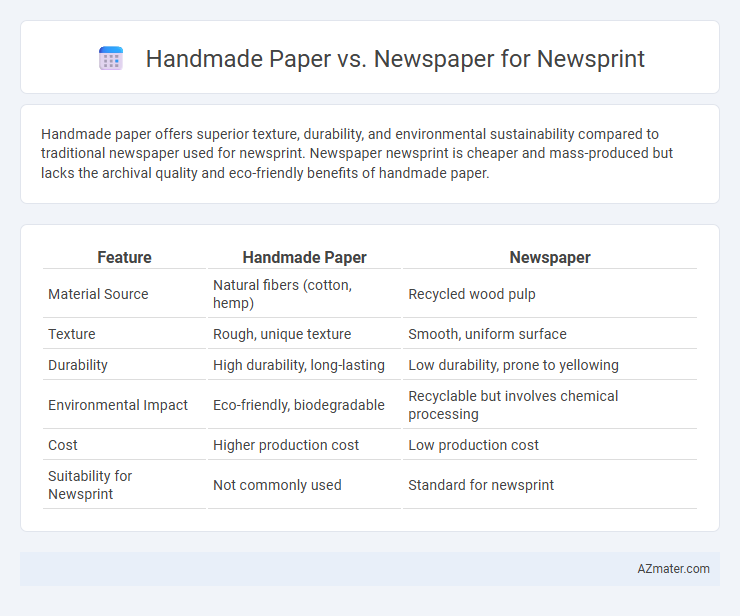
Handmade paper offers superior texture, durability, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional newspaper used for newsprint. Newspaper newsprint is cheaper and mass-produced but lacks the archival quality and eco-friendly benefits of handmade paper.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Handmade Paper | Newspaper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural fibers (cotton, hemp) | Recycled wood pulp |
| Texture | Rough, unique texture | Smooth, uniform surface |
| Durability | High durability, long-lasting | Low durability, prone to yellowing |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Recyclable but involves chemical processing |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Low production cost |
| Suitability for Newsprint | Not commonly used | Standard for newsprint |
Introduction to Newsprint Materials
Newsprint traditionally relies on wood pulp for mass production, offering cost-efficiency and high printability for newspapers. Handmade paper, made from natural fibers like cotton or recycled materials, provides superior texture and durability but remains impractical for large-scale newsprint due to limited production capacity. Understanding these material differences highlights the trade-off between economic scalability and artisanal quality in newsprint manufacturing.
Overview of Handmade Paper
Handmade paper offers a unique texture and durability compared to traditional newspaper newsprint, making it ideal for artisanal and archival purposes. This type of paper is crafted from natural fibers through manual processes, resulting in a thicker, more absorbent surface that enhances ink retention and visual appeal. Unlike mass-produced newsprint made from wood pulp, handmade paper emphasizes eco-friendliness and craftsmanship, often used for limited edition publications or artistic prints.
Characteristics of Newspaper Paper
Newspaper paper is typically made from low-cost, wood pulp-based newsprint designed for high-speed printing and mass distribution, featuring a lightweight, porous, and low-opacity structure that absorbs ink quickly but may smudge. Its rough texture and lower durability compared to handmade paper result in easy yellowing and brittleness over time, optimized for single-use readability rather than longevity. Compared to handmade paper, newspaper paper's mass production emphasizes cost efficiency and rapid degradation, serving the specific demands of daily newsprint circulation.
Production Process: Handmade vs Newspaper Paper
Handmade paper is produced using traditional methods involving manual pulping, sheet formation, and drying, resulting in unique texture and thickness variations. Newspaper paper is manufactured through large-scale industrial processes involving wood pulp, chemical treatments, and high-speed machines producing uniform, lightweight sheets optimized for fast printing and cost-efficiency. The production process differences significantly impact the durability, feel, and environmental footprint of the final newsprint.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Handmade paper offers a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to traditional newspaper newsprint, as it uses recycled fibers and minimal chemicals during production, reducing deforestation and pollution. Newspaper newsprint relies heavily on wood pulp, contributing to extensive tree harvesting, higher energy consumption, and substantial wastewater discharge. Choosing handmade paper supports sustainability by promoting biodegradable materials and conserving natural resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative for newsprint applications.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Handmade paper for newsprint incurs higher production costs due to labor-intensive processes and limited scalability, making it less economically viable for mass circulation compared to newspaper-grade paper. Newspaper paper leverages automated manufacturing and recycled fibers, significantly reducing material and operational expenses, thus optimizing cost-efficiency for large-scale printing. Economic considerations favor newspaper paper's affordability and availability, crucial for sustaining high-volume newsprint demand in commercial publishing.
Print Quality and Readability
Handmade paper offers superior print quality for newsprint due to its textured surface and high absorbency, which enhances ink retention and sharpness of images. Newspaper paper, typically made from recycled wood pulp, provides a smoother yet less durable surface, often resulting in faster ink bleed and lower readability under bright lighting. The choice between handmade paper and newspaper hinges on balancing artisanal print clarity against mass-produced cost-efficiency for newsprint distribution.
Durability and Longevity
Handmade paper offers superior durability and longevity compared to newspaper newsprint, as its fibers are longer and less chemically treated, resulting in greater resistance to tearing and yellowing over time. Newspaper newsprint is typically made from low-quality wood pulp with high lignin content, causing it to become brittle and degrade quickly when exposed to light and air. For archival purposes, handmade paper is preferred due to its enhanced strength and ability to maintain structural integrity for decades.
Accessibility and Sustainability
Handmade paper offers enhanced sustainability through biodegradable fibers and eco-friendly production methods, contrasting with the mass-produced, chemically treated newspaper rolls. Accessibility of newspaper as a daily news source is unmatched due to its widespread distribution and low cost, while handmade paper remains more niche and less commercially accessible. The environmental footprint of handmade paper is lower, supporting sustainable forestry and reduced chemical pollution compared to traditional newsprint manufacturing.
Future Trends in Newsprint Choices
Handmade paper in newsprint is gaining attention for its sustainability and unique texture, appealing to eco-conscious publishers aiming to reduce environmental impact. Newspaper newsprint continues to dominate due to cost-effectiveness and high availability, but innovations in recycled fibers and biodegradable coatings are shaping its future. Emerging trends indicate a hybrid approach where recycled newspaper stocks integrate with handmade fibers, promoting durability and eco-friendliness while maintaining affordability in newsprint production.
Infographic: Handmade paper vs Newspaper for Newsprint
 azmater.com
azmater.com