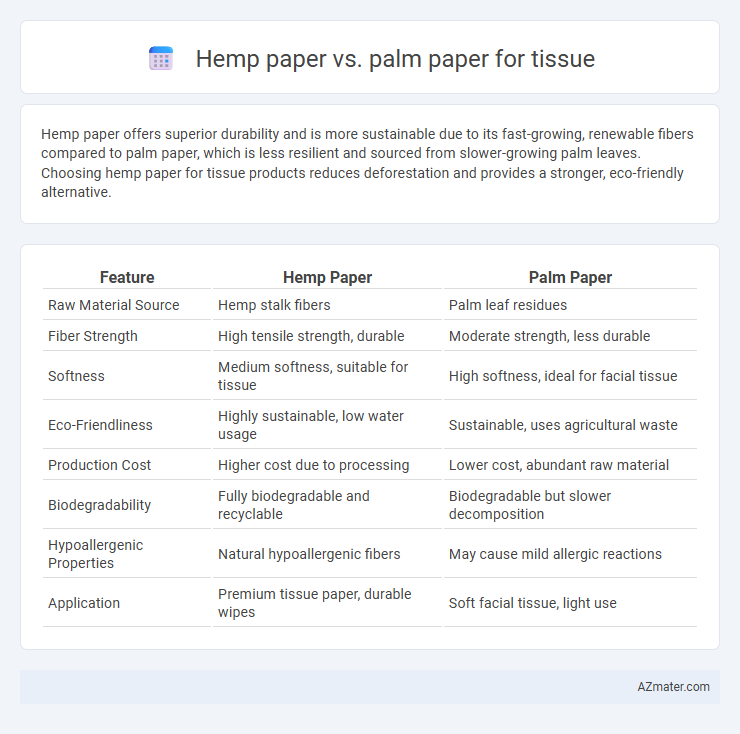
Hemp paper offers superior durability and is more sustainable due to its fast-growing, renewable fibers compared to palm paper, which is less resilient and sourced from slower-growing palm leaves. Choosing hemp paper for tissue products reduces deforestation and provides a stronger, eco-friendly alternative.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Palm Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | Hemp stalk fibers | Palm leaf residues |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Softness | Medium softness, suitable for tissue | High softness, ideal for facial tissue |
| Eco-Friendliness | Highly sustainable, low water usage | Sustainable, uses agricultural waste |
| Production Cost | Higher cost due to processing | Lower cost, abundant raw material |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable and recyclable | Biodegradable but slower decomposition |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Natural hypoallergenic fibers | May cause mild allergic reactions |
| Application | Premium tissue paper, durable wipes | Soft facial tissue, light use |
Introduction to Hemp Paper and Palm Paper
Hemp paper, derived from the fibrous stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers superior durability and sustainability compared to traditional tree-based papers. Palm paper, made from the fibrous material of palm leaves or trunks, is valued for its biodegradability and renewable resource status in tropical regions. Both hemp and palm paper present eco-friendly alternatives for tissue products, with hemp paper excelling in strength and longevity, while palm paper provides a renewable, fast-growing raw material option.
Environmental Impact of Hemp vs Palm in Tissue Production
Hemp paper production significantly reduces deforestation compared to palm paper, as hemp grows rapidly and requires fewer pesticides and less water than palm plantations. The cultivation of hemp enhances soil health through phytoremediation and carbon sequestration, while palm oil plantations often contribute to habitat destruction and biodiversity loss. Lifecycle assessments reveal hemp tissue generates lower greenhouse gas emissions and waste, offering a more sustainable alternative to palm-based tissue products.
Raw Material Availability and Sustainability
Hemp paper for tissue is derived from hemp fibers, which grow rapidly and require fewer pesticides, offering a highly renewable raw material compared to palm paper made from palm leaves or fibers harvested from palm trees, often linked to deforestation concerns. The global availability of hemp as a raw material supports sustainable production due to its low water usage and ability to regenerate soil health, whereas palm paper raw material availability fluctuates with palm oil industry demands, impacting biodiversity and contributing to habitat loss. Choosing hemp paper enhances sustainability by reducing reliance on palm plantations, promoting environmental balance and resource efficiency in tissue manufacturing.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Hemp paper manufacturing involves longer fiber retention and fewer chemical treatments, resulting in a more sustainable and durable tissue product compared to palm paper, which relies heavily on pulping palm leaves with intensive chemical processing. The hemp pulping process uses mechanical and chemical methods that preserve fiber length and strength, enhancing softness and absorbency in tissues. In contrast, palm paper production requires more bleaching and refining steps due to shorter, lignin-rich fibers, leading to increased energy consumption and lower overall environmental efficiency.
Biodegradability and Compostability of Hemp and Palm Tissue
Hemp paper tissue demonstrates superior biodegradability and compostability compared to palm paper tissue due to its natural fiber structure and minimal chemical processing. Hemp fibers break down rapidly in composting environments, enriching soil without leaving harmful residues, whereas palm paper often contains additives that slow decomposition. The high lignin content in palm tissues can hinder biodegradability, making hemp tissue a more sustainable option for eco-friendly tissue products.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Viability
Hemp paper offers greater cost efficiency for tissue production due to its higher yield per acre and faster growth cycle compared to palm paper, reducing raw material expenses. Palm paper relies heavily on palm oil by-products, which are subject to market volatility and higher processing costs, impacting overall economic viability. Integrating hemp paper into tissue manufacturing can lower production costs and provide a more sustainable, economically feasible alternative amidst fluctuating palm product prices.
Durability and Softness: Which Paper Performs Better?
Hemp paper offers superior durability due to its long fibers, making it more resistant to tearing compared to palm paper, which has shorter fibers and tends to be less strong. In terms of softness, palm paper often feels gentler on the skin, providing a smoother texture ideal for sensitive tissue applications. Balancing these factors, hemp paper is preferred for lasting durability, while palm paper excels in delivering a softer touch for comfort.
Chemical Use and Allergens in Tissue Papers
Hemp paper for tissue production involves minimal chemical processing due to its natural resistance to pests and diseases, resulting in fewer bleaching agents and additives compared to palm paper. Palm paper often requires more intensive chemical treatments to break down lignin and remove natural oils, increasing the risk of residual allergens and irritants in the final tissue product. Selecting hemp-based tissue paper reduces exposure to harsh chemicals and potential allergens, offering a safer option for sensitive skin and environmentally conscious consumers.
Market Adoption and Consumer Preferences
Hemp paper demonstrates higher durability and eco-friendliness, driving increased market adoption in sustainable tissue segments, particularly in North America and Europe. Palm paper, derived from abundant palm fibers, appeals to cost-conscious consumers in Southeast Asia due to its affordability and local availability. Consumer preferences increasingly favor hemp paper for its biodegradability and reduced environmental impact, despite palm paper maintaining strong regional demand linked to price sensitivity.
Future Prospects for Hemp and Palm Tissue Papers
Hemp paper offers superior durability, biodegradability, and a faster growth cycle compared to palm paper, making it a promising sustainable alternative for tissue production. Palm tissue paper, while abundant in regions with large palm plantations, faces environmental concerns due to deforestation and habitat loss, potentially limiting its long-term viability. Advances in hemp cultivation technology and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products signal a strong future growth trajectory for hemp-based tissues in global markets.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Palm paper for Tissue
 azmater.com
azmater.com