Newsprint is a low-cost, uncoated paper primarily used for printing newspapers due to its high opacity and absorbency, while tissue paper is thinner, softer, and more porous, designed for hygiene and comfort rather than durability. Newspapers printed on newsprint offer clearer text and images, whereas tissue paper lacks the strength and print quality required for mass print media.
Table of Comparison
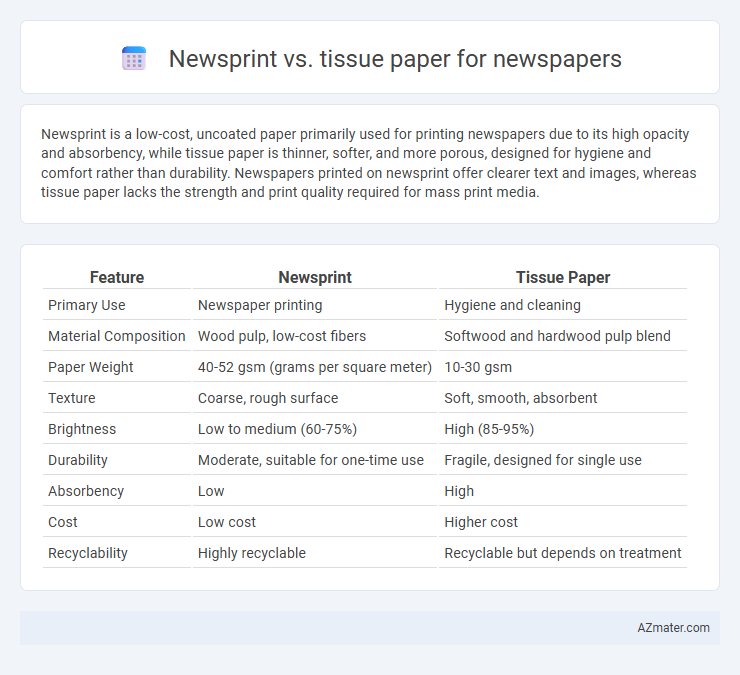
| Feature | Newsprint | Tissue Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Newspaper printing | Hygiene and cleaning |
| Material Composition | Wood pulp, low-cost fibers | Softwood and hardwood pulp blend |
| Paper Weight | 40-52 gsm (grams per square meter) | 10-30 gsm |
| Texture | Coarse, rough surface | Soft, smooth, absorbent |
| Brightness | Low to medium (60-75%) | High (85-95%) |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for one-time use | Fragile, designed for single use |
| Absorbency | Low | High |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Recyclable but depends on treatment |
Introduction to Newsprint and Tissue Paper
Newsprint is a low-cost, lightweight paper primarily used for printing newspapers due to its high opacity and quick ink absorption qualities. Tissue paper, on the other hand, is a thin, soft paper designed for hygienic purposes such as facial tissues and toilet paper, emphasizing absorption and softness rather than printability. While newsprint prioritizes durability and cost-effectiveness for mass circulation, tissue paper focuses on softness and flexibility for personal use.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Newsprint primarily consists of mechanical pulp with high lignin content, resulting in lower brightness and durability, while tissue paper is made from chemical pulp with refined fibers for softness and strength. Newsprint manufacturing involves high-speed rotary printing processes on large rolls using lower-cost pulps, whereas tissue production includes creping and embossing steps to create absorbency and texture suitable for hygiene products. The differing fiber treatments and additives in each process tailor the papers for print quality in newspapers versus softness and absorbency in tissue paper.
Cost Comparison Analysis
Newsprint generally offers a lower cost per ton compared to tissue paper, making it the preferred choice for mass newspaper production due to its affordability and lower raw material expenses. Tissue paper, while providing a softer texture, incurs higher costs stemming from its refined production processes and superior fiber quality. Cost comparison analysis reveals that newsprint can reduce overall printing expenses by up to 40%, making it a more economical option for large-scale newspaper printing.
Print Quality and Readability
Newsprint offers high opacity and smooth surface suitable for detailed text and images, enhancing print quality in newspaper production. Tissue paper, being thinner and more absorbent, tends to blur ink and reduce sharpness, negatively impacting readability. Optimal newspaper printing relies on newsprint's balanced weight and texture to ensure crisp text and clear visuals for reader comfort.
Durability and Longevity
Newsprint is engineered for durability and longevity, providing a strong, flexible surface that withstands frequent handling and maintains print clarity over time. In contrast, tissue paper for newspapers offers limited durability due to its thin, lightweight construction, resulting in easy tearing and faster degradation. Newsprint's composition enhances its resistance to wear and environmental factors, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting newspaper print quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Newsprint, primarily made from virgin wood pulp, consumes substantial natural resources and generates higher carbon emissions during production compared to tissue paper, which often incorporates recycled fibers and requires less energy. Tissue paper's use of post-consumer recycled content reduces deforestation and waste, promoting a more sustainable lifecycle for newspaper production. Evaluating environmental impact shows tissue paper as a preferable option for newspapers aiming to minimize ecological footprints through improved resource efficiency and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
User Experience and Handling
Newsprint offers a smooth surface and better ink absorption for clear, sharp text and images, enhancing readability and user engagement. Tissue paper, being thinner and more delicate, can lead to tearing and smudging, negatively impacting handling and overall user experience. Newspapers printed on newsprint maintain durability during handling, folding, and storage, ensuring convenience for daily readers.
Popularity and Industry Preferences
Newsprint remains the dominant choice for newspapers due to its cost-effectiveness and suitability for high-volume printing, while tissue paper is rarely used given its delicate texture and higher price point. Industry preferences heavily favor newsprint for its opacity and ability to hold ink well, ensuring clear text and images. Despite the rise of digital media, publishers prioritize newsprint for physical distribution because of its established supply chains and recyclability.
Innovations in Newspaper Paper Materials
Innovations in newspaper paper materials have focused on balancing print quality and environmental impact, with newsprint traditionally made from recycled wood pulp offering affordability and good opacity. Tissue paper, though less common, is being explored for specialty newspapers due to its softness and biodegradability, enhancing sustainability efforts. Advances in biodegradable coatings and recycled fiber content in both newsprint and tissue paper aim to reduce carbon footprints while maintaining durability for readers.
Future Trends in Newspaper Production
Advancements in sustainable materials are driving a shift from traditional newsprint to eco-friendly tissue paper alternatives in newspaper production. Innovations in biodegradable and recyclable tissue papers enhance print quality while reducing environmental impact, aligning with growing consumer demand for green products. Future trends emphasize lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials that support circular economy principles in the publishing industry.
Infographic: Newsprint vs Tissue paper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com