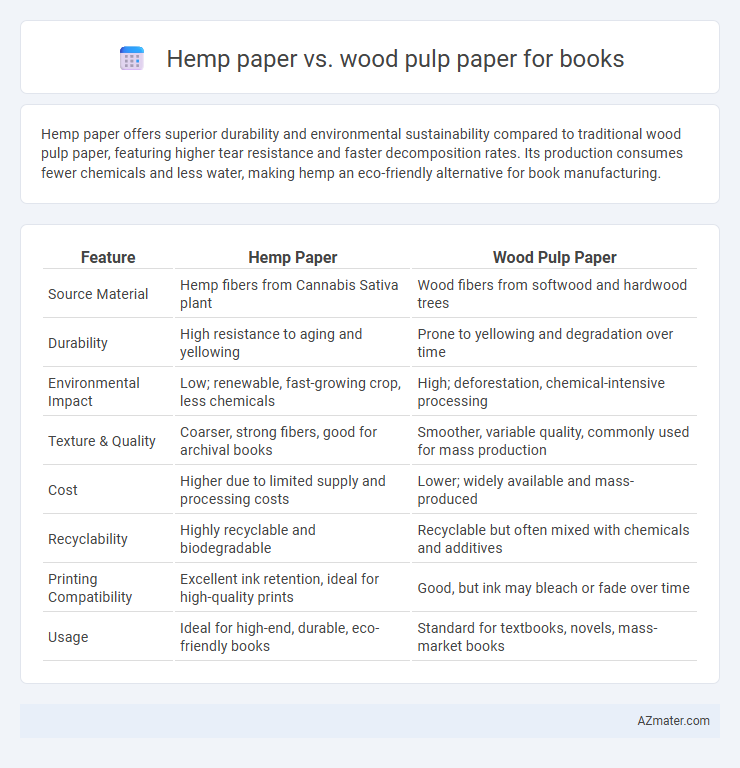
Hemp paper offers superior durability and environmental sustainability compared to traditional wood pulp paper, featuring higher tear resistance and faster decomposition rates. Its production consumes fewer chemicals and less water, making hemp an eco-friendly alternative for book manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Wood Pulp Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Hemp fibers from Cannabis Sativa plant | Wood fibers from softwood and hardwood trees |
| Durability | High resistance to aging and yellowing | Prone to yellowing and degradation over time |
| Environmental Impact | Low; renewable, fast-growing crop, less chemicals | High; deforestation, chemical-intensive processing |
| Texture & Quality | Coarser, strong fibers, good for archival books | Smoother, variable quality, commonly used for mass production |
| Cost | Higher due to limited supply and processing costs | Lower; widely available and mass-produced |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable and biodegradable | Recyclable but often mixed with chemicals and additives |
| Printing Compatibility | Excellent ink retention, ideal for high-quality prints | Good, but ink may bleach or fade over time |
| Usage | Ideal for high-end, durable, eco-friendly books | Standard for textbooks, novels, mass-market books |
Introduction: Understanding Paper Sources
Hemp paper, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers higher durability and sustainability compared to traditional wood pulp paper made from tree fibers. Hemp fibers are longer and stronger, resulting in paper with superior tensile strength and resistance to yellowing, ideal for archival-quality books. Wood pulp paper production relies heavily on deforestation and chemical processing, whereas hemp paper supports eco-friendly practices with faster crop regeneration and reduced environmental impact.
Overview of Hemp Paper
Hemp paper, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp paper with a higher cellulose content and faster growth cycle, enabling more efficient production. It exhibits superior durability, resistance to yellowing, and longer lifespan, making it ideal for archival-quality book printing. Unlike wood pulp paper, hemp paper requires fewer chemicals during processing, reducing environmental impact and enhancing recyclability.
Overview of Wood Pulp Paper
Wood pulp paper, derived from the cellulose fibers of softwood and hardwood trees, remains the dominant material in book publishing due to its availability and cost-effectiveness. This type of paper often undergoes chemical treatments and bleaching processes, which can impact its acidity and longevity, making it prone to yellowing and brittleness over time. Advances in pulping technology aim to improve durability and environmental sustainability, yet wood pulp paper still presents challenges related to deforestation and resource consumption.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp paper production generates significantly less pollution and requires up to 50% less water compared to wood pulp paper, drastically reducing its ecological footprint. Unlike wood pulp, hemp grows rapidly and can be harvested annually without deforestation, promoting sustainable land use and preserving biodiversity. Additionally, hemp fibers break down more easily during recycling, lowering energy consumption and minimizing chemical waste in paper manufacturing processes.
Raw Material Sustainability
Hemp paper offers superior raw material sustainability compared to wood pulp paper due to hemp's rapid growth cycle, regenerating within four months versus decades for trees used in wood pulp. Hemp cultivation requires fewer pesticides and less water, reducing environmental impact and promoting soil health. Additionally, hemp's higher cellulose content results in stronger fibers, enabling more efficient paper production with less resource depletion.
Production Process Differences
Hemp paper production involves harvesting hemp stalks, retting to break down fibers, and mechanical or chemical pulping to separate fibers, resulting in a durable, long-fiber pulp. Wood pulp paper production uses timber logging, debarking, chipping, and chemical pulping methods like Kraft or sulfite to obtain shorter fibers prone to degradation. The hemp process yields stronger, more sustainable fibers with fewer chemicals, while wood pulp production is energy-intensive and relies heavily on chemical treatments.
Paper Quality: Durability and Appearance
Hemp paper offers superior durability compared to wood pulp paper due to its longer fibers, which result in stronger, more tear-resistant pages that withstand aging and handling better. The appearance of hemp paper is often smoother and less prone to yellowing, maintaining a fresh look over time, while wood pulp paper tends to degrade faster and develop brittleness. These qualities make hemp paper an ideal choice for high-quality books requiring longevity and a pristine aesthetic.
Cost Analysis: Hemp vs. Wood Pulp Paper
Hemp paper production involves higher initial costs due to specialized processing equipment and limited supply chains, making it more expensive than conventional wood pulp paper. Wood pulp paper benefits from established infrastructure and economies of scale, resulting in lower production and retail costs for books. Despite higher upfront expenses, hemp paper's durability and sustainability position it as a cost-effective alternative over the long term.
Printing and Publishing Considerations
Hemp paper offers superior durability and resistance to yellowing compared to wood pulp paper, making it ideal for archival-quality books in printing and publishing. Its higher lignin content reduces the need for harsh chemical treatments during manufacturing, resulting in more environmentally friendly ink absorption and clearer print quality. Wood pulp paper, while more affordable and widely available, often requires significant bleaching and chemical processing that can affect print longevity and overall book durability.
Conclusion: Future of Book Publishing
Hemp paper offers superior durability, faster growth cycles, and environmental benefits compared to traditional wood pulp paper, making it a sustainable alternative for the future of book publishing. As demand for eco-friendly materials rises, publishers are increasingly adopting hemp paper to reduce deforestation and carbon footprints. The integration of hemp paper in book production signals a significant shift towards greener, more sustainable publishing practices.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Wood pulp paper for Book
 azmater.com
azmater.com