Seed paper exhibits superior biodegradability and compostability compared to cardboard, as it is embedded with natural seeds that decompose fully while promoting plant growth. Unlike traditional cardboard, which primarily breaks down into organic material without providing ecological benefits, seed paper transforms waste into vegetation, enhancing soil quality during composting. Both materials are biodegradable, but seed paper offers added environmental value by supporting sustainable plant regeneration.
Manufacturing Processes
Seed paper manufacturing involves embedding biodegradable seeds into recycled paper pulp, requiring a delicate balance of moisture and seed placement to ensure germination while maintaining paper strength. Cardboard production utilizes layers of kraft paper bonded with adhesives through a corrugation process to create a durable, recyclable material designed for heavy-duty packaging. Seed paper emphasizes eco-friendly, low-impact techniques with limited chemical use, whereas cardboard manufacturing relies on industrial-scale pulping, pressing, and drying for structural integrity and mass production.
Customization and Design Options
Seed paper offers unique customization options with embedded seeds that can be shaped, colored, and printed to create eco-friendly packaging that promotes brand sustainability. Cardboard provides versatile design possibilities including embossing, debossing, and digital printing, making it ideal for detailed graphics and structural variations. Both materials support high-quality branding, but seed paper adds a distinctive interactive element by encouraging plant growth after use.
Cost Considerations
Seed paper typically incurs higher production costs due to embedded biodegradable seeds and specialized manufacturing processes, making it more expensive than traditional cardboard. Cardboard offers a cost-effective and widely available packaging solution with lower raw material and processing expenses. Businesses must weigh the premium investment in seed paper against environmental benefits and brand differentiation when considering packaging costs.
Strength and Durability
Seed paper offers moderate strength and biodegradability, making it ideal for lightweight packaging with eco-friendly branding. Cardboard provides superior durability and structural integrity, supporting heavier loads and offering better protection during shipping. Choosing between the two depends on balancing environmental impact with packaging strength requirements.
Branding and Consumer Appeal
Seed paper packaging enhances branding by offering an eco-friendly, innovative touch that resonates with environmentally conscious consumers, creating a memorable unboxing experience. Cardboard packaging provides versatility and durability, allowing for vibrant prints and structural customization that effectively showcases brand identity. Consumers increasingly prefer seed paper for its sustainable appeal, while cardboard remains favored for practical protection and prominent brand display.
End-of-Life Disposal Methods
Seed paper decomposes naturally in soil, promoting plant growth as it breaks down into organic matter, making it an eco-friendly option for sustainable packaging disposal. Cardboard is widely recyclable and biodegradable, but its environmental impact depends on local recycling facilities and whether it is contaminated with food or adhesives. Proper disposal of both materials reduces landfill waste, with seed paper offering a unique benefit through its ability to germinate, whereas cardboard supports circular economy practices through recycling streams.
Choosing the Best Sustainable Packaging
Seed paper offers an eco-friendly packaging option that embeds plant seeds, allowing for biodegradability and plant growth after use, making it ideal for brands emphasizing sustainability and customer engagement. Cardboard provides durability, recyclability, and cost-effectiveness, suited for protective packaging and large-scale shipping needs while maintaining environmental responsibility. Choosing the best sustainable packaging depends on product type, brand values, and lifecycle impact, with seed paper excelling in promotional or gift packaging and cardboard serving practical shipping applications.
Infographic: Seed paper vs Cardboard for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com