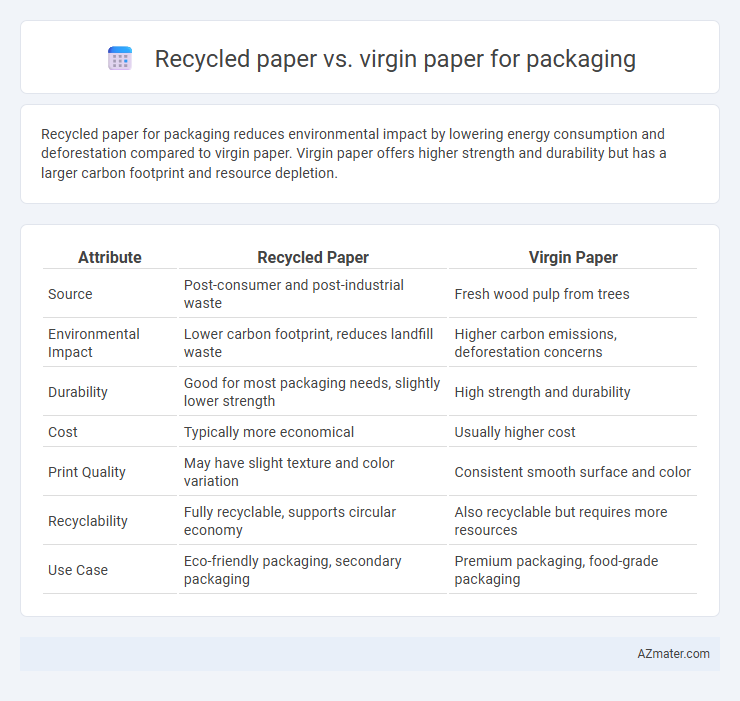
Recycled paper for packaging reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and deforestation compared to virgin paper. Virgin paper offers higher strength and durability but has a larger carbon footprint and resource depletion.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Recycled Paper | Virgin Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Fresh wood pulp from trees |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon emissions, deforestation concerns |
| Durability | Good for most packaging needs, slightly lower strength | High strength and durability |
| Cost | Typically more economical | Usually higher cost |
| Print Quality | May have slight texture and color variation | Consistent smooth surface and color |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable, supports circular economy | Also recyclable but requires more resources |
| Use Case | Eco-friendly packaging, secondary packaging | Premium packaging, food-grade packaging |
Introduction to Paper Packaging: Recycled vs. Virgin
Recycled paper packaging utilizes fibers recovered from used paper products, reducing reliance on fresh wood pulp and minimizing environmental impact through decreased deforestation and lower energy consumption. Virgin paper packaging, made directly from newly harvested wood fibers, typically offers higher strength and durability but involves greater resource extraction and carbon emissions. Choosing between recycled and virgin paper packaging involves balancing sustainability goals with performance requirements and supply chain considerations.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Paper vs. Virgin Paper
Recycled paper significantly reduces deforestation by utilizing post-consumer waste, lowering the demand for virgin wood pulp and preserving natural habitats. It consumes up to 60% less energy and decreases greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 40% compared to virgin paper production. Despite slightly lower durability, recycled paper dramatically mitigates landfill waste and water pollution, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Production Process Differences
Recycled paper for packaging is produced by reprocessing used paper fibers, which involves de-inking, pulping, and refining, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced water usage compared to virgin paper production. Virgin paper manufacturing starts from harvesting wood pulp, requiring chemical treatments to break down lignin and cellulose and yielding stronger, cleaner fibers suitable for high-quality packaging. The production process of recycled paper emits fewer greenhouse gases and reduces deforestation impacts, while virgin paper production demands more intensive resource inputs for fiber extraction and processing.
Resource Consumption and Sustainability
Recycled paper for packaging significantly reduces resource consumption by using 40-70% less water and 60-80% less energy compared to virgin paper, which is derived from newly harvested trees. Sustainability improves as recycled paper limits deforestation, decreases landfill waste, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions associated with paper production. Virgin paper's environmental impact is higher due to intensive logging, water use, and chemical processing, making recycled paper the preferred choice for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Quality and Performance Comparison
Recycled paper for packaging offers comparable durability and strength to virgin paper while providing enhanced environmental benefits through reduced deforestation and lower energy consumption. Virgin paper typically exhibits superior brightness, smoothness, and print quality, making it ideal for premium packaging applications requiring high aesthetic standards. Advances in recycling technology have minimized the quality gap, enabling recycled paper to perform well in barrier properties and structural integrity, although virgin fibers still lead in consistent performance under high-stress conditions.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs. Virgin Paper
Recycled paper for packaging typically costs 10-20% less than virgin paper due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. Virgin paper, made from fresh wood pulp, incurs higher costs linked to extensive resource extraction and processing, impacting overall packaging budgets. Cost analysis favors recycled paper for sustainable packaging solutions, balancing affordability with environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Recycled paper used in packaging must comply with regulatory standards such as ASTM D6868 and EN 13432, ensuring biodegradability and compostability, whereas virgin paper adheres primarily to standards like FSC and PEFC certification for sustainable forest management. Certifications like Blue Angel and Cradle to Cradle validate environmental claims, with recycled paper often demonstrating lower carbon footprints and reduced chemical usage. Regulatory frameworks from the FDA and EU regulate safety for food-contact packaging, requiring both recycled and virgin papers to meet strict migration limits for contaminants and heavy metals.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception favors recycled paper for packaging due to increasing environmental awareness and preference for sustainable products, driving demand in eco-conscious markets. Market trends indicate a significant shift towards recycled paper as brands leverage its lower carbon footprint and resource efficiency to enhance corporate social responsibility profiles. Despite slight concerns over durability compared to virgin paper, advancements in recycling technologies have improved quality, making recycled paper a competitive option in packaging industries.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Option
Recycled paper for packaging often faces challenges related to lower fiber strength and reduced durability compared to virgin paper, limiting its use in heavy-duty or moisture-sensitive applications. Virgin paper provides superior quality and consistency but involves higher environmental costs due to increased deforestation, energy consumption, and water usage. Both options require careful consideration of product protection needs and sustainability goals to determine the optimal packaging solution.
Choosing the Right Paper for Sustainable Packaging
Recycled paper reduces environmental impact by minimizing deforestation and conserving water, making it a preferred choice for sustainable packaging. Virgin paper offers superior strength and durability but comes with higher resource consumption and carbon emissions. Balancing performance requirements with eco-friendly goals helps businesses select the right paper for packaging that supports sustainability and reduces overall waste.
Infographic: Recycled paper vs Virgin paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com