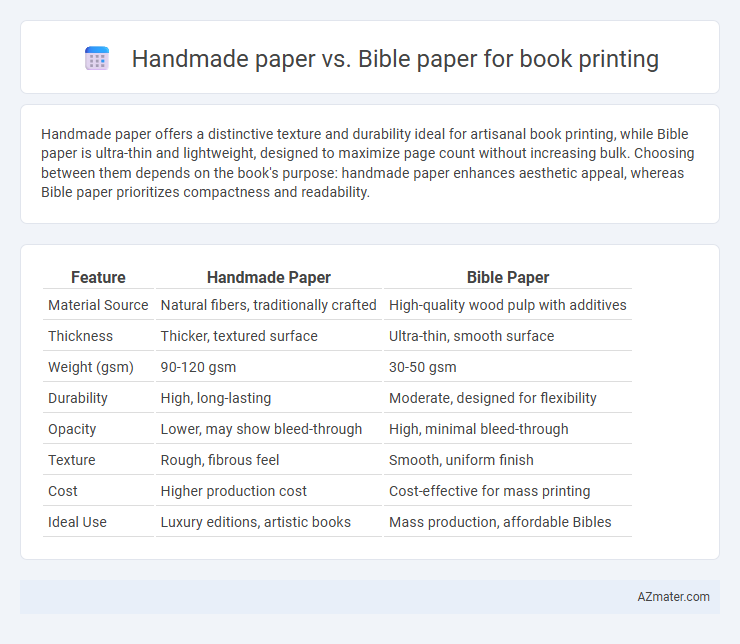
Handmade paper offers a distinctive texture and durability ideal for artisanal book printing, while Bible paper is ultra-thin and lightweight, designed to maximize page count without increasing bulk. Choosing between them depends on the book's purpose: handmade paper enhances aesthetic appeal, whereas Bible paper prioritizes compactness and readability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Handmade Paper | Bible Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural fibers, traditionally crafted | High-quality wood pulp with additives |
| Thickness | Thicker, textured surface | Ultra-thin, smooth surface |
| Weight (gsm) | 90-120 gsm | 30-50 gsm |
| Durability | High, long-lasting | Moderate, designed for flexibility |
| Opacity | Lower, may show bleed-through | High, minimal bleed-through |
| Texture | Rough, fibrous feel | Smooth, uniform finish |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Cost-effective for mass printing |
| Ideal Use | Luxury editions, artistic books | Mass production, affordable Bibles |
Introduction to Handmade Paper and Bible Paper
Handmade paper is crafted using traditional methods involving natural fibers like cotton, hemp, or flax, resulting in a textured, durable, and eco-friendly material ideal for artisanal book printing. Bible paper, also known as India paper, is a thin, opaque, and lightweight material engineered to maximize readability and durability while minimizing bulk, commonly used in printing Bibles and other compact books. Each paper type offers distinct qualities: handmade paper emphasizes aesthetic uniqueness and environmental sustainability, whereas Bible paper focuses on practicality and text density for lightweight volumes.
History and Origins of Book Printing Papers
Handmade paper, originating from ancient China around 105 AD, was the primary medium for early manuscripts and contributed to the spread of knowledge through tactile, fibrous textures. Bible paper, developed in the 19th century during the industrial revolution, offered a thinner, lighter alternative using wood pulp and advanced manufacturing techniques to accommodate the production of compact, portable books. The evolution from handmade to Bible paper reflects technological advancements driven by the demand for cost-effective, durable, and mass-produced printed materials.
Material Composition: Handmade vs. Bible Paper
Handmade paper is crafted from natural fibers like cotton or linen, resulting in a thicker, more textured, and durable material, while Bible paper is made primarily from wood pulp combined with cotton or linen rag, designed for thinness and opacity to accommodate high page counts. The distinct fiber composition in handmade paper enhances its strength and aesthetic appeal, whereas Bible paper utilizes chemically treated wood pulp to maintain lightweight, flexible qualities without sacrificing readability. This difference in material composition directly influences the tactile experience, longevity, and printing suitability of books produced with each type.
Texture and Aesthetic Appeal Comparison
Handmade paper offers a distinctive texture characterized by irregular fibers and a tactile, artisanal feel that enhances the aesthetic appeal of premium or artistic book editions. Bible paper, also known as India paper, is ultra-thin with a smooth, lightweight texture designed for high-density text printing, providing durability and minimal bulk in religious or reference books. While handmade paper emphasizes uniqueness and visual richness, Bible paper prioritizes functionality and readability without compromising elegance.
Durability and Longevity in Book Printing
Handmade paper offers exceptional durability due to its thick fibers and natural pulp, making it ideal for preserving books over long periods with minimal wear. Bible paper, characterized by its thin, lightweight composition, prioritizes compactness but can be more prone to tearing and yellowing over time under frequent use. For book printing demanding longevity, handmade paper ensures greater resilience and aging resistance compared to the delicate, economy-driven qualities of Bible paper.
Print Quality: Ink Absorption and Clarity
Handmade paper offers superior ink absorption due to its fibrous texture, resulting in rich, vivid print clarity ideal for artistic or specialty books. Bible paper, designed to be thin yet opaque, provides consistent ink hold with minimal bleed-through, ensuring sharp text and fine detail in high-volume book printing. The choice between handmade and Bible paper significantly impacts print quality, balancing texture and precision for the intended reading experience.
Weight, Thickness, and Handling Differences
Handmade paper typically weighs between 80 to 120 gsm and has a thickness ranging from 0.1 to 0.3 mm, offering a textured, thicker feel that enhances durability and a premium tactile experience. Bible paper, often used for printing large volumes of text, usually weighs around 35 to 50 gsm with a thickness of approximately 0.05 to 0.07 mm, making it extremely thin and lightweight to reduce bulk and improve handling in compact books. Handling differences show that handmade paper provides a more rigid and substantial grip, while Bible paper is delicate and requires careful handling to avoid tearing due to its thinness and light weight.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Handmade paper in book printing offers exceptional sustainability due to its use of recycled fibers and minimal chemical processing, significantly reducing environmental harm compared to conventional options. Bible paper, typically a thin, high-opacity wood pulp paper, demands intensive resource use and chemical bleaching, contributing to deforestation and high energy consumption. Opting for handmade paper supports eco-friendly practices by promoting biodiversity conservation and lowering carbon footprint throughout the book production lifecycle.
Cost and Accessibility for Publishers
Handmade paper is significantly more expensive than Bible paper due to its labor-intensive production process, making it less accessible for most publishers aiming for cost-efficiency. Bible paper, designed for lightweight and high opacity, offers an economical choice that balances print quality and affordability, ideal for high-volume runs. This cost and accessibility contrast influences publishers' material selection, especially when budget constraints and scalability are critical factors.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Paper Type
Handmade paper is ideal for limited edition books, art prints, and high-end journals due to its unique texture, durability, and aesthetic appeal that enhance the tactile reading experience. Bible paper excels in mass-market book printing where lightweight, thin pages are essential to produce compact, easy-to-carry volumes without compromising readability. Choosing handmade paper suits projects emphasizing craftsmanship and luxury, while Bible paper serves well in high-volume, cost-effective production with space-saving requirements.
Infographic: Handmade paper vs Bible paper for Book printing
 azmater.com
azmater.com