Rice paper offers a smooth, absorbent surface ideal for detailed ink and watercolor drawings, enhancing brushstroke precision. Graph paper provides a grid structure that supports accurate alignment and proportional sketches, perfect for technical or architectural drawings.
Table of Comparison
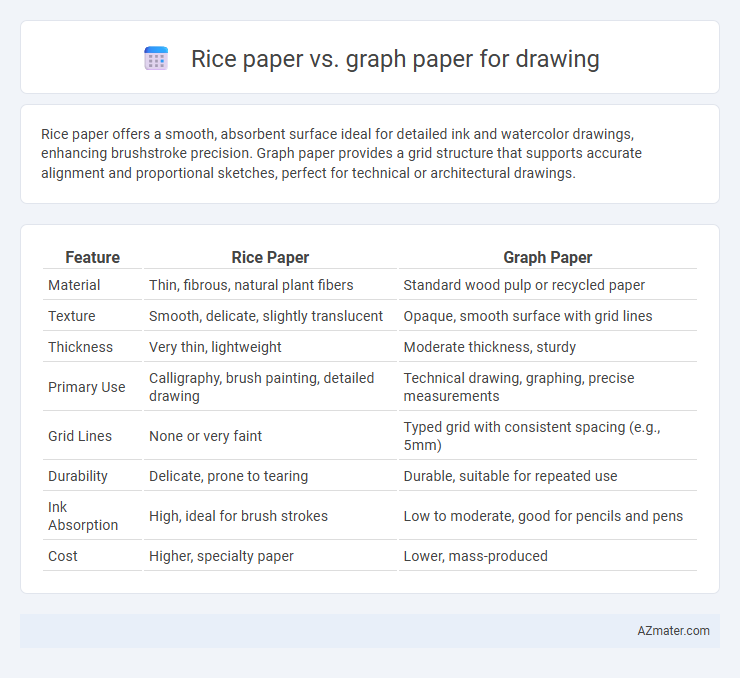
| Feature | Rice Paper | Graph Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thin, fibrous, natural plant fibers | Standard wood pulp or recycled paper |
| Texture | Smooth, delicate, slightly translucent | Opaque, smooth surface with grid lines |
| Thickness | Very thin, lightweight | Moderate thickness, sturdy |
| Primary Use | Calligraphy, brush painting, detailed drawing | Technical drawing, graphing, precise measurements |
| Grid Lines | None or very faint | Typed grid with consistent spacing (e.g., 5mm) |
| Durability | Delicate, prone to tearing | Durable, suitable for repeated use |
| Ink Absorption | High, ideal for brush strokes | Low to moderate, good for pencils and pens |
| Cost | Higher, specialty paper | Lower, mass-produced |
Introduction: Rice Paper vs Graph Paper for Drawing
Rice paper offers a delicate and textured surface favored for traditional ink and brush drawings, enhancing fluid strokes and natural absorption, while graph paper provides a structured grid ideal for precise layouts, architectural sketches, and geometric designs. Artists select rice paper for organic, expressive work and graph paper for technical accuracy, making both essential depending on the drawing style and purpose. Understanding the contrasting qualities of rice paper's fiber composition and graph paper's printed grid allows artists to optimize their drawing techniques and outcomes.
Understanding Rice Paper: Characteristics and Uses
Rice paper, traditionally made from the pith of the rice plant or other natural fibers, is prized for its delicate texture and absorbent qualities, making it ideal for ink brush painting and calligraphy. Its translucent and lightweight nature allows artists to achieve subtle washes and fine details, which are difficult to replicate on the more rigid and grid-structured surface of graph paper. While graph paper is designed for precision and measurement with its uniform grid lines, rice paper offers superior flexibility and organic flow, essential for expressive and traditional art forms.
Graph Paper Basics: Types and Technical Features
Graph paper is available in various types such as quad, isometric, and logarithmic, each designed to support specific drawing needs like technical sketches or 3D representations. Its defining features include a precise grid pattern with evenly spaced horizontal and vertical lines, allowing for accurate measurements and alignment in drawings or diagrams. The paper's durability and smooth surface accommodate a range of drawing instruments, making it essential for engineering, architecture, and detailed artistic work.
Surface Texture: How It Affects Drawing Techniques
Rice paper features a delicate, fibrous surface texture that absorbs ink and paint differently, allowing for smooth, fluid brush strokes ideal for calligraphy and watercolor techniques. Graph paper has a smooth, uniform surface with printed grids that provide precision but may restrict blending and freeform strokes due to limited texture variation. The porous nature of rice paper enhances ink diffusion and texture depth, while graph paper's matte finish supports detailed, structured sketches without ink bleeding.
Durability and Strength: Comparing Materials
Rice paper, made from natural fibers like mulberry or hemp, offers delicate texture but tends to be fragile and prone to tearing under heavy pressure or repeated erasing. Graph paper, typically composed of sturdier wood pulp or synthetic fibers, provides greater durability and strength, making it more suitable for detailed technical drawings that require multiple corrections. The heavier weight and smooth surface of graph paper enhance its resilience, ensuring longevity and consistent support for various drawing tools.
Line Precision: Accuracy on Rice Paper vs Graph Paper
Graph paper offers superior line precision due to its pre-printed grid, enabling artists and designers to maintain consistent proportions and accurate measurements effortlessly. Rice paper, while prized for its texture and absorbency in traditional ink and brush techniques, lacks the structured guidance that graph paper provides, making line accuracy more challenging to achieve. For technical drawings demanding exactness, graph paper is the optimal choice, whereas rice paper suits freeform artistic expression where precise line placement is less critical.
Best Suited Drawing Styles for Each Paper
Rice paper excels in traditional Asian ink painting and calligraphy, offering a smooth texture that absorbs ink gracefully for fluid brush strokes and delicate shading. Graph paper is ideal for technical drawing, architectural sketches, and geometric designs, providing precise grid lines that facilitate accurate measurements and symmetry. Artists seeking expressive, freeform strokes benefit from rice paper, while those requiring structured, detailed layouts prefer graph paper.
Ink and Pencil Compatibility: Performance on Both Papers
Rice paper offers excellent ink absorption, resulting in sharp, vibrant lines without much bleeding, making it ideal for ink drawings but less suited for pencil work due to its textured surface which can cause uneven graphite application. Graph paper, with its smooth, coated finish, provides consistent pencil performance, allowing for precise shading and line work, while ink may sit on top longer and be prone to smudging if not dried properly. Artists often prefer rice paper for traditional brush and ink techniques and graph paper for detailed pencil sketches or technical drawings requiring grid alignment.
Cost and Accessibility: Which Is More Practical?
Rice paper offers an affordable and accessible option for artists who prioritize traditional Asian painting techniques, often found at specialty art stores or online, though its delicate texture may limit frequent use. Graph paper, widely available in office supply stores and educational outlets, provides a cost-effective and practical choice for precise technical drawings and layout planning due to its uniform grid. For artists balancing budget and accessibility, graph paper generally presents a more practical and economical solution for regular drawing needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Paper for Your Artistic Needs
Rice paper offers a delicate, textured surface ideal for ink wash and traditional Asian painting techniques, enhancing fluid brush strokes and subtle gradients. Graph paper provides structured grid lines that support precise geometric drawings, technical sketches, and design layouts, ensuring accuracy and proportion. Selecting between rice paper and graph paper depends on whether the focus is on expressive, organic artwork or detailed, measurement-based drafting.
Infographic: Rice paper vs Graph paper for Drawing
 azmater.com
azmater.com