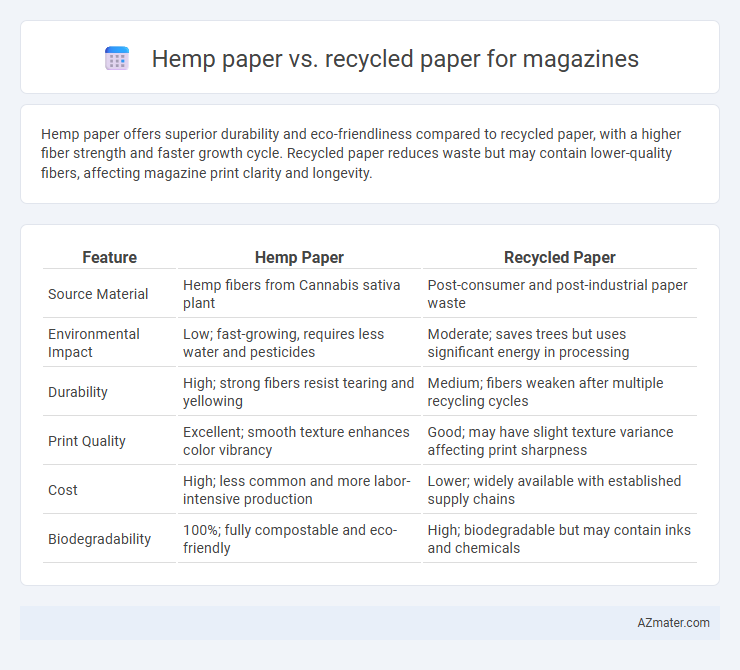
Hemp paper offers superior durability and eco-friendliness compared to recycled paper, with a higher fiber strength and faster growth cycle. Recycled paper reduces waste but may contain lower-quality fibers, affecting magazine print clarity and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Hemp fibers from Cannabis sativa plant | Post-consumer and post-industrial paper waste |
| Environmental Impact | Low; fast-growing, requires less water and pesticides | Moderate; saves trees but uses significant energy in processing |
| Durability | High; strong fibers resist tearing and yellowing | Medium; fibers weaken after multiple recycling cycles |
| Print Quality | Excellent; smooth texture enhances color vibrancy | Good; may have slight texture variance affecting print sharpness |
| Cost | High; less common and more labor-intensive production | Lower; widely available with established supply chains |
| Biodegradability | 100%; fully compostable and eco-friendly | High; biodegradable but may contain inks and chemicals |
Introduction: The Search for Sustainable Magazine Paper
Hemp paper offers a renewable and fast-growing fiber source that significantly reduces deforestation compared to traditional wood-pulp recycled paper. Its higher cellulose content ensures greater durability and a smoother printing surface, ideal for high-quality magazine production. Choosing hemp paper over recycled alternatives supports eco-friendly practices with lower environmental footprints and less chemical processing.
What Is Hemp Paper?
Hemp paper is a sustainable alternative made from the fibers of the hemp plant, known for its strength and durability compared to traditional wood pulp paper. It requires less water and fewer chemicals during production, resulting in a smaller environmental footprint. Hemp paper features high tear resistance and longer lifespan, making it ideal for eco-friendly magazine printing.
What Is Recycled Paper?
Recycled paper is produced from recovered paper fibers that have been processed and reformed to create new sheets, reducing the need for virgin pulp and minimizing environmental impact. It often contains a blend of post-consumer and post-industrial waste, making it an eco-friendly choice that conserves natural resources and energy. Compared to hemp paper, recycled paper typically has a lower fiber strength and durability, which can affect the longevity and print quality for magazine production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp paper significantly reduces environmental impact compared to recycled paper for magazines due to its faster growth cycle, requiring only 3-4 months versus decades for trees used in recycled paper production. Hemp's high cellulose content allows for fewer chemical processes and less water consumption, decreasing pollution and energy usage. While recycled paper saves trees and landfill space, hemp paper's biodegradability and lower carbon footprint make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious publishing.
Production Process: Hemp vs Recycled Paper
Hemp paper production involves harvesting the hemp plant, retting the fibers, and mechanically separating them to create a durable pulp with minimal chemical use, resulting in a sustainable and eco-friendly option. Recycled paper production relies on collecting used paper, de-inking, and breaking it down into pulp, though this process can degrade fiber quality and often requires more chemical treatments. Hemp fibers provide a longer-lasting, higher-quality pulp that supports magazine printing better than the shorter fibers found in recycled paper.
Print Quality and Visual Appeal
Hemp paper offers superior print quality for magazines due to its stronger fibers, resulting in sharper images and vibrant colors that enhance visual appeal. Recycled paper often contains shorter fibers, which can lead to a rougher texture and less precise print results, potentially diminishing image clarity. For high-end magazine production, hemp paper's durability and smooth surface provide a premium finish that elevates reader experience.
Durability and Longevity
Hemp paper offers superior durability compared to recycled paper due to its longer cellulose fibers, which result in stronger and more tear-resistant pages ideal for magazine use. The natural resistance of hemp fibers to yellowing and degradation ensures magazines maintain their quality and readability over extended periods. Recycled paper, while eco-friendly, tends to have shorter fibers that weaken the structure, causing faster wear and reduced lifespan in high-traffic reading materials.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp paper typically costs 20-30% more than recycled paper due to higher raw material processing expenses and limited large-scale production facilities. Recycled paper enjoys widespread market availability with numerous suppliers, making it a more accessible and budget-friendly option for magazine printing. The limited hemp cultivation and processing infrastructure restrict its supply, keeping hemp paper niches primarily in sustainable and premium sectors.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Option
Hemp paper for magazines faces challenges such as higher production costs and limited large-scale manufacturing infrastructure compared to traditional paper, impacting its widespread adoption. Recycled paper often suffers from lower durability and print quality due to fiber degradation, which can compromise the vibrant visuals required in magazine printing. Both options pose environmental trade-offs, with hemp requiring significant agricultural resources and recycled paper relying on energy-intensive deinking processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Paper for Magazines
Hemp paper offers superior durability, resistance to yellowing, and environmental benefits due to its rapid renewability and lower chemical processing compared to recycled paper. Recycled paper remains a cost-effective choice with a reduced carbon footprint by repurposing existing materials, but it often compromises on texture and longevity important for magazine quality. Selecting the best paper for magazines depends on balancing sustainability priorities, budget constraints, and desired print quality for optimal reader experience.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Recycled paper for Magazine
 azmater.com
azmater.com