Handmade paper offers a textured, eco-friendly alternative with natural fibers, enhancing document aesthetics and sustainability. Copy paper provides smooth, uniform surfaces ideal for precise printing and high-speed copying.
Table of Comparison
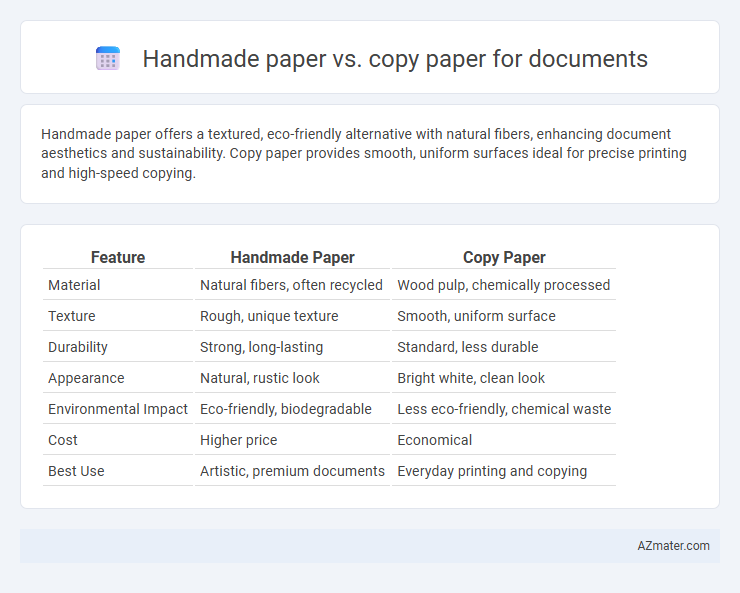
| Feature | Handmade Paper | Copy Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural fibers, often recycled | Wood pulp, chemically processed |
| Texture | Rough, unique texture | Smooth, uniform surface |
| Durability | Strong, long-lasting | Standard, less durable |
| Appearance | Natural, rustic look | Bright white, clean look |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Less eco-friendly, chemical waste |
| Cost | Higher price | Economical |
| Best Use | Artistic, premium documents | Everyday printing and copying |
What is Handmade Paper?
Handmade paper is a traditional form of paper produced by manually pressing pulp from fibers such as cotton, linen, or recycled materials, resulting in a textured and durable surface ideal for artistic and archival documents. It offers superior strength and unique aesthetic qualities compared to mass-produced copy paper, making it preferred for special presentations and official certificates. The environmental impact is also lower with handmade paper due to its natural fibers and production methods without chemical additives.
What is Copy Paper?
Copy paper is a type of lightweight, smooth paper specifically designed for use in printers, copiers, and fax machines, optimized for consistent ink absorption and minimal smudging. Typically made from wood pulp, it offers high brightness and uniform texture, ensuring clear text reproduction and reliable feed through office equipment. Unlike handmade paper, copy paper prioritizes functionality and efficiency, making it the standard choice for everyday document printing and copying tasks.
Differences in Production Process
Handmade paper is produced through a labor-intensive process involving natural fibers, water, and manual sheet formation using a mould and deckle, resulting in textured, unique sheets with irregular edges. Copy paper, by contrast, is mass-produced using wood pulp in highly automated machines, ensuring uniform thickness, smooth surface, and consistent weight optimized for printer compatibility and ink absorption. The handmade process emphasizes craftsmanship and sustainability, while the industrial method prioritizes efficiency, standardization, and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Handmade paper is produced using traditional methods that rely on recycled fibers and natural processes, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced chemical use compared to mass-produced copy paper. Copy paper manufacturing typically involves bleaching, chemicals, and significant water and energy resources, leading to higher environmental pollution and carbon emissions. Choosing handmade paper supports sustainable practices by minimizing waste and conserving natural resources, making it a more eco-friendly option for document use.
Texture and Appearance Contrasts
Handmade paper features a rough, fibrous texture with natural irregularities and subtle color variations, giving documents a unique, artisanal appearance that enhances tactile appeal. Copy paper, in contrast, has a smooth, uniform surface designed for consistent ink absorption, resulting in clean, sharp text and images ideal for professional and everyday printing. The distinct texture and visual character of handmade paper make it suitable for artistic or specialty documents, while copy paper prioritizes functionality and clarity in mass printing.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Handmade paper exhibits superior durability and strength compared to standard copy paper, owing to its longer natural fibers and traditional crafting methods that enhance fiber bonding. The density and texture of handmade paper resist tearing and wear, making it ideal for archival documents and artistic prints requiring longevity. In contrast, copy paper, produced from shorter wood pulp fibers, tends to be more prone to tearing and degradation over time under frequent handling.
Printability and Ink Absorption
Handmade paper exhibits superior ink absorption due to its fibrous texture, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting prints with minimal smudging. Copy paper, designed for high-speed printers, offers smooth surfaces for consistent ink distribution but may cause ink to sit on top, leading to slower drying times and potential smearing. The choice between handmade and copy paper significantly impacts print clarity and durability, with handmade paper favored for artistic and archival documents, while copy paper suits everyday printing needs.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Handmade paper is typically more expensive than copy paper due to labor-intensive production and limited availability, making it less accessible for everyday document use. Copy paper is mass-produced, widely available, and cost-effective, ideal for high-volume printing and standard office tasks. Choosing between the two depends largely on budget constraints and the need for unique texture versus practicality in document handling.
Best Uses for Handmade Paper
Handmade paper is ideal for special documents, certificates, art prints, and high-end invitations due to its unique texture, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Its natural fibers and eco-friendly production process make it a sustainable choice for archival-quality records and premium stationary. In contrast, copy paper suits everyday printing and mass document reproduction, lacking the tactile richness and longevity of handmade paper.
Ideal Applications for Copy Paper
Copy paper is designed for high-volume printing and copying, providing smooth, consistent texture ideal for laser and inkjet printers. It performs best in everyday office documents, reports, and memos where clarity and quick drying are essential. Unlike handmade paper, copy paper ensures efficient feed through machines, reducing jams and maintaining sharp text quality.
Infographic: Handmade paper vs Copy paper for Document
 azmater.com
azmater.com