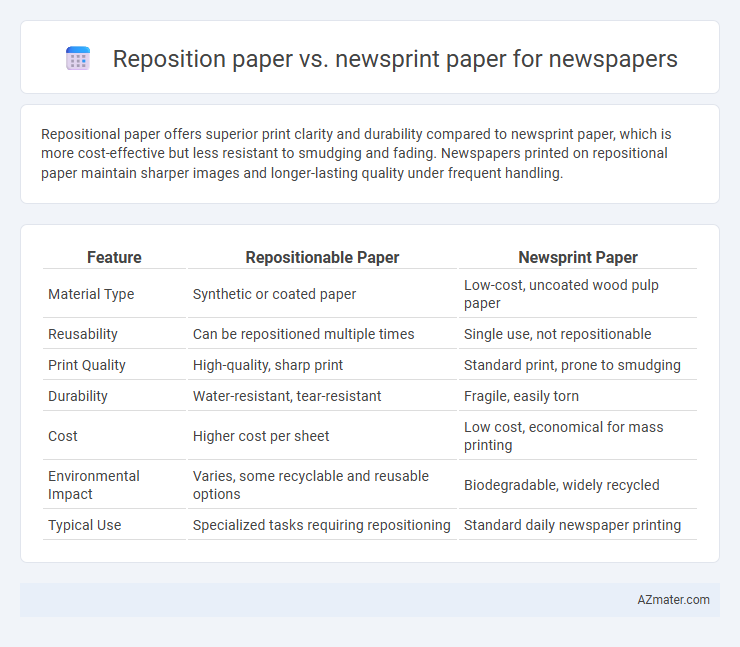
Repositional paper offers superior print clarity and durability compared to newsprint paper, which is more cost-effective but less resistant to smudging and fading. Newspapers printed on repositional paper maintain sharper images and longer-lasting quality under frequent handling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Repositionable Paper | Newsprint Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic or coated paper | Low-cost, uncoated wood pulp paper |
| Reusability | Can be repositioned multiple times | Single use, not repositionable |
| Print Quality | High-quality, sharp print | Standard print, prone to smudging |
| Durability | Water-resistant, tear-resistant | Fragile, easily torn |
| Cost | Higher cost per sheet | Low cost, economical for mass printing |
| Environmental Impact | Varies, some recyclable and reusable options | Biodegradable, widely recycled |
| Typical Use | Specialized tasks requiring repositioning | Standard daily newspaper printing |
Introduction to Newspaper Printing Papers
Newspaper printing relies primarily on newsprint paper, a lightweight, inexpensive material designed for high-speed presses and rapid ink absorption to produce crisp text and images. Repositional paper, though less common in traditional newspapers, offers temporary adhesion properties ideal for specialized uses such as inserts or prototype layouts, but lacks the cost-efficiency and print quality consistency required for mass newspaper production. Understanding the specific properties of newsprint versus repositional paper is crucial for selecting the optimal material based on print durability, cost, and functional requirements in newspaper manufacturing.
What is Repositional Paper?
Repositional paper is a lightweight, semi-transparent paper coated with a low-tack adhesive that allows it to be easily peeled off and repositioned without leaving residue, making it ideal for temporary newspaper layouts or overlays. Unlike standard newsprint paper, which is designed for one-time printing and circulation, repositional paper offers flexibility in editing and design adjustments before final publication. Its unique adhesive properties and smooth surface optimize print clarity and facilitate error correction during the newspaper production process.
Defining Newsprint Paper
Newsprint paper is a low-cost, lightweight paper primarily used for printing newspapers, characterized by its high bulk, low brightness, and moderate opacity, designed to absorb ink quickly for fast printing processes. Compared to repositional paper, newsprint lacks the adhesive properties that allow repositioning and is not suitable for reuse or notes. The primary function of newsprint paper is efficient mass production and readability, whereas repositional paper focuses on temporary adhesion and flexibility for annotations or labels.
Key Physical Characteristics Comparison
Repositional paper for newspapers features a smooth, coated surface designed for easy adhesion and reusability, with higher opacity and brightness levels compared to newsprint. Newsprint paper typically has lower basis weight, a more porous texture, and reduced opacity, which allows faster ink absorption but results in less durability. The improved caliper and surface smoothness of repositional paper contribute to superior print clarity and minimal ink bleed compared to traditional newsprint.
Print Quality: Repositional vs Newsprint
Repositional paper offers higher print quality for newspapers due to its smooth surface and superior ink absorption, resulting in sharper text and vibrant images compared to traditional newsprint. Newsprint paper often shows ink bleed and lower resolution, which diminishes overall clarity and detail in printed content. Using repositional paper enhances reader experience by producing clearer graphics and more legible headlines, especially for high-resolution color prints.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
Repositional paper for newspapers offers cost efficiency by reducing waste through easy repositioning during printing, leading to fewer misprints and lower material loss compared to traditional newsprint paper. Newsprint paper remains more budget-friendly upfront due to its lower material cost, making it suitable for high-volume, cost-sensitive newspaper production. Choosing between repositionable and newsprint paper depends on balancing the initial paper cost against potential savings in waste reduction and print accuracy.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Repositional paper, often coated with synthetic polymers, typically poses greater environmental challenges due to its lower recyclability and higher energy consumption during production compared to newsprint paper. Newsprint paper, derived from sustainably managed wood pulp, is more biodegradable and widely recyclable, reducing landfill waste and promoting circularity in newspaper production. Choosing newsprint paper aligns better with sustainability goals by minimizing carbon footprint and supporting eco-friendly forestry practices.
Reader Experience and Paper Handling
Repositional paper offers a smooth texture and moderate gloss, enhancing readability by reducing glare and improving print clarity, which leads to a more comfortable reader experience compared to traditional newsprint. Its lighter weight and improved surface strength allow for easier folding and less paper dust, facilitating better handling during printing and distribution processes. Newsprint paper, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to absorb more ink leading to potential smudging and lower print sharpness, which can slightly degrade the reader's visual comfort and complicate handling due to its coarser texture.
Suitability for Modern Printing Technology
Repositional paper offers high compatibility with modern digital printing technologies due to its smooth surface and consistent weight, ensuring excellent ink adhesion and vibrant color reproduction. Newsprint paper, traditionally made from lower-quality pulp, is less suited for advanced printing methods as it absorbs more ink, resulting in lower print clarity and durability. Modern printing presses favor repositional paper for high-speed, high-resolution output, enhancing overall print quality and operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Newspaper
Choosing the right paper for your newspaper is crucial for print quality, cost efficiency, and environmental impact. Repositional paper offers superior print clarity and better ink absorption, ideal for high-quality images and sharp text, while newsprint paper is more cost-effective and widely used for mass-distributed newspapers due to its lightweight and recyclable properties. Evaluating factors such as budget, print-run size, and the desired durability will help determine whether repositional or newsprint paper best suits your newspaper production needs.
Infographic: Repositional paper vs Newsprint paper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com