Seed paper contains embedded plant seeds that sprout when planted, making it an eco-friendly choice for art projects with a sustainable message. Blotting paper is highly absorbent, ideal for drying ink or paint quickly, but it lacks the organic planting feature seed paper offers.
Table of Comparison
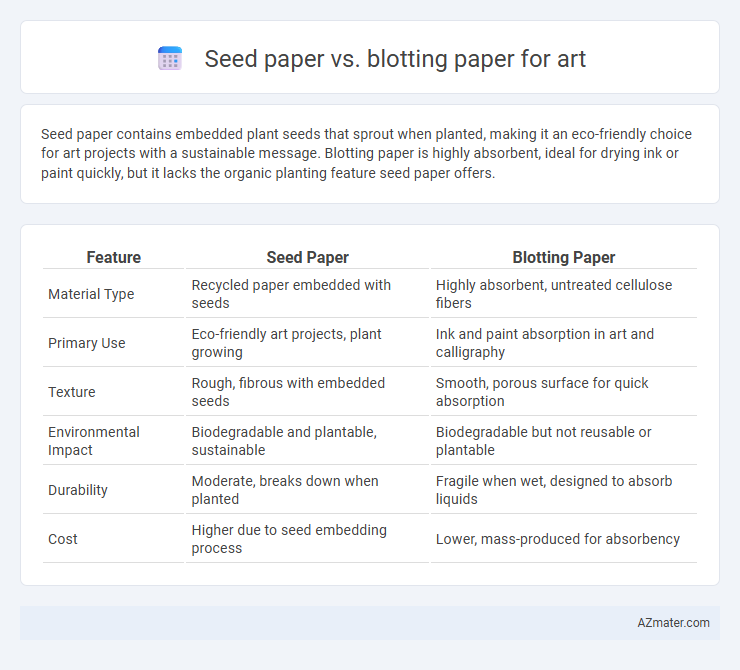
| Feature | Seed Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Recycled paper embedded with seeds | Highly absorbent, untreated cellulose fibers |
| Primary Use | Eco-friendly art projects, plant growing | Ink and paint absorption in art and calligraphy |
| Texture | Rough, fibrous with embedded seeds | Smooth, porous surface for quick absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and plantable, sustainable | Biodegradable but not reusable or plantable |
| Durability | Moderate, breaks down when planted | Fragile when wet, designed to absorb liquids |
| Cost | Higher due to seed embedding process | Lower, mass-produced for absorbency |
Introduction to Seed Paper and Blotting Paper
Seed paper is a type of eco-friendly paper embedded with seeds that can be planted to grow flowers, herbs, or vegetables, making it popular for sustainable art projects and green giveaways. Blotting paper, made from highly absorbent materials, is traditionally used to absorb excess ink or moisture, making it essential for calligraphy and watercolor artworks. Both papers serve distinct purposes in art, with seed paper emphasizing environmental sustainability and blotting paper focusing on functional utility in creative processes.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Seed paper incorporates recycled fibers blended with embedded seeds such as wildflowers or herbs, allowing it to be planted after use; its manufacturing involves mixing pulp with seeds and pressing the mixture into sheets, then drying gently to preserve seed viability. Blotting paper, made primarily from highly absorbent cotton or linen fibers without additives, undergoes a refining process to create a porous, soft surface ideal for absorbing inks and oils; its production includes pulping, beating to loosen fibers, and pressing to achieve desired thickness and texture. The key difference lies in seed paper's biological composition aimed at growth, contrasting with blotting paper's refined, uniform fibers designed for absorption and smoothness in artistic applications.
Physical Properties and Texture Comparison
Seed paper features a fibrous, rough texture embedded with biodegradable seeds that encourage plant growth and provide a tactile, eco-friendly surface for artistic projects. Blotting paper is highly absorbent with a smooth yet porous texture designed to quickly soak up excess ink or moisture, making it ideal for controlling media in art. The distinct physical properties--seed paper's thickness and seed integration versus blotting paper's thin, absorbent structure--directly influence their respective artistic applications and handling techniques.
Absorbency and Ink Handling
Seed paper features moderate absorbency ideal for water-based inks and light washes, allowing pigments to settle without excessive bleeding, making it suitable for eco-friendly art projects. Blotting paper has high absorbency designed to quickly soak up excess ink or moisture, reducing smudging but causing ink to disperse more rapidly, which can affect fine details in drawings or paintings. Artists should choose seed paper for controlled ink flow and texture, while blotting paper is preferable for drying techniques and ink absorption during sketching or calligraphy.
Role in Different Art Techniques
Seed paper incorporates embedded seeds that germinate when planted, making it ideal for eco-friendly art projects like handmade cards or invitations that double as plantable gifts. Blotting paper excels in absorbing excess ink or moisture, playing a crucial role in calligraphy, watercolor, and printmaking by preventing smudges and controlling ink flow. Both papers serve distinct artistic functions: seed paper emphasizes sustainability and interactive art experiences, while blotting paper focuses on technical precision and drying control in various art techniques.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Seed paper enhances environmental sustainability by embedding biodegradable seeds that grow into plants, reducing waste and promoting green living. Blotting paper, typically made from absorbent cotton fibers, is biodegradable but lacks regenerative benefits, resulting in a lower environmental impact compared to conventional paper but without contributing to reforestation or biodiversity. Artists seeking eco-friendly materials prioritize seed paper for its dual function as an art medium and a tool for ecological restoration, aligning with sustainable art practices and circular economy principles.
Artistic Results: Color Vibrancy and Blending
Seed paper tends to enhance color vibrancy by absorbing pigments deeply, resulting in rich and vivid artistic results, while blotting paper often diffuses colors more softly, creating subtle blends but less intense hues. Artists favor seed paper for projects requiring bold, saturated effects, whereas blotting paper excels in achieving delicate gradients and smooth transitions in watercolor techniques. The choice between these papers significantly impacts the final artwork's texture and color dynamics, influencing both the blending process and overall visual impact.
Durability and Longevity in Artwork
Seed paper, embedded with plant seeds, is biodegradable and ideal for eco-friendly projects but generally less durable and prone to quicker wear compared to blotting paper. Blotting paper, made from absorbent cotton fibers, offers superior durability and longevity, remaining stable over time and resisting deterioration in artwork applications. Artists prioritizing archival quality and preservation typically prefer blotting paper for its ability to maintain integrity under various environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability for Artists
Seed paper typically costs more than blotting paper due to its embedded biodegradable seeds and eco-friendly production process, making it a pricier option for artists seeking sustainable materials. Blotting paper is more widely available and affordable, found in most art supply stores and online, making it a practical choice for artists prioritizing budget and accessibility. While seed paper offers a unique texture and environmental benefit, blotting paper remains a cost-effective, readily accessible option for absorbent surfaces in artwork.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Art Project
Seed paper contains embedded seeds that sprout when planted, offering an eco-friendly option ideal for sustainable art projects focused on environmental themes. Blotting paper excels at absorbing excess ink or paint, making it perfect for techniques that require controlled drying and preventing smudging in detailed artwork. Selecting between seed paper and blotting paper depends on whether the project prioritizes environmental impact or functional absorption for specific artistic mediums.
Infographic: Seed paper vs Blotting paper for Art
 azmater.com
azmater.com